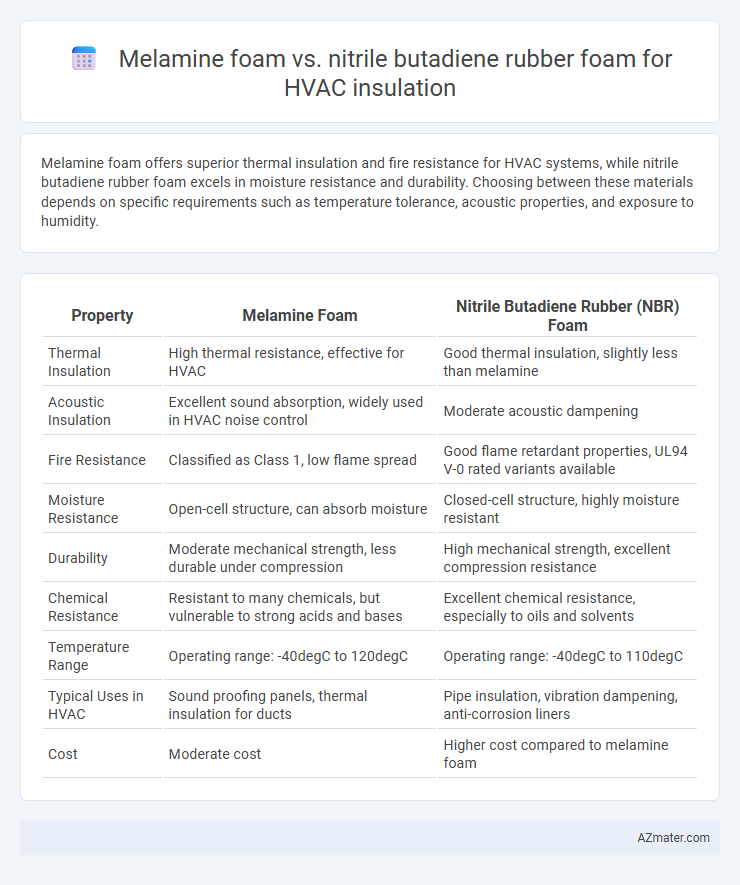
Melamine foam offers superior thermal insulation and fire resistance for HVAC systems, while nitrile butadiene rubber foam excels in moisture resistance and durability. Choosing between these materials depends on specific requirements such as temperature tolerance, acoustic properties, and exposure to humidity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Melamine Foam | Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High thermal resistance, effective for HVAC | Good thermal insulation, slightly less than melamine |
| Acoustic Insulation | Excellent sound absorption, widely used in HVAC noise control | Moderate acoustic dampening |
| Fire Resistance | Classified as Class 1, low flame spread | Good flame retardant properties, UL94 V-0 rated variants available |
| Moisture Resistance | Open-cell structure, can absorb moisture | Closed-cell structure, highly moisture resistant |
| Durability | Moderate mechanical strength, less durable under compression | High mechanical strength, excellent compression resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to many chemicals, but vulnerable to strong acids and bases | Excellent chemical resistance, especially to oils and solvents |
| Temperature Range | Operating range: -40degC to 120degC | Operating range: -40degC to 110degC |
| Typical Uses in HVAC | Sound proofing panels, thermal insulation for ducts | Pipe insulation, vibration dampening, anti-corrosion liners |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost compared to melamine foam |
Introduction to HVAC Insulation Materials
Melamine foam and nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam serve distinct roles in HVAC insulation, with melamine foam offering excellent thermal resistance, fire retardancy, and sound absorption due to its open-cell structure. Nitrile butadiene rubber foam provides superior flexibility, oil resistance, and durability, making it ideal for sealing and vibration damping in HVAC systems. Understanding the characteristics of these materials helps optimize energy efficiency, noise control, and system longevity in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning applications.
What is Melamine Foam?
Melamine foam is a lightweight, open-cell material known for its exceptional thermal insulation, sound absorption, and fire-resistant properties, making it ideal for HVAC insulation applications. Its unique microstructure allows it to effectively reduce heat transfer and control noise while being resistant to moisture and chemicals. Compared to nitrile butadiene rubber foam, melamine foam offers superior fire retardancy and lightweight characteristics but generally has lower durability and compressive strength.
What is Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) Foam?
Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) foam is a synthetic rubber material widely used in HVAC insulation due to its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, as well as its superior durability and flexibility. Compared to melamine foam, NBR foam provides enhanced thermal insulation and moisture resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring reliable temperature control and vapor barrier properties. Its closed-cell structure ensures effective noise reduction and energy efficiency in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
Thermal Insulation Properties Comparison
Melamine foam offers low thermal conductivity around 0.035 W/m*K, providing excellent thermal insulation ideal for HVAC systems requiring fire resistance and sound absorption. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam typically has a thermal conductivity of approximately 0.037 to 0.045 W/m*K, balancing flexibility and moisture resistance but generally providing slightly less insulation efficiency than melamine foam. The choice between melamine foam and NBR foam depends on specific HVAC applications prioritizing either superior thermal insulation combined with fire retardancy or enhanced durability and moisture resistance.
Fire Resistance: Melamine Foam vs NBR Foam
Melamine foam demonstrates superior fire resistance in HVAC insulation due to its inherent flame-retardant properties and ability to self-extinguish, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam, while providing good thermal insulation and flexibility, exhibits lower fire resistance and tends to melt or burn when exposed to intense heat. Selecting melamine foam over NBR foam enhances fire safety compliance in HVAC systems, especially in environments requiring stringent flame-retardant standards.
Sound Absorption Capabilities
Melamine foam offers superior sound absorption with an open-cell structure that effectively dampens airborne noise in HVAC systems, providing excellent acoustic insulation. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam, while more resilient and moisture-resistant, generally exhibits lower sound absorption coefficients compared to melamine foam, limiting its effectiveness in noise reduction applications. Selecting melamine foam enhances HVAC noise control by minimizing reverberation and maintaining quiet operation in residential and commercial environments.
Durability and Longevity
Melamine foam offers moderate durability for HVAC insulation but tends to degrade faster when exposed to moisture and UV light compared to nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam. NBR foam exhibits superior resistance to wear, chemicals, and environmental factors, ensuring longer-lasting performance in HVAC applications. This enhanced durability of NBR foam significantly reduces maintenance and replacement frequency, making it a more cost-effective option over time.
Ease of Installation and Flexibility
Melamine foam offers superior flexibility and compressibility, making it easy to install around complex HVAC shapes and tight spaces without requiring special tools. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam provides excellent elasticity and durability but can be less pliable, requiring precise cutting and fitting during installation. Overall, melamine foam's lightweight and flexible nature significantly reduce installation time compared to the firmer, thicker NBR foam.
Cost Analysis and ROI
Melamine foam offers a lower initial cost compared to nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam, making it a budget-friendly option for HVAC insulation projects with tight budgets. Despite its affordability, NBR foam provides superior durability and resistance to moisture and chemicals, which can lead to longer service life and reduced replacement frequency, enhancing overall ROI. When evaluating cost analysis, the higher upfront expense of NBR foam is often offset by its extended lifespan and energy efficiency benefits, resulting in improved long-term savings and return on investment for commercial HVAC systems.
Ideal Applications for Melamine Foam and NBR Foam
Melamine foam excels in HVAC insulation due to its exceptional fire resistance, lightweight structure, and superior sound absorption, making it ideal for environments requiring high thermal performance and fire safety, such as commercial buildings and industrial facilities. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam offers excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and moisture, along with good thermal insulation properties, making it suitable for HVAC applications in automotive, marine, and environments exposed to harsh chemical conditions. Choosing between melamine foam and NBR foam depends on specific application needs like fire resistance, chemical exposure, and acoustic requirements in HVAC systems.
Infographic: Melamine foam vs Nitrile butadiene rubber foam for HVAC insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com