Polysulfone offers exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance for shoe soles, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate provides superior flexibility and lightweight cushioning, enhancing comfort and impact absorption in footwear.
Table of Comparison
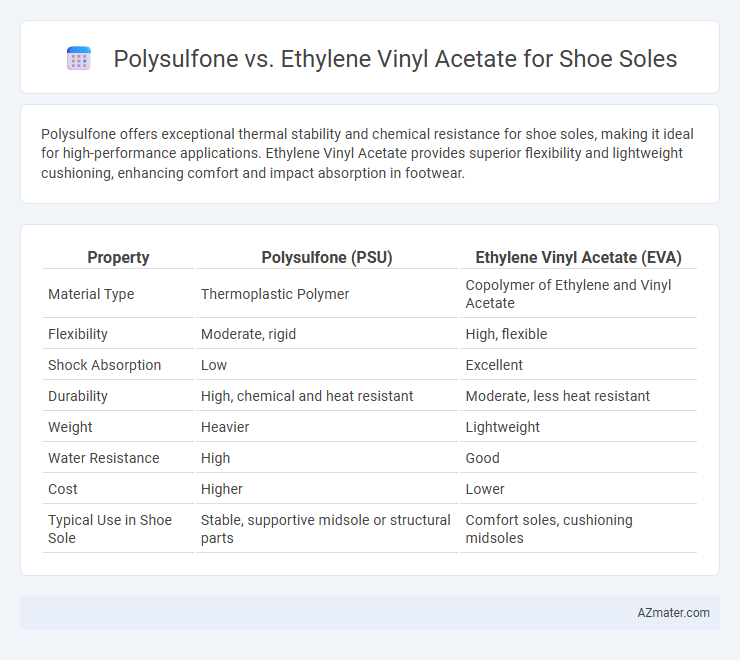
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Copolymer of Ethylene and Vinyl Acetate |
| Flexibility | Moderate, rigid | High, flexible |
| Shock Absorption | Low | Excellent |
| Durability | High, chemical and heat resistant | Moderate, less heat resistant |
| Weight | Heavier | Lightweight |
| Water Resistance | High | Good |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Use in Shoe Sole | Stable, supportive midsole or structural parts | Comfort soles, cushioning midsoles |
Introduction to Shoe Sole Materials
Polysulfone offers exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for durable and high-performance shoe soles used in industrial and protective footwear. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) provides lightweight, flexible, and shock-absorbing properties, widely favored in athletic and casual shoe soles for enhanced comfort and cushioning. Both materials contribute uniquely to sole functionality, with polysulfone excelling in strength and EVA dominating in cushioning and flexibility.
Overview of Polysulfone and Ethylene Vinyl Acetate
Polysulfone (PSU) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent mechanical strength, thermal stability up to 190degC, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for durable, heat-resistant shoe soles. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a lightweight, flexible copolymer widely used in shoe soles due to its superior cushioning, shock absorption, and resistance to cracking at low temperatures. While PSU provides structural durability and heat resistance, EVA offers enhanced comfort and flexibility for everyday footwear applications.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polysulfone features a rigid backbone with aromatic rings and sulfone groups, providing high thermal stability and excellent chemical resistance, making it suitable for durable shoe soles. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a copolymer composed of ethylene and vinyl acetate units, offering flexibility, lightweight properties, and good cushioning due to its semi-crystalline structure. The chemical composition of polysulfone results in a tougher, more heat-resistant material, whereas EVA's composition delivers superior shock absorption and comfort in footwear applications.
Durability and Flexibility Comparison
Polysulfone offers superior durability due to its high heat resistance and excellent mechanical strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty shoe soles that require long-lasting wear. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) provides exceptional flexibility and shock absorption, ensuring comfort and better foot movement in athletic and casual shoes. While polysulfone excels in toughness and chemical resistance, EVA outperforms in cushioning and flexibility, defining their use based on footwear performance needs.
Comfort and Cushioning Properties
Polysulfone shoe soles offer exceptional durability and heat resistance but lack the flexibility and cushioning properties found in Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), making them less ideal for comfort-focused footwear. EVA soles provide superior shock absorption and lightweight cushioning, enhancing foot comfort during prolonged wear and high-impact activities. The elasticity and softness of EVA contribute to better energy return and reduced foot fatigue compared to the rigid structure of polysulfone.
Water and Chemical Resistance
Polysulfone exhibits superior water and chemical resistance compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), making it ideal for shoe soles exposed to harsh environments. Polysulfone's high thermal stability and resistance to hydrocarbons and acids provide enhanced durability against degradation. EVA, while flexible and lightweight, tends to absorb water and degrade faster when exposed to oils and solvents, limiting its application in chemically demanding conditions.
Weight and Design Versatility
Polysulfone offers a higher strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for lightweight shoe soles without compromising durability. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) provides superior design versatility due to its flexible nature and ease of molding into complex sole shapes. Weight-conscious footwear often favors polysulfone for its performance, while EVA is preferred for customizable, ergonomic designs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polysulfone is a durable, high-temperature resistant polymer with limited biodegradability, contributing to long-term environmental persistence and challenging recycling processes. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) offers enhanced flexibility and cushioning in shoe soles while being more environmentally sustainable due to its lower carbon footprint and better recyclability options, including partial biodegradability in newer formulations. Choosing EVA over polysulfone can reduce environmental impact by enabling more sustainable manufacturing and end-of-life disposal practices in the footwear industry.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Polysulfone shoe soles tend to have higher manufacturing costs due to complex production processes and raw material expenses, limiting their market availability predominantly to specialized or high-performance footwear. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) offers a cost-effective alternative with lower production costs and widespread market availability, making it a preferred choice for mass-produced and budget-friendly shoe soles. The price disparity between polysulfone and EVA significantly influences consumer demand and production scalability in the footwear industry.
Final Verdict: Which Material is Better for Shoe Soles?
Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and durability, making it ideal for high-performance shoe soles that require long-lasting wear and structural integrity. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) excels in lightweight cushioning, flexibility, and shock absorption, providing enhanced comfort and impact protection for everyday footwear. For shoe soles needing robust endurance and resistance, Polysulfone is better suited, while EVA is preferable for lightweight, comfortable shoes designed for casual or athletic use.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Ethylene Vinyl Acetate for Shoe Sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com