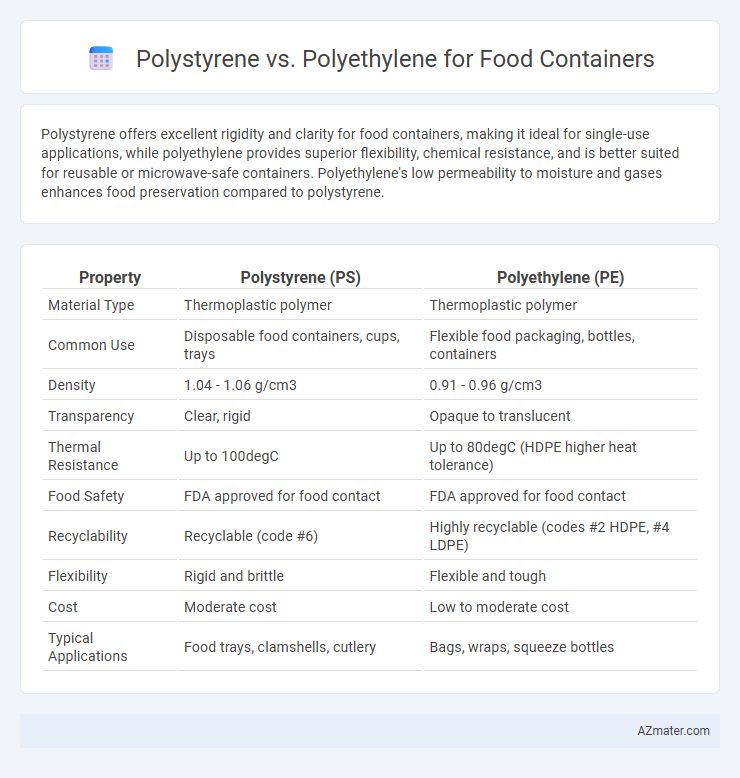
Polystyrene offers excellent rigidity and clarity for food containers, making it ideal for single-use applications, while polyethylene provides superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and is better suited for reusable or microwave-safe containers. Polyethylene's low permeability to moisture and gases enhances food preservation compared to polystyrene.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polystyrene (PS) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Common Use | Disposable food containers, cups, trays | Flexible food packaging, bottles, containers |
| Density | 1.04 - 1.06 g/cm3 | 0.91 - 0.96 g/cm3 |
| Transparency | Clear, rigid | Opaque to translucent |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 100degC | Up to 80degC (HDPE higher heat tolerance) |
| Food Safety | FDA approved for food contact | FDA approved for food contact |
| Recyclability | Recyclable (code #6) | Highly recyclable (codes #2 HDPE, #4 LDPE) |
| Flexibility | Rigid and brittle | Flexible and tough |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Low to moderate cost |
| Typical Applications | Food trays, clamshells, cutlery | Bags, wraps, squeeze bottles |
Introduction to Food-Safe Plastics
Food-safe plastics like polystyrene and polyethylene are widely used in packaging due to their non-toxic properties and ability to maintain food quality. Polystyrene offers rigidity and clarity, making it ideal for containers that display food, while polyethylene provides flexibility and excellent moisture resistance, suitable for bags and wraps. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA ensure that both plastics meet safety standards for direct food contact applications.
Overview: Polystyrene and Polyethylene
Polystyrene (PS) and polyethylene (PE) are widely used plastics in food container applications due to their distinct properties and performance. Polystyrene offers rigidity, clarity, and excellent insulating properties, making it suitable for disposable cups, plates, and take-out containers. Polyethylene, available in high-density (HDPE) and low-density (LDPE) forms, provides flexibility, chemical resistance, and moisture barrier capabilities, ideal for food storage bags and reusable containers.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polystyrene features a benzene ring in its backbone, resulting in rigidity and excellent clarity, making it ideal for food containers requiring visibility and shape retention. Polyethylene consists of a simple hydrocarbon chain, providing flexibility, chemical resistance, and moisture barrier properties suitable for packaging. The aromatic structure of polystyrene offers brittleness and lower heat resistance, while polyethylene's saturated alkane structure contributes to toughness and higher thermal stability in food storage applications.
Food Safety and Regulatory Standards
Polystyrene and polyethylene differ significantly in food safety and regulatory standards, with polyethylene widely regarded as safer due to its chemical stability and resistance to leaching harmful substances into food. Polystyrene can release styrene monomers, which are under scrutiny by agencies like the FDA and EFSA for potential health risks, making its use limited in food contact applications. Polyethylene complies with stringent FDA regulations for food-grade plastics, ensuring minimal risk of contaminant migration, making it the preferred choice for food containers in terms of safety and regulatory approval.
Temperature and Chemical Resistance
Polystyrene offers excellent clarity and rigidity but has limited temperature resistance, typically withstanding up to 70degC before deformation, making it suitable for cold and room temperature food containers but less ideal for hot foods. Polyethylene, especially high-density polyethylene (HDPE), demonstrates superior chemical resistance and can endure higher temperatures up to 120degC, allowing it to be used safely for both hot and acidic foods without leaching harmful substances. The choice between polystyrene and polyethylene fundamentally relies on the specific temperature range and chemical exposure requirements of the food storage application.
Durability and Structural Integrity
Polystyrene offers rigid structure and excellent clarity, making it ideal for disposable food containers that require visibility and moderate durability. Polyethylene provides superior flexibility and impact resistance, enhancing durability and structural integrity for reusable or heavy-use food containers. The choice depends on the container's intended use, with polystyrene excelling in rigidity and polyethylene in toughness and longevity.
Environmental Impact: Recycling and Biodegradability
Polystyrene (PS) is less environmentally friendly compared to polyethylene (PE) due to its limited recycling options and slow biodegradability, often persisting in landfills for centuries. Polyethylene, especially HDPE and LDPE, has a higher recycling rate and is more commonly accepted by recycling programs, which reduces its environmental footprint. Despite both being plastics, polyethylene's chemical structure allows for slightly better biodegradation under specific conditions, making it a preferable choice for sustainable food container packaging.
Cost-Effectiveness for Manufacturers
Polystyrene offers manufacturers lower raw material costs and excellent rigidity, making it a cost-effective choice for disposable food containers requiring shape retention. Polyethylene provides greater chemical resistance and flexibility, often leading to longer product lifespan but at a higher initial material expense. For cost-sensitive manufacturers, polystyrene's affordability and ease of thermoforming outweigh polyethylene's durability benefits in high-volume food packaging applications.
Common Uses in Food Packaging
Polystyrene (PS) is widely used in food packaging for disposable items such as foam cups, takeout containers, and protective trays due to its rigidity and excellent insulating properties. Polyethylene (PE), including both low-density (LDPE) and high-density (HDPE) types, is commonly found in flexible packaging like plastic bags, shrink wraps, and squeeze bottles because of its durability and moisture resistance. Both materials serve distinct roles in food packaging, with polystyrene preferred for solid, protective containers and polyethylene favored for flexible, moisture-barrier applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Food Containers
Polystyrene offers excellent rigidity and clarity, making it ideal for disposable food containers requiring precise shape and presentation. Polyethylene provides superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and is better suited for reusable or flexible packaging applications. Selecting the right material depends on the intended use, durability requirements, and exposure to heat or chemicals in food storage.
Infographic: Polystyrene vs Polyethylene for Food Container
 azmater.com
azmater.com