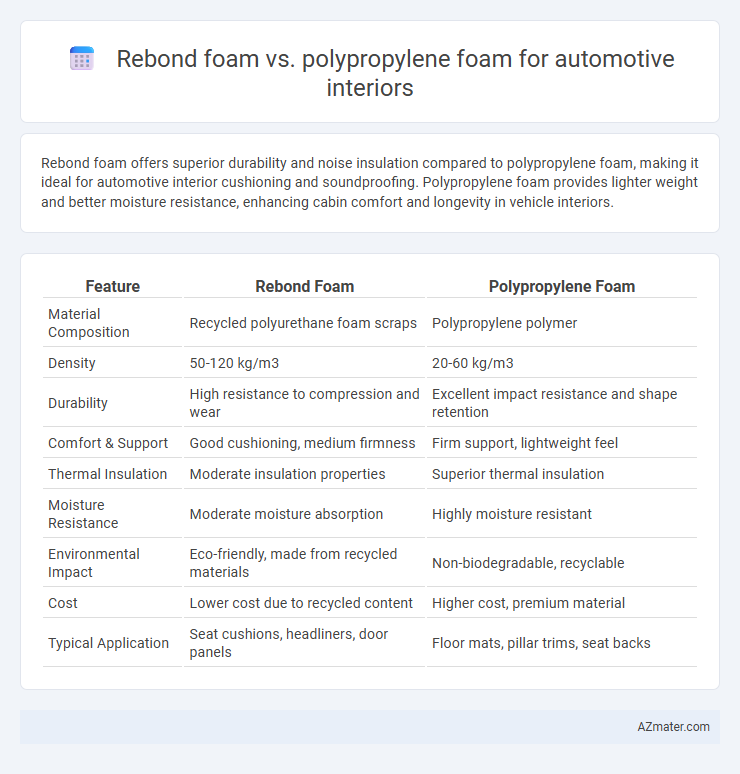
Rebond foam offers superior durability and noise insulation compared to polypropylene foam, making it ideal for automotive interior cushioning and soundproofing. Polypropylene foam provides lighter weight and better moisture resistance, enhancing cabin comfort and longevity in vehicle interiors.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rebond Foam | Polypropylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Recycled polyurethane foam scraps | Polypropylene polymer |
| Density | 50-120 kg/m3 | 20-60 kg/m3 |
| Durability | High resistance to compression and wear | Excellent impact resistance and shape retention |
| Comfort & Support | Good cushioning, medium firmness | Firm support, lightweight feel |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation properties | Superior thermal insulation |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate moisture absorption | Highly moisture resistant |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, made from recycled materials | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
| Cost | Lower cost due to recycled content | Higher cost, premium material |
| Typical Application | Seat cushions, headliners, door panels | Floor mats, pillar trims, seat backs |
Overview of Rebond Foam and Polypropylene Foam
Rebond foam, made from shredded scrap foam bonded together, offers excellent sound absorption and cushioning properties, making it ideal for automotive interior applications focused on comfort and noise reduction. Polypropylene foam is a lightweight, rigid material with high chemical resistance and excellent durability, commonly used for structural components and impact protection in vehicle interiors. Both materials serve distinct purposes, with rebond foam enhancing interior acoustics and comfort, while polypropylene foam provides robust, lightweight support and insulation.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Rebond foam is made by recycling shredded scrap polyurethane foam bonded together using adhesives or heat, creating a dense and durable material ideal for automotive interior padding and sound insulation. Polypropylene foam consists of expanded polypropylene beads fused through steam or heat, producing a lightweight, rigid, and chemically resistant foam commonly used for impact protection and structural components in cars. Manufacturing rebond foam involves compression molding recycled foam pieces, while polypropylene foam is created through bead expansion and fusion, resulting in distinct properties catering to diverse automotive interior requirements.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Rebond foam offers superior durability compared to polypropylene foam due to its high density and resistance to compression, making it ideal for automotive interior applications subject to frequent use. Polypropylene foam, while lightweight and resistant to moisture and chemicals, tends to degrade faster under constant mechanical stress and exposure to automotive temperature fluctuations. The longevity of rebond foam in seats and interior padding ensures prolonged shape retention and comfort, whereas polypropylene foam may require more frequent replacement due to its comparatively lower mechanical resilience.
Comfort and Ergonomic Support
Rebond foam offers superior cushioning and durability for automotive interiors, providing enhanced comfort by evenly distributing pressure and reducing fatigue during long drives. Polypropylene foam excels in lightweight ergonomic support and moisture resistance, making it ideal for seats requiring breathability and quick drying. Both materials balance comfort and support differently, with rebond foam prioritizing impact absorption and polypropylene foam emphasizing structural resilience and ventilation.
Weight and Density Differences
Rebond foam typically exhibits a higher density, ranging from 30 to 80 kg/m3, compared to polypropylene foam, which generally falls between 10 and 40 kg/m3, resulting in a notable weight difference in automotive interior applications. The increased density of rebond foam provides enhanced cushioning and durability but adds extra weight to vehicle components, affecting overall fuel efficiency. Polypropylene foam's lighter weight contributes to improved fuel economy and easier handling while maintaining sufficient cushioning properties for interior trim and seating.
Noise Reduction and Vibration Dampening
Rebond foam offers superior noise reduction and vibration dampening properties due to its dense, multi-layered recycled rubber composition, making it highly effective in automotive interiors for minimizing road noise and engine vibrations. Polypropylene foam provides lightweight and cost-effective noise insulation but lacks the same level of vibration absorption as rebond foam, often requiring additional treatments for optimal performance. Choosing rebond foam enhances acoustic comfort and durability in vehicles, especially in areas prone to high vibration and noise exposure.
Cost-Effectiveness and Affordability
Rebond foam offers a cost-effective solution for automotive interiors due to its recycled content and dense structure, providing durability at a lower price compared to polypropylene foam. Polypropylene foam, while lightweight and resistant to moisture and chemicals, typically incurs higher manufacturing costs, impacting overall affordability. Choosing rebond foam enhances budget efficiency in interior applications without compromising on comfort and support.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Rebond foam, made from recycled scrap polyurethane, offers a sustainable option with high recyclability, reducing landfill waste in automotive interiors. Polypropylene foam, derived from petroleum, has lower environmental impact during production due to energy efficiency but poses challenges in recycling because of mixed automotive composites. Choosing rebond foam supports circular economy goals, while polypropylene foam's recyclability depends on advancements in separation technologies.
Safety and Fire Resistance in Automotive Applications
Rebond foam offers superior fire resistance with inherent flame-retardant properties essential for automotive interior safety, while polypropylene foam provides high impact absorption but may require additional fire retardants to meet automotive fire safety standards. Rebond foam's dense structure enhances energy absorption during collisions, reducing injury risk, whereas polypropylene foam's lightweight nature aids in fuel efficiency without compromising thermal insulation. Both materials comply with FMVSS 302, yet rebond foam is preferred for applications demanding higher durability and fire safety.
Best Use Cases for Automotive Interiors
Rebond foam excels in automotive interiors requiring high durability and superior cushioning, making it ideal for seat padding and headrests due to its excellent impact absorption and resilience. Polypropylene foam is preferred for trim components and door panels where lightweight properties and resistance to moisture and chemicals enhance longevity and ease of maintenance. Selecting rebond foam supports areas with heavy wear, while polypropylene foam optimizes structural parts needing lightweight and weather-resistant materials.
Infographic: Rebond foam vs Polypropylene foam for Automotive interior
 azmater.com
azmater.com