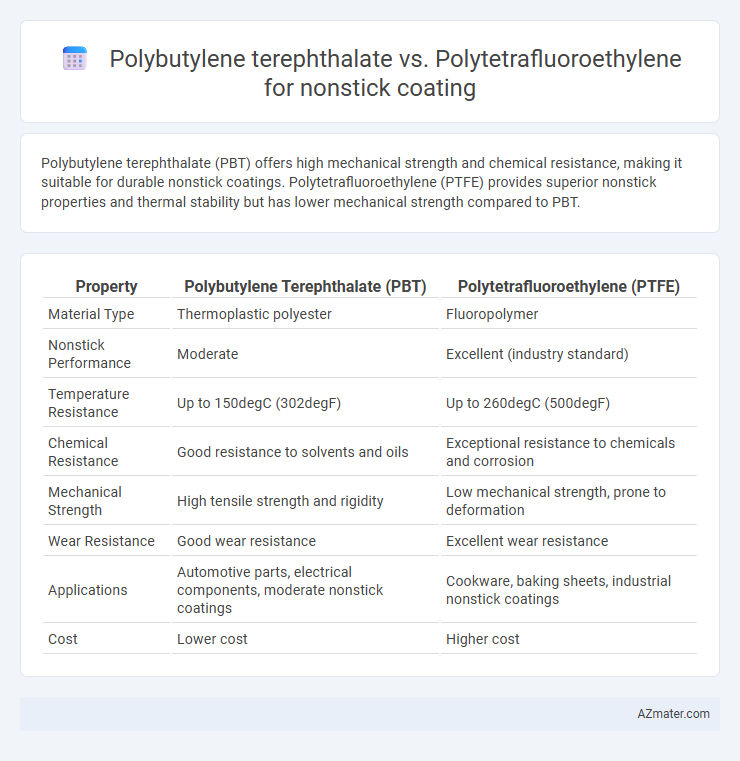
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers high mechanical strength and chemical resistance, making it suitable for durable nonstick coatings. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides superior nonstick properties and thermal stability but has lower mechanical strength compared to PBT.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polyester | Fluoropolymer |
| Nonstick Performance | Moderate | Excellent (industry standard) |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 150degC (302degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to solvents and oils | Exceptional resistance to chemicals and corrosion |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and rigidity | Low mechanical strength, prone to deformation |
| Wear Resistance | Good wear resistance | Excellent wear resistance |
| Applications | Automotive parts, electrical components, moderate nonstick coatings | Cookware, baking sheets, industrial nonstick coatings |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Polybutylene Terephthalate and Polytetrafluoroethylene
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its durability, chemical resistance, and excellent electrical properties, commonly used in engineering applications requiring toughness and dimensional stability. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), widely recognized under the brand name Teflon, is a fluoropolymer characterized by its exceptional nonstick properties, high thermal resistance, and low friction coefficient, making it ideal for nonstick coatings in cookware. Compared to PBT, PTFE offers superior nonstick performance and heat endurance, which is critical for applications involving high-temperature exposure and easy food release.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polyester composed of repeating butylene terephthalate units, characterized by ester linkages that provide rigidity and thermal resistance. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) consists of a carbon backbone fully fluorinated with fluorine atoms, creating strong carbon-fluorine bonds that result in exceptional chemical inertness and low surface energy. The chemical composition of PBT offers good mechanical strength and moderate chemical resistance, while PTFE's unique fluoropolymer structure delivers superior nonstick properties and resistance to most chemicals.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers moderate thermal stability with a maximum service temperature around 150degC, making it less suitable for high-heat nonstick applications. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits exceptional heat resistance, withstanding continuous use temperatures up to 260degC and short-term peaks near 350degC, ideal for cookware and industrial nonstick coatings. PTFE's superior thermal stability and low surface energy provide excellent nonstick properties even under extreme heat, outperforming PBT in demanding thermal environments.
Nonstick Properties and Performance Analysis
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers moderate nonstick properties with good thermal stability and resistance to solvents but exhibits lower friction coefficients compared to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). PTFE is renowned for its superior nonstick surface, outstanding chemical inertness, and excellent performance at high temperatures, making it the preferred choice in cookware and industrial applications requiring minimal adhesion. Performance analysis shows PTFE coatings maintain durability and nonstick effectiveness under prolonged heat exposure better than PBT, which can degrade faster and lose its release properties over time.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits high mechanical strength and excellent impact resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring durability under stress. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), while renowned for its superior nonstick properties and chemical resistance, has lower mechanical strength and can deform under high mechanical loads. In nonstick coatings, PBT offers enhanced structural integrity and wear resistance, whereas PTFE provides outstanding nonstick performance but requires reinforcement or backing materials to improve durability.
Resistance to Chemicals and Staining
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers good resistance to a range of chemicals but is prone to staining and degradation when exposed to strong acids, alkalis, and harsh solvents. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) demonstrates superior chemical inertness, resisting nearly all chemicals and eliminating staining due to its non-reactive, low surface energy properties. PTFE's exceptional resistance makes it the preferred choice for durable, nonstick coatings in chemically aggressive environments.
Applications in Nonstick Coating Technologies
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance, making it suitable for durable nonstick coatings in cookware and industrial molds. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), known for its superior nonstick properties, high thermal stability, and low friction, is widely used in pans, bakeware, and release coatings for food processing equipment. PTFE's exceptional resistance to chemical corrosion and high temperatures makes it the preferred choice for applications requiring enhanced nonstick performance and longevity.
Safety and Food Contact Compliance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) and Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) differ significantly in safety and food contact compliance for nonstick coatings. PBT offers good chemical resistance and complies with FDA regulations for food contact materials, making it a safe choice for cookware applications. PTFE, widely used in nonstick coatings like Teflon, is also FDA-approved but raises concerns over potential release of toxic fumes at high temperatures above 260degC, necessitating careful temperature control during cooking.
Cost-Effectiveness and Production Efficiency
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior cost-effectiveness compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) due to its lower raw material expenses and faster curing times in nonstick coating applications. PBT's enhanced production efficiency stems from its thermoplastic properties, enabling quicker molding and reduced cycle times, whereas PTFE requires specialized sintering processes that increase manufacturing complexity and costs. Consequently, PBT provides a more economical solution for large-scale nonstick coatings without compromising durability and performance.
Polybutylene Terephthalate vs Polytetrafluoroethylene: Which is Better for Nonstick Coatings?
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance, making it suitable for nonstick coatings in high-wear applications. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is renowned for its superior nonstick properties, high thermal stability up to 260degC, and minimal friction, which makes it the preferred choice for cookware and industrial nonstick surfaces. While PBT provides durability and structural integrity, PTFE surpasses in low-friction performance and temperature tolerance, making PTFE generally better for nonstick coatings.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Nonstick coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com