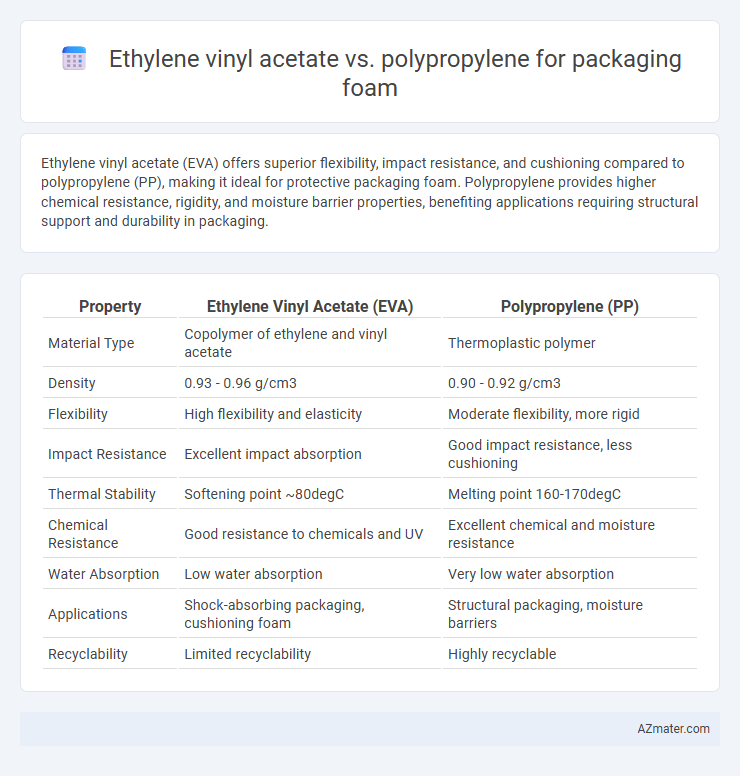
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility, impact resistance, and cushioning compared to polypropylene (PP), making it ideal for protective packaging foam. Polypropylene provides higher chemical resistance, rigidity, and moisture barrier properties, benefiting applications requiring structural support and durability in packaging.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Density | 0.93 - 0.96 g/cm3 | 0.90 - 0.92 g/cm3 |
| Flexibility | High flexibility and elasticity | Moderate flexibility, more rigid |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent impact absorption | Good impact resistance, less cushioning |
| Thermal Stability | Softening point ~80degC | Melting point 160-170degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to chemicals and UV | Excellent chemical and moisture resistance |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption | Very low water absorption |
| Applications | Shock-absorbing packaging, cushioning foam | Structural packaging, moisture barriers |
| Recyclability | Limited recyclability | Highly recyclable |
Introduction to Packaging Foam Materials
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) and polypropylene (PP) are widely used materials in packaging foam due to their distinct physical and chemical properties. EVA offers excellent flexibility, resilience, and clarity, making it suitable for cushioning fragile items and shock absorption in packaging applications. Polypropylene, characterized by its higher rigidity, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, is preferred for protective packaging that requires durable and lightweight foam solutions.
Overview of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is a copolymer composed of ethylene and vinyl acetate, widely used in packaging foam due to its excellent flexibility, clarity, and toughness. EVA foam provides superior cushioning, impact resistance, and resilience compared to polypropylene (PP), making it ideal for protective packaging applications. Its low-temperature toughness and resistance to UV radiation enhance durability, while EVA's non-toxic, closed-cell structure ensures moisture resistance and lightweight performance.
Key Properties of Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) for packaging foam offers exceptional chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and high tensile strength, making it ideal for durable protective applications. Its thermal stability and resistance to fatigue enhance packaging longevity during transportation and storage. PP's lightweight nature combined with excellent impact resistance delivers efficient cushioning without significantly increasing shipping costs.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) exhibits superior flexibility and tensile strength compared to polypropylene (PP), making it more resistant to cracking under stress in packaging foam applications. Polypropylene offers higher stiffness and better impact resistance, providing enhanced structural support for protective packaging. The choice between EVA and PP depends on the required balance between flexibility and rigidity in packaging foam performance.
Cushioning and Shock Absorption
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior cushioning and shock absorption compared to polypropylene (PP) due to its softer, more flexible structure and higher elasticity. EVA foam effectively dissipates impact energy, making it ideal for delicate item packaging, while polypropylene foam tends to be stiffer with lower resilience, providing firmer support but less shock absorption. The closed-cell nature of EVA also enhances its ability to absorb vibrations and reduce impact forces, outperforming polypropylene in protective packaging applications.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility and impact resistance but has lower thermal stability compared to polypropylene (PP), which withstands higher temperatures up to 160degC without deforming. EVA exhibits better resistance to UV radiation and chemical exposure such as oils and solvents, whereas PP shows excellent chemical resistance to acids and bases but can degrade under prolonged UV exposure. For packaging foam, EVA is preferred for applications needing cushioning and chemical durability, while PP excels in high-temperature environments requiring rigid structural foam.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers flexibility and cushioning but presents challenges in recycling due to its mixed polymer structure, often leading to landfill disposal and environmental persistence. Polypropylene (PP) foam is more environmentally favorable, featuring higher recyclability and lower carbon footprint due to its single-polymer composition and widespread recycling infrastructure. Choosing PP foam enhances sustainable packaging strategies by reducing plastic waste and facilitating material recovery in circular economy models.
Cost-Effectiveness in Packaging Applications
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior cushioning and flexibility at a moderate cost, making it highly cost-effective for protective packaging of fragile products. Polypropylene (PP), while generally less expensive and providing excellent rigidity and chemical resistance, may require additional processing to match EVA's shock-absorbing qualities, impacting overall packaging costs. Evaluating total lifecycle expenses, including material durability and performance in specific packaging environments, is crucial for determining the most economical choice between EVA and PP foams.
Common Packaging Uses: EVA vs PP
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is widely used in packaging for its excellent flexibility, cushioning properties, and resistance to stress cracking, making it ideal for protective foam packaging and shock absorption in electronics and fragile items. Polypropylene (PP) offers superior rigidity, chemical resistance, and moisture barrier qualities, which suit it well for rigid foam packaging such as food containers, automotive parts, and reusable packaging solutions. EVA excels in applications requiring soft, impact-absorbing foam, while PP is preferred for durable, lightweight, and moisture-resistant packaging materials.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Packaging Needs
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility, cushioning, and resistance to stress cracking, making it ideal for delicate or irregularly shaped items in packaging foam applications. Polypropylene (PP) excels in rigidity, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for protective packaging that demands structural support and durability. Carefully assessing product fragility, environmental exposure, and budget constraints ensures the optimal selection of EVA or PP for customized packaging solutions.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Polypropylene for Packaging foam
 azmater.com
azmater.com