Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers impact resistance and affordability for safety goggles, while polycarbonate provides superior optical clarity and higher impact strength for enhanced eye protection. Polycarbonate's lightweight nature and UV resistance make it the preferred material in demanding safety environments.
Table of Comparison
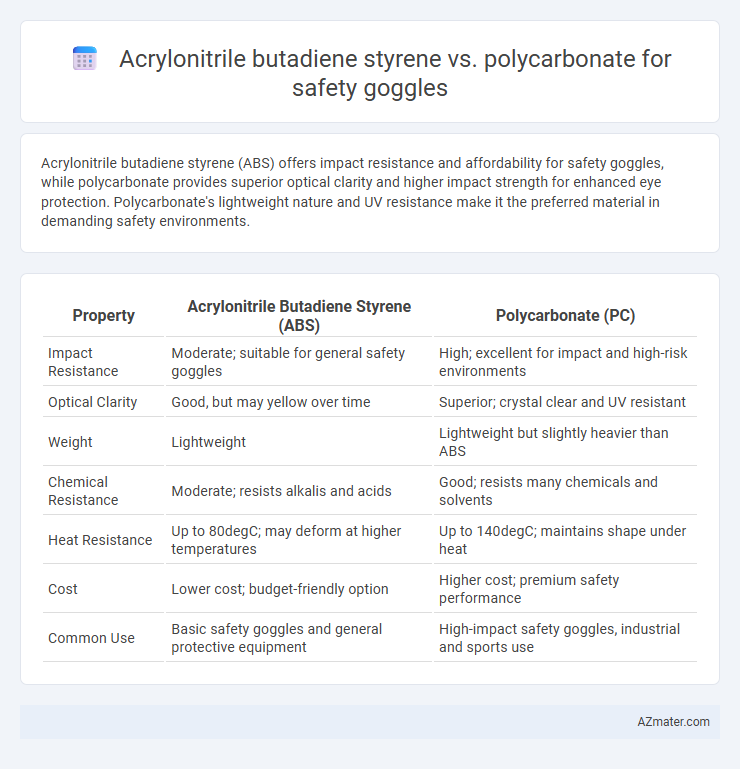
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | Moderate; suitable for general safety goggles | High; excellent for impact and high-risk environments |
| Optical Clarity | Good, but may yellow over time | Superior; crystal clear and UV resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight but slightly heavier than ABS |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate; resists alkalis and acids | Good; resists many chemicals and solvents |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 80degC; may deform at higher temperatures | Up to 140degC; maintains shape under heat |
| Cost | Lower cost; budget-friendly option | Higher cost; premium safety performance |
| Common Use | Basic safety goggles and general protective equipment | High-impact safety goggles, industrial and sports use |
Introduction to Safety Goggles: Importance of Material Choice
Safety goggles require materials with high impact resistance and clarity to ensure effective eye protection in hazardous environments. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent toughness and chemical resistance, making it suitable for lightweight, cost-effective goggles. Polycarbonate provides superior impact strength and optical clarity, essential for environments demanding maximum protection and durability.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent impact resistance and toughness, making it a popular choice for safety goggle frames that require durability and flexibility. ABS offers good resistance to chemical corrosion and physical impacts, ensuring reliable protection in various industrial and laboratory environments. Compared to Polycarbonate, ABS is generally more cost-effective but offers lower optical clarity and UV resistance, influencing its suitability for specific goggle lens applications.
Overview of Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC) is a highly durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic commonly used for safety goggles due to its superior optical clarity and excellent protection against high-velocity impacts. It offers UV resistance and inherent flame retardancy, making it ideal for environments requiring robust eye protection. Compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), PC provides enhanced toughness, better scratch resistance, and greater flexibility, ensuring long-lasting performance in industrial and laboratory settings.
Impact Resistance: ABS vs Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate exhibits significantly higher impact resistance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making it the preferred choice for safety goggles in high-risk environments. Polycarbonate can withstand impacts equivalent to a 6 mm steel ball traveling at 150 feet per second without cracking, whereas ABS offers moderate toughness but is more prone to cracking or fracturing under similar conditions. The superior impact resistance of polycarbonate ensures enhanced eye protection against flying debris and accidental impacts in industrial or laboratory settings.
Optical Clarity and Visibility Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polycarbonate differ significantly in optical clarity and visibility for safety goggles, with polycarbonate offering superior transparency and light transmission rates up to 90%. ABS typically exhibits lower optical clarity due to its amorphous structure, resulting in reduced visibility and potential haze that can impair visual performance. Polycarbonate's high impact resistance combined with its excellent optical properties makes it the preferred material for safety goggles requiring maximum visibility and eye protection.
Weight and Comfort in Goggles Design
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers a lightweight structure, enhancing comfort for extended wear in safety goggles, while polycarbonate is slightly heavier but provides superior impact resistance. ABS's lower density reduces overall goggle weight, minimizing user fatigue during prolonged use. Polycarbonate, despite its marginally higher weight, allows for thinner lens design, balancing protection and comfort effectively.
Chemical and Heat Resistance: Which is Superior?
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers good chemical resistance against acids and alkalis but tends to degrade under prolonged exposure to solvents, whereas polycarbonate exhibits superior resistance to many chemicals, including dilute acids and alcohols. Polycarbonate outperforms ABS in heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 140degC, compared to ABS which softens around 105degC. For safety goggles, polycarbonate's better chemical and heat resistance ensures enhanced durability and protection in hazardous environments.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers a cost-effective solution for safety goggles due to its lower material and manufacturing expenses compared to polycarbonate, making it widely accessible for budget-conscious applications. Polycarbonate provides superior impact resistance and optical clarity but comes at a higher price point, which may affect availability in large-scale or low-cost safety eyewear production. The widespread production and distribution networks of ABS ensure greater availability, while polycarbonate's enhanced properties justify its investment in environments demanding maximum safety performance.
Typical Applications in Safety Eyewear
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is commonly used in safety goggles for its high impact resistance and affordability, making it ideal for protective eyewear in construction and industrial environments. Polycarbonate offers superior optical clarity, UV protection, and exceptional impact resistance, frequently used in safety goggles for laboratories, sports, and manufacturing settings requiring enhanced eye protection. Both materials meet safety standards, but polycarbonate is preferred where high impact and clarity are critical for user safety.
Conclusion: Which Material is Ideal for Safety Goggles?
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and chemical stability, making it durable for safety goggles in industrial environments. Polycarbonate stands out for superior optical clarity and higher impact strength, providing enhanced eye protection against high-velocity particles and UV radiation. Polycarbonate is ideal for safety goggles due to its combination of lightweight comfort, exceptional impact resistance, and clear vision performance.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polycarbonate for Safety goggle
 azmater.com
azmater.com