Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior heat resistance, mechanical strength, and chemical stability compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for durable electronic housings. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and easy to mold, lacks the thermal and impact resistance required for long-term electronic device protection.
Table of Comparison
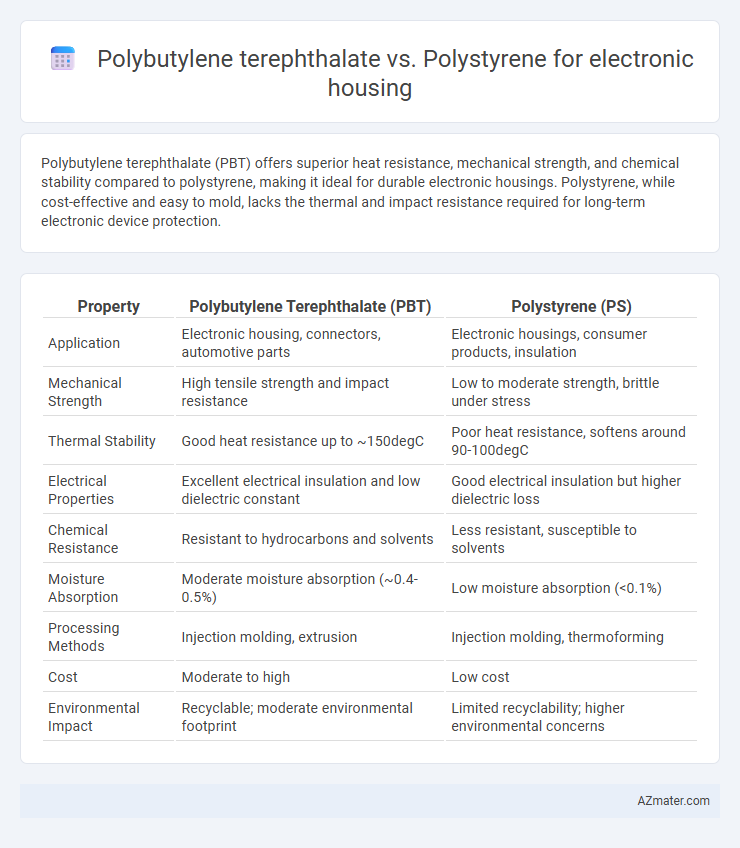
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Electronic housing, connectors, automotive parts | Electronic housings, consumer products, insulation |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and impact resistance | Low to moderate strength, brittle under stress |
| Thermal Stability | Good heat resistance up to ~150degC | Poor heat resistance, softens around 90-100degC |
| Electrical Properties | Excellent electrical insulation and low dielectric constant | Good electrical insulation but higher dielectric loss |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to hydrocarbons and solvents | Less resistant, susceptible to solvents |
| Moisture Absorption | Moderate moisture absorption (~0.4-0.5%) | Low moisture absorption (<0.1%) |
| Processing Methods | Injection molding, extrusion | Injection molding, thermoforming |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low cost |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable; moderate environmental footprint | Limited recyclability; higher environmental concerns |
Introduction to Electronic Housing Materials
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dimensional accuracy compared to polystyrene (PS), making it a preferred choice for electronic housings exposed to heat and mechanical stress. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and easy to mold, lacks the durability and heat resistance necessary for high-performance electronics, limiting its applications to low-stress environments. PBT's enhanced electrical insulation properties and flame retardancy provide critical safety features for electronic enclosures, ensuring long-term reliability and protection of internal components.
Overview of Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polyester known for its high mechanical strength, excellent electrical insulation properties, and resistance to heat and chemicals, making it ideal for electronic housing applications. PBT exhibits superior dimensional stability and impact resistance compared to polystyrene, ensuring durability in harsh electrical environments. Its low moisture absorption and flame-retardant characteristics further enhance safety and longevity in electronic component enclosures.
Overview of Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene (PS) is a versatile thermoplastic polymer widely used in electronic housing due to its excellent electrical insulation properties and ease of molding. It offers good dimensional stability, moderate impact resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for components requiring precise detail and surface finish. However, PS generally has lower heat resistance and mechanical strength compared to Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT), limiting its use in high-temperature or mechanically demanding electronic applications.
Mechanical Properties: PBT vs Polystyrene
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior mechanical properties compared to polystyrene (PS) for electronic housing, including higher tensile strength, impact resistance, and dimensional stability under thermal stress. PBT's enhanced toughness and resistance to creep make it ideal for applications requiring durability and structural integrity over time, while polystyrene tends to be more brittle and less resistant to impact and heat deformation. The superior mechanical robustness of PBT ensures better performance and longevity in electronic enclosures exposed to mechanical loads and thermal cycling.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior thermal performance for electronic housings compared to polystyrene (PS), with a higher heat deflection temperature typically around 140-150degC versus PS's 70-90degC. PBT exhibits better dimensional stability and resistance to thermal deformation under continuous heat exposure, making it ideal for components subjected to elevated operating temperatures. Polystyrene's lower thermal resistance and susceptibility to warping limit its use in high-temperature electronic applications where PBT's improved thermal endurance ensures long-term reliability.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance compared to polystyrene, effectively withstanding exposure to oils, solvents, and cleaning agents commonly encountered in electronic housing environments. PBT's high mechanical strength and thermal stability provide enhanced durability, ensuring reliable performance under mechanical stress and elevated temperatures. Polystyrene, while cost-effective, tends to be more brittle and less resistant to chemical degradation, making it less suitable for demanding electronic housing applications.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior electrical insulation properties compared to polystyrene, making it a preferred choice for electronic housings requiring high dielectric strength and dimensional stability under thermal stress. PBT exhibits excellent resistance to electrical tracking and arc formation, maintaining insulation integrity even in harsh environments. Polystyrene, while cost-effective, has lower dielectric strength and is more susceptible to cracking and degradation under electrical and thermal stress, limiting its use in high-performance electronic applications.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior cost efficiency for electronic housings due to its excellent dimensional stability and resistance to heat, reducing manufacturing defects and rework expenses. Polystyrene (PS), while generally less expensive per kilogram, often incurs higher total costs because of its lower thermal resistance and mechanical strength, leading to increased failure rates in demanding electronic applications. PBT's widespread availability in the electronics industry and compatibility with precision molding further enhance its cost-effectiveness compared to the more brittle and less durable polystyrene.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers a lower environmental impact compared to polystyrene (PS) due to its higher thermal stability and chemical resistance, which extends the lifespan of electronic housings and reduces waste. PBT is more recyclable through existing industrial processes, supporting circular economy initiatives by allowing efficient recovery and reuse of materials. In contrast, polystyrene's lower durability leads to more frequent replacement and challenges in recycling due to contamination and limited processing methods.
Application Suitability in Electronics Housing
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation, making it highly suitable for electronic housings exposed to heat and moisture. Polystyrene (PS), while cost-effective and easy to mold, lacks the mechanical strength and heat resistance required for durable electronic enclosures. PBT's dimensional stability and flame retardancy further enhance its application in safety-critical electronic housing components.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polystyrene for Electronic housing
 azmater.com
azmater.com