High-resilience foam offers superior cushioning and durability for packaging delicate items, absorbing shocks more effectively than polyethylene foam. Polyethylene foam provides lightweight, moisture-resistant protection ideal for cost-effective, general-purpose packaging applications.
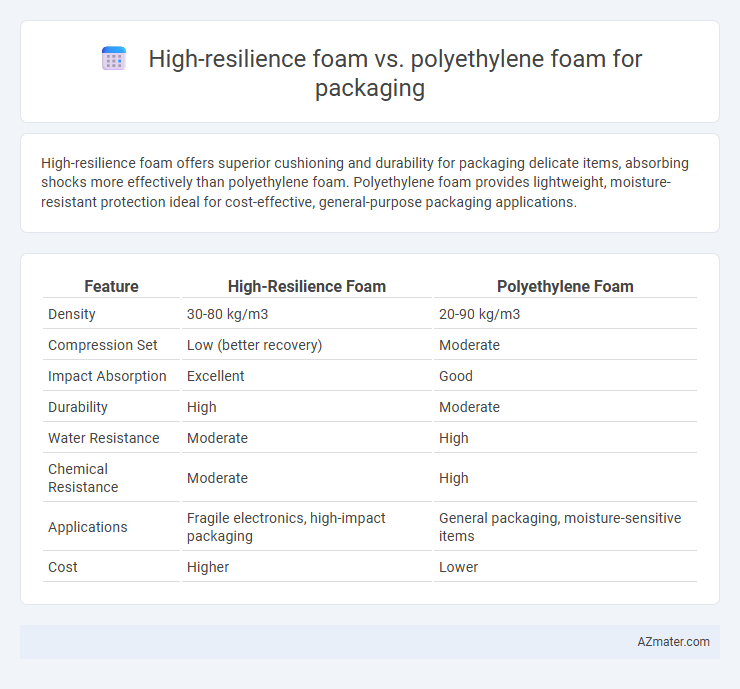
Table of Comparison
| Feature | High-Resilience Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 30-80 kg/m3 | 20-90 kg/m3 |
| Compression Set | Low (better recovery) | Moderate |
| Impact Absorption | Excellent | Good |
| Durability | High | Moderate |
| Water Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Applications | Fragile electronics, high-impact packaging | General packaging, moisture-sensitive items |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to High-Resilience Foam and Polyethylene Foam
High-resilience foam offers superior cushioning and durability due to its open-cell structure and high rebound rate, making it ideal for protecting delicate or heavy items during shipping. Polyethylene foam features a closed-cell structure that provides excellent water resistance, lightweight cushioning, and impact absorption, suitable for a wide range of packaging applications. Both foams enhance product safety but differ in flexibility, recovery, and environmental resistance properties.
Key Material Properties Compared
High-resilience foam offers superior elasticity and energy absorption compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for cushioning fragile items during transit. Polyethylene foam is denser and provides excellent water resistance and chemical stability, which enhances protection against moisture and corrosion. Both materials vary in compression set, with high-resilience foam recovering faster, while polyethylene foam demonstrates better impact resistance under heavy loads.
Cushioning Performance and Shock Absorption
High-resilience foam offers superior cushioning performance with its open-cell structure that provides excellent energy absorption and rapid recovery after compression, making it ideal for protecting delicate items during impact. Polyethylene foam, characterized by its closed-cell composition, delivers reliable shock absorption by resisting compression and distributing force evenly, which makes it suitable for heavier or more rigid products. Choosing between high-resilience and polyethylene foam depends on the specific packaging requirements, such as the level of fragility and weight of the item being protected.
Durability and Longevity
High-resilience foam offers superior durability and longevity compared to polyethylene foam due to its open-cell structure that provides better shock absorption and quicker recovery after compression. Polyethylene foam, while cost-effective, tends to compress permanently under prolonged stress, leading to reduced protective performance over time. High-resilience foam's resilience to repeated impacts and environmental wear makes it ideal for packaging fragile or high-value items requiring long-term protection.
Weight and Density Considerations
High-resilience foam offers lower density options compared to polyethylene foam, resulting in lighter packaging solutions that reduce shipping costs and improve handling efficiency. Polyethylene foam typically exhibits higher density, providing increased durability and superior impact resistance for heavier or more fragile items. Choosing between these foams depends on balancing weight requirements with protective performance to optimize packaging effectiveness.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
High-resilience foam offers improved durability and cushioning with moderate environmental impact due to its synthetic polymer composition, but it is less recyclable compared to polyethylene foam, which is widely recognized for its eco-friendly properties and higher recyclability rates. Polyethylene foam, often derived from recyclable materials, supports circular economy initiatives by being easier to process and reuse in packaging applications. Choosing between these foams depends on balancing packaging performance with the environmental footprint, favoring polyethylene foam where sustainability is a primary concern.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
High-resilience foam generally incurs higher initial costs compared to polyethylene foam due to its superior durability and cushioning properties, impacting overall packaging budgets. Polyethylene foam offers a cost-effective solution with lower material expenses and adequate protection for lighter or less fragile items. Budget considerations should balance the foam's price against the value of product protection, shipping conditions, and long-term savings from reduced damage rates.
Typical Packaging Applications
High-resilience foam offers superior cushioning and impact absorption, making it ideal for packaging delicate electronics, medical devices, and fragile glassware. Polyethylene foam provides excellent moisture resistance and chemical inertness, commonly used for packaging food products, automotive parts, and heavy machinery components. Each foam type serves distinct packaging needs based on durability, flexibility, and protection requirements.
Customization and Design Flexibility
High-resilience foam offers superior customization and design flexibility compared to polyethylene foam, enabling precise contouring and tailored density variations to protect delicate items effectively. Its open-cell structure allows for easy shaping and cutting, making it ideal for bespoke packaging solutions requiring intricate designs. Polyethylene foam, while durable and lightweight, provides less adaptability in customization due to its closed-cell composition, limiting the complexity of shapes and density adjustments in packaging applications.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Packaging Needs
High-resilience foam offers superior cushioning and durability, making it ideal for packaging fragile or heavy items that require long-term protection. Polyethylene foam provides excellent impact resistance and moisture resistance, suitable for lightweight or moisture-sensitive products. Selecting the right foam depends on product weight, fragility, and environmental exposure, ensuring optimal protection and cost-efficiency.
Infographic: High-resilience foam vs Polyethylene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com