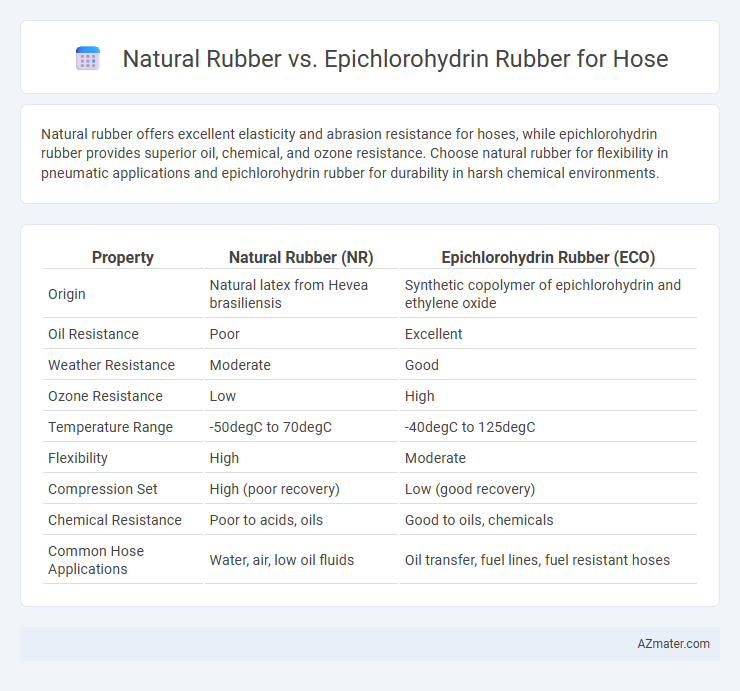
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance for hoses, while epichlorohydrin rubber provides superior oil, chemical, and ozone resistance. Choose natural rubber for flexibility in pneumatic applications and epichlorohydrin rubber for durability in harsh chemical environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Natural Rubber (NR) | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural latex from Hevea brasiliensis | Synthetic copolymer of epichlorohydrin and ethylene oxide |
| Oil Resistance | Poor | Excellent |
| Weather Resistance | Moderate | Good |
| Ozone Resistance | Low | High |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 70degC | -40degC to 125degC |
| Flexibility | High | Moderate |
| Compression Set | High (poor recovery) | Low (good recovery) |
| Chemical Resistance | Poor to acids, oils | Good to oils, chemicals |
| Common Hose Applications | Water, air, low oil fluids | Oil transfer, fuel lines, fuel resistant hoses |
Overview of Natural Rubber and Epichlorohydrin Rubber
Natural rubber offers exceptional elasticity, tensile strength, and tear resistance, making it ideal for hoses requiring high flexibility and resilience under dynamic conditions. Epichlorohydrin rubber excels in oil, chemical, and ozone resistance, providing superior durability in industrial hose applications exposed to harsh environments. Choosing between natural rubber and epichlorohydrin rubber depends on specific hose performance requirements such as temperature range, chemical compatibility, and mechanical stress.
Material Composition and Properties
Natural rubber is primarily composed of polyisoprene, characterized by excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for flexible and durable hoses. Epichlorohydrin rubber consists of copolymers of epichlorohydrin and ethylene oxide, offering superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance along with good heat stability. The material choice impacts hose performance significantly: natural rubber excels in mechanical strength and flexibility, while epichlorohydrin rubber provides enhanced resistance to aging, solvents, and harsh environments.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility Comparison
Natural rubber exhibits superior mechanical strength with high tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty hose applications. Epichlorohydrin rubber offers enhanced flexibility and oil resistance while maintaining moderate mechanical strength, suitable for hoses exposed to harsh chemical environments. The balance between tensile strength and flexibility in these elastomers dictates their optimal use based on specific hose performance requirements.
Chemical Resistance in Hose Applications
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to natural rubber, particularly against oils, fuels, and various solvents, making it ideal for hose applications exposed to harsh chemicals. Natural rubber tends to swell and degrade when in contact with petroleum-based fluids, limiting its use in industrial environments with aggressive substances. The enhanced resistance of epichlorohydrin rubber significantly extends hose lifespan and reliability in chemical processing, automotive fuel lines, and hydraulic systems.
Temperature Performance: Heat and Cold Tolerance
Natural rubber offers excellent flexibility and resilience at low temperatures, maintaining performance down to approximately -50degC, but it degrades rapidly above 70degC due to thermal oxidation. Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) excels in moderate heat resistance, sustaining properties up to 125degC while also providing superior resistance to ozone and chemical exposure compared to natural rubber. For hose applications requiring consistent performance in both extreme cold and elevated temperatures, epichlorohydrin rubber provides a broader operational temperature range with enhanced durability.
Durability and Longevity in Service
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and resilience, making it suitable for hoses requiring high flexibility and abrasion resistance, but it is susceptible to degradation from oils, ozone, and chemicals. Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior resistance to oils, ozone, weather, and chemical exposure, significantly enhancing hose durability and longevity in harsh industrial environments. For applications demanding extended service life and resistance to aggressive substances, epichlorohydrin rubber hoses provide a more reliable and long-lasting solution.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Natural rubber offers superior elasticity and abrasion resistance at a lower cost, making it highly cost-effective for general hose applications. Epichlorohydrin rubber, though more expensive, provides excellent oil, heat, and ozone resistance, enhancing durability in specialized industrial environments. Availability of natural rubber is widespread due to extensive plantations, while epichlorohydrin rubber is less common and typically sourced from chemical manufacturers, potentially limiting supply and increasing lead times.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Natural rubber, derived from renewable Hevea brasiliensis trees, offers superior biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint compared to epichlorohydrin rubber, which is a petroleum-based synthetic polymer with limited biodegradability and greater environmental persistence. The sustainable harvesting practices of natural rubber plantations contribute to carbon sequestration and biodiversity, whereas epichlorohydrin rubber production involves energy-intensive processes and hazardous chemicals that pose disposal and recycling challenges. Choosing natural rubber for hoses supports circular economy principles and reduces ecological impact, making it a more environmentally responsible material in applications requiring flexibility and resilience.
Common Industrial Applications for Hoses
Natural rubber hoses are widely used in water suction and discharge, air, and oil-resistant applications due to their excellent elasticity, abrasion resistance, and flexibility. Epichlorohydrin rubber hoses are preferred in fuel oil, chemical, and hydraulic fluid transfer industries because of their superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and a broad range of chemicals. Industrial sectors such as mining, agriculture, and automotive rely on natural rubber for pneumatic and vacuum hoses, whereas epichlorohydrin is favored in chemical plants and marine environments for fuel and oil transfer hoses.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Hose Requirements
Natural rubber offers excellent flexibility, abrasion resistance, and elasticity, making it ideal for hoses requiring superior toughness and durability in moderate chemical environments. Epichlorohydrin rubber provides outstanding resistance to oils, fuels, and ozone, suitable for hoses exposed to harsh chemicals and extreme weather conditions. Selecting the right rubber depends on the hose's operating environment, including temperature ranges, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress, to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Natural rubber vs Epichlorohydrin rubber for Hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com