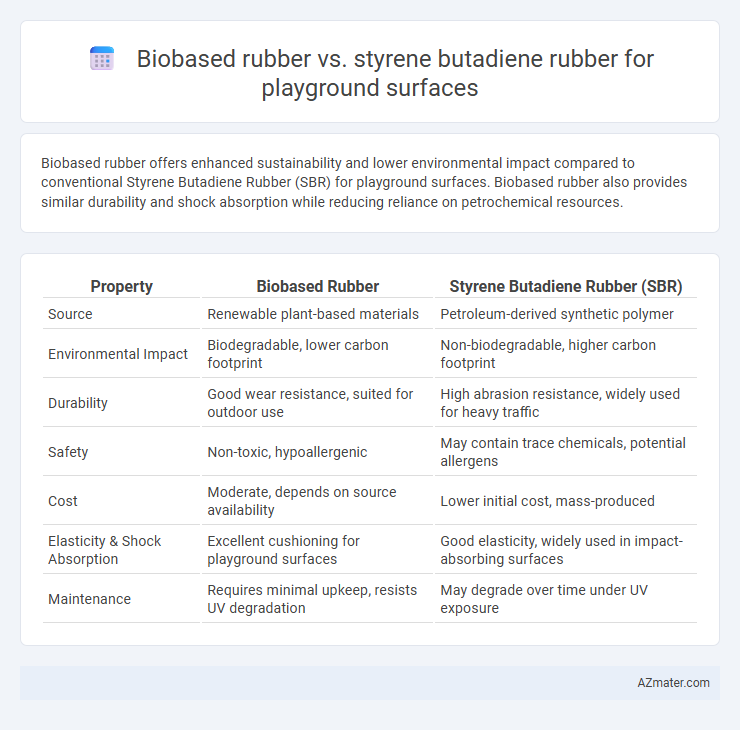
Biobased rubber offers enhanced sustainability and lower environmental impact compared to conventional Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) for playground surfaces. Biobased rubber also provides similar durability and shock absorption while reducing reliance on petrochemical resources.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Biobased Rubber | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable plant-based materials | Petroleum-derived synthetic polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, lower carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Durability | Good wear resistance, suited for outdoor use | High abrasion resistance, widely used for heavy traffic |
| Safety | Non-toxic, hypoallergenic | May contain trace chemicals, potential allergens |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on source availability | Lower initial cost, mass-produced |
| Elasticity & Shock Absorption | Excellent cushioning for playground surfaces | Good elasticity, widely used in impact-absorbing surfaces |
| Maintenance | Requires minimal upkeep, resists UV degradation | May degrade over time under UV exposure |
Introduction to Playground Surfacing Materials
Biobased rubber offers an eco-friendly alternative to traditional Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) in playground surfacing, providing durable cushioning derived from renewable resources. SBR, a synthetic polymer made from styrene and butadiene, is known for its resilience and cost-effectiveness but relies on petroleum-based raw materials. Choosing biobased rubber enhances sustainability by reducing carbon footprint while maintaining safety standards and impact absorption for playground environments.
Overview of Biobased Rubber and Its Composition
Biobased rubber for playground surfaces is primarily derived from renewable natural resources such as guayule, dandelion, and Hevea brasiliensis latex, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional synthetic rubbers. Its composition mainly includes natural polyisoprene polymers with minimal chemical additives, enhancing biodegradability and reducing environmental impact compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), which is petroleum-based and contains styrene and butadiene monomers. The biobased rubber's natural origin improves sustainability and promotes healthier play environments by minimizing toxic emissions and microplastic contamination.
Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR): Properties and Applications
Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance, durability, and cost-effectiveness, making it a preferred material for playground surfaces that require high wear tolerance and safety. Its superior flexibility and weather resistance ensure long-lasting performance under varying environmental conditions, supporting shock absorption and reducing injury risks. SBR's widespread availability and recyclability further enhance its practicality in playground surfacing applications, balancing performance with sustainability concerns.
Environmental Impact: Biobased Rubber vs SBR
Biobased rubber for playground surfaces significantly reduces carbon footprint by utilizing renewable resources and enhancing biodegradability compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), which is petroleum-derived with limited environmental degradation. The production of biobased rubber emits fewer greenhouse gases and reduces dependence on fossil fuels, contributing to sustainability goals. In contrast, SBR contributes to microplastic pollution and has a longer decomposition period, raising concerns about soil and water contamination in playground environments.
Safety and Health Considerations for Children
Biobased rubber offers enhanced safety and health benefits for playground surfaces by reducing exposure to harmful chemicals commonly found in Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and residual styrene. Studies indicate that biobased rubber materials have lower allergenic potential and emit fewer toxic substances, promoting better indoor and outdoor air quality and minimizing respiratory risks for children. The biodegradability and natural composition of biobased rubber further decrease environmental pollutants, aligning with health-conscious playground design standards.
Durability and Weather Resistance Comparison
Biobased rubber exhibits superior weather resistance due to its natural polymer structure, allowing it to better withstand UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations on playground surfaces. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), a synthetic polymer, offers high abrasion resistance but tends to degrade faster under prolonged sun exposure and harsh weather conditions. Durability assessments show biobased rubber maintains elasticity and structural integrity longer, reducing maintenance needs compared to SBR-based playground surfaces.
Cost Analysis: Biobased Rubber versus SBR
Biobased rubber for playground surfaces often presents higher initial costs compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) due to raw material sourcing and processing complexities. SBR remains cost-effective with established manufacturing infrastructure and lower petroleum-based feedstock prices. Long-term economic analysis factors in biobased rubber's potential for sustainability incentives and lower environmental compliance expenses, which may offset upfront cost differences over time.
Performance and Shock Absorption Capabilities
Biobased rubber offers enhanced environmental sustainability and comparable durability to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) for playground surfaces, with superior biodegradability that reduces ecological impact. Its shock absorption capabilities are often improved due to its natural polymer structure, providing better energy dissipation and impact attenuation than traditional SBR. While SBR remains valued for cost-effectiveness and consistent performance, biobased rubber advances playground safety by combining effective cushioning performance with eco-friendly material benefits.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Biobased rubber playground surfaces require specialized installation techniques to ensure proper adhesion and curing, often involving eco-friendly adhesives and precise temperature control. Maintenance for biobased rubber is generally lower due to its natural resistance to UV degradation and chemical wear, resulting in longer surface durability and reduced need for repairs. In contrast, styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) surfaces demand more frequent upkeep to address brittleness and cracking issues, with routine inspections and patching to maintain safety standards.
Future Trends in Sustainable Playground Surfaces
Biobased rubber offers a renewable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) in playground surfaces, reducing reliance on petroleum-based materials and lowering carbon footprints. Innovations in biopolymer composites and microbial synthesis are driving the development of durable, non-toxic, and biodegradable playground materials that enhance safety and environmental sustainability. Increasing regulatory pressure and consumer demand for green products are accelerating the adoption of biobased rubber, positioning it as a key material in the future of sustainable playground surfaces.
Infographic: Biobased rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Playground surface
 azmater.com
azmater.com