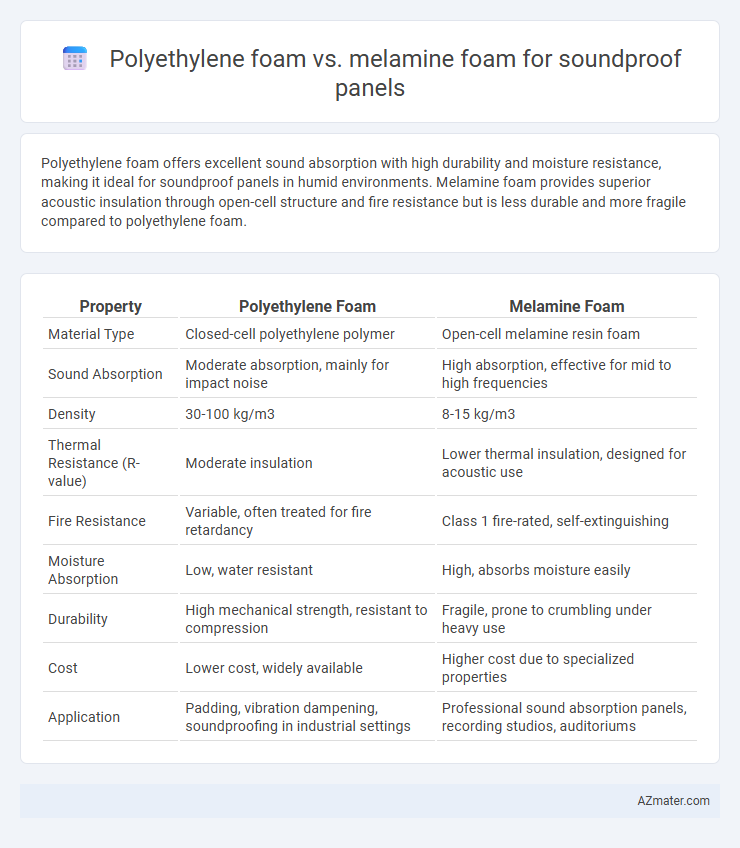
Polyethylene foam offers excellent sound absorption with high durability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for soundproof panels in humid environments. Melamine foam provides superior acoustic insulation through open-cell structure and fire resistance but is less durable and more fragile compared to polyethylene foam.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Foam | Melamine Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Closed-cell polyethylene polymer | Open-cell melamine resin foam |
| Sound Absorption | Moderate absorption, mainly for impact noise | High absorption, effective for mid to high frequencies |
| Density | 30-100 kg/m3 | 8-15 kg/m3 |
| Thermal Resistance (R-value) | Moderate insulation | Lower thermal insulation, designed for acoustic use |
| Fire Resistance | Variable, often treated for fire retardancy | Class 1 fire-rated, self-extinguishing |
| Moisture Absorption | Low, water resistant | High, absorbs moisture easily |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, resistant to compression | Fragile, prone to crumbling under heavy use |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost due to specialized properties |
| Application | Padding, vibration dampening, soundproofing in industrial settings | Professional sound absorption panels, recording studios, auditoriums |
Introduction to Soundproof Panels
Soundproof panels are essential in controlling echo and reducing noise transmission, with Polyethylene foam and Melamine foam being popular materials. Polyethylene foam offers excellent durability and moisture resistance while providing effective sound absorption, particularly in lower frequency ranges. Melamine foam features an open-cell structure that excels at high-frequency noise reduction and fire retardancy, making it suitable for diverse acoustic environments.
What is Polyethylene Foam?
Polyethylene foam is a lightweight, closed-cell material known for its excellent impact absorption and moisture resistance, making it suitable for soundproof panels in environments prone to humidity and mechanical stress. It provides moderate acoustic insulation by dampening airborne noise and vibrations, though it is less effective at absorbing high-frequency sounds compared to melamine foam. Its durability and resistance to chemicals position polyethylene foam as a cost-effective solution for soundproofing applications requiring long-lasting performance.
What is Melamine Foam?
Melamine foam is a highly porous, open-cell material known for its exceptional sound absorption and thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for soundproof panels in studios and offices. Unlike polyethylene foam, melamine foam effectively reduces mid to high-frequency noise with its fine, lightweight structure that traps sound waves and reduces reverberation. Its fire-resistant, non-toxic, and moisture-resistant characteristics offer enhanced durability and safety in acoustic applications compared to traditional polyethylene foam panels.
Acoustic Performance: Polyethylene vs. Melamine
Polyethylene foam offers excellent sound absorption with higher density and durability, effectively reducing noise in mid to high-frequency ranges, while melamine foam excels in absorbing a broader frequency spectrum, including low frequencies, due to its open-cell structure and lightweight composition. Melamine foam demonstrates superior acoustic performance in environments requiring enhanced speech clarity and noise reduction, owing to its fire-resistant and moisture-resistant properties. Polyethylene foam provides better impact resistance and longevity, making it suitable for applications with mechanical stress, though melamine foam remains preferred for optimized soundproofing and acoustic treatment.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Polyethylene foam offers superior durability and resistance to compression, making it ideal for long-term use in soundproof panels exposed to physical stress. Melamine foam, while lightweight and highly effective in sound absorption, tends to degrade faster under prolonged mechanical strain and humidity. Polyethylene foam's robustness ensures extended longevity in harsh environments, whereas melamine foam requires more frequent replacement to maintain acoustic performance.
Fire Resistance and Safety Features
Polyethylene foam offers moderate fire resistance with a tendency to melt and release toxic fumes under high heat, making it less ideal for stringent safety requirements. Melamine foam exhibits superior fire resistance due to its inherent mineral-based composition, resisting ignition and producing minimal smoke or toxic gases when exposed to flames. For soundproof panels, melamine foam's enhanced fire safety features make it a preferable choice in environments demanding higher fire performance and non-toxic smoke emissions.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Polyethylene foam offers easy installation due to its lightweight and flexible structure, allowing it to be cut and shaped effortlessly for custom soundproof panels, while melamine foam, being more rigid and brittle, requires careful handling and precise fitting during installation. Maintenance of polyethylene foam is straightforward, as it is resistant to moisture and can be cleaned with mild soap and water, whereas melamine foam is more delicate, prone to crumbling, and should be cleaned gently with a vacuum or a damp cloth to prevent damage. The durability and water resistance of polyethylene foam make it a preferred choice for long-term maintenance, whereas melamine foam's sensitivity demands more cautious upkeep to maintain its sound-absorbing properties.
Cost Analysis: Polyethylene vs. Melamine
Polyethylene foam typically costs less per cubic foot than melamine foam, making it a budget-friendly option for soundproof panels in large-scale projects or DIY applications. Melamine foam, while more expensive, offers superior fire resistance and higher acoustic absorption, justifying its price in commercial or high-performance environments. Evaluating project requirements against budget constraints helps determine whether the better acoustic properties of melamine foam offset its higher cost compared to the economical polyethylene alternative.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene foam, derived from petrochemicals, has limited biodegradability and poses environmental concerns due to its non-renewable origin and difficulty in recycling. Melamine foam, made from melamine resin, offers a more sustainable option by being lightweight, fire-resistant, and partially recyclable, though it still relies on synthetic materials. In soundproof panel applications, melamine foam's lower environmental footprint and enhanced thermal properties make it a preferable choice for eco-conscious construction projects.
Choosing the Right Foam for Soundproof Panels
Polyethylene foam offers excellent sound absorption for low to mid-frequency ranges due to its closed-cell structure and durability, making it ideal for environments requiring impact noise reduction and thermal insulation. Melamine foam excels at absorbing high-frequency sounds with its open-cell, porous structure, providing superior acoustic treatment for echo and reverberation control in recording studios and office spaces. Selecting the right foam for soundproof panels depends on the specific acoustic challenges, with polyethylene foam suited for broad-spectrum noise mitigation and melamine foam preferred for targeted high-frequency sound absorption.
Infographic: Polyethylene foam vs Melamine foam for Soundproof panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com