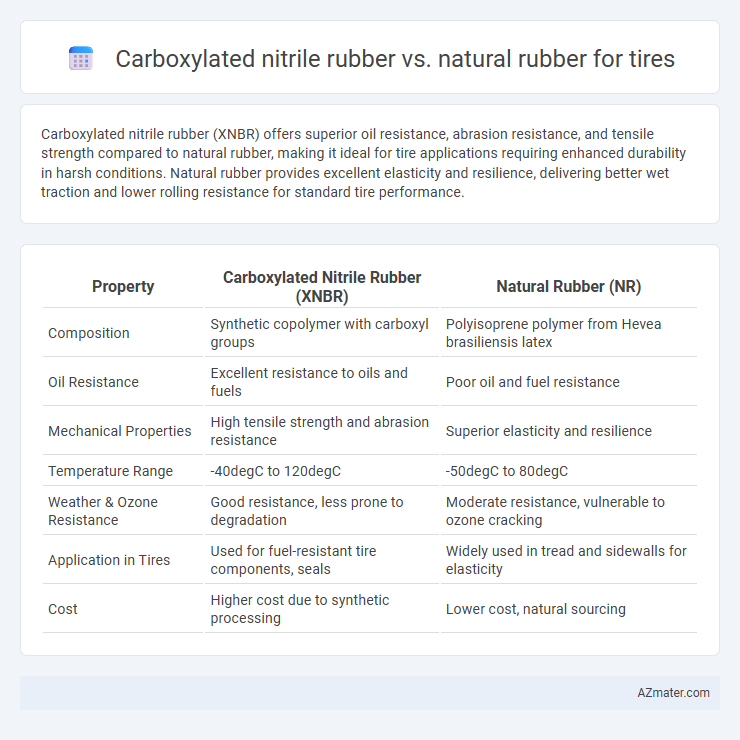
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance, abrasion resistance, and tensile strength compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for tire applications requiring enhanced durability in harsh conditions. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and resilience, delivering better wet traction and lower rolling resistance for standard tire performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Natural Rubber (NR) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Synthetic copolymer with carboxyl groups | Polyisoprene polymer from Hevea brasiliensis latex |
| Oil Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils and fuels | Poor oil and fuel resistance |
| Mechanical Properties | High tensile strength and abrasion resistance | Superior elasticity and resilience |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -50degC to 80degC |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Good resistance, less prone to degradation | Moderate resistance, vulnerable to ozone cracking |
| Application in Tires | Used for fuel-resistant tire components, seals | Widely used in tread and sidewalls for elasticity |
| Cost | Higher cost due to synthetic processing | Lower cost, natural sourcing |
Introduction to Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber and Natural Rubber
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for enhanced oil resistance, abrasion resistance, and improved mechanical strength due to the presence of carboxyl groups in its polymer chain. Natural rubber (NR), derived from latex of the Hevea brasiliensis tree, offers exceptional tensile strength, elasticity, and resilience, making it ideal for applications requiring dynamic performance and flexibility. Both materials serve distinct roles in tire manufacturing, with XNBR typically used for inner liners and specialized components, while natural rubber is favored for tread and sidewall due to its superior wear resistance and grip.
Material Composition and Chemical Structure
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) contains nitrile groups and carboxyl functional groups, enhancing oil resistance and abrasion resistance compared to natural rubber, which is primarily composed of cis-1,4-polyisoprene. The chemical structure of XNBR includes polar carboxylate groups that improve adhesion and tensile strength, whereas natural rubber's non-polar hydrocarbon chains provide high elasticity and resilience but lower chemical resistance. These differences in material composition and molecular architecture impact tire performance, with XNBR offering superior durability in harsh chemical environments and natural rubber excelling in flexibility and grip.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to natural rubber (NR), making it highly effective in tire applications requiring enhanced durability. XNBR offers improved oil and fuel resistance with higher hardness and better tear resistance, while natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and resilience, contributing to better ride comfort and traction. The mechanical performance of XNBR ensures longer tire life under harsh conditions, whereas NR maintains superior wet grip and flexibility at low temperatures.
Resistance to Oil, Fuel, and Chemicals
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior resistance to oil, fuel, and chemicals compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for tire applications exposed to harsh environments. Its chemical structure provides enhanced barrier properties and durability against hydrocarbon oils and aggressive fuels, reducing degradation and swelling. Natural rubber, while offering excellent mechanical properties and flexibility, tends to exhibit lower resistance to petroleum-based substances, resulting in faster wear and potential failures in chemically challenging conditions.
Heat and Oxidation Stability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior heat and oxidation stability compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for tire applications exposed to high temperatures and oxidative environments. The presence of carboxyl groups in XNBR enhances cross-linking density, which significantly improves its resistance to thermal degradation and ozone aging. Natural rubber, while flexible and resilient, tends to deteriorate faster under heat and oxidative stress, leading to reduced tire lifespan in demanding conditions.
Wear and Abrasion Performance in Tires
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior wear and abrasion resistance compared to natural rubber, making it highly suitable for tire treads exposed to harsh conditions. XNBR's enhanced cross-linking density and polar functional groups improve polymer-filler interaction, resulting in increased durability and reduced tread wear. In contrast, natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and grip but typically shows higher abrasion rates under heavy-duty or high-temperature use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals compared to natural rubber, but it is derived from synthetic polymers based on petrochemicals, leading to higher carbon emissions and limited biodegradability. Natural rubber, harvested from Hevea brasiliensis trees, is renewable and biodegradable, promoting carbon sequestration and supporting biodiversity; however, large-scale plantations can contribute to deforestation and habitat loss. Sustainable tire manufacturing increasingly integrates natural rubber for reduced environmental impact, while research into bio-based synthetic alternatives aims to improve the ecological footprint of carboxylated nitrile rubber.
Processing and Manufacturing Differences
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance and enhanced abrasion durability compared to natural rubber (NR), influencing processing conditions such as cure time and temperature. XNBR requires higher vulcanization temperatures and longer cure times due to its polar carboxyl groups, resulting in firmer, more stable crosslinks during tire manufacturing. Natural rubber, favored for its elasticity and ease of processing, cures faster at lower temperatures but may require additional additives to match the performance and longevity of XNBR-based tire compounds.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced oil resistance and durability compared to natural rubber, but its production costs are higher due to complex synthesis and raw material expenses, impacting overall tire manufacturing budgets. Natural rubber remains more cost-effective and widely available, benefiting from extensive global plantations and established supply chains, making it the preferred choice for mainstream tire markets. Market availability favors natural rubber in large-scale tire production, while XNBR is targeted towards specialty tires requiring superior chemical and abrasion resistance despite its premium pricing.
Applications and Suitability for Modern Tires
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance, abrasion resistance, and tensile strength compared to natural rubber, making it highly suitable for modern tire components exposed to harsh environments such as inner liners and sidewalls. Natural rubber provides excellent flexibility, resilience, and low rolling resistance, which enhances grip and ride comfort, making it ideal for tire treads in passenger vehicles and heavy-duty applications. The combination of XNBR and natural rubber in tire manufacturing optimizes durability, performance, and safety for diverse tire applications.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Natural rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com