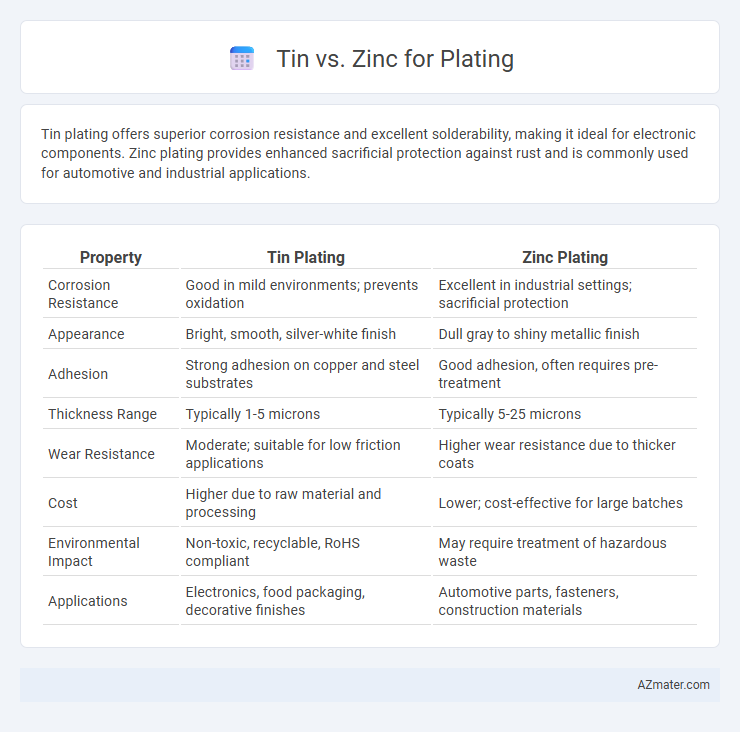
Tin plating offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent solderability, making it ideal for electronic components. Zinc plating provides enhanced sacrificial protection against rust and is commonly used for automotive and industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tin Plating | Zinc Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Good in mild environments; prevents oxidation | Excellent in industrial settings; sacrificial protection |
| Appearance | Bright, smooth, silver-white finish | Dull gray to shiny metallic finish |
| Adhesion | Strong adhesion on copper and steel substrates | Good adhesion, often requires pre-treatment |
| Thickness Range | Typically 1-5 microns | Typically 5-25 microns |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate; suitable for low friction applications | Higher wear resistance due to thicker coats |
| Cost | Higher due to raw material and processing | Lower; cost-effective for large batches |
| Environmental Impact | Non-toxic, recyclable, RoHS compliant | May require treatment of hazardous waste |
| Applications | Electronics, food packaging, decorative finishes | Automotive parts, fasteners, construction materials |
Introduction to Plating: Importance and Applications
Tin and zinc are widely used metals for plating due to their corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness. Tin plating provides excellent solderability and protects steel parts in electronics, while zinc plating offers robust protection against rust in automotive and construction applications. Both metals enhance the durability and performance of metal components across various industries, making them essential choices in surface finishing processes.
Overview of Tin Plating
Tin plating offers excellent corrosion resistance and solderability, making it ideal for electronic components and food packaging. With its bright, smooth finish, tin plating provides a protective barrier against oxidation and enhances adhesion for subsequent coatings. Its ability to prevent metal fatigue and maintain electrical conductivity distinguishes it from zinc plating in various industrial applications.
Overview of Zinc Plating
Zinc plating provides excellent corrosion resistance by creating a sacrificial barrier that protects the underlying metal from rust and oxidation, making it ideal for automotive and hardware applications. Its ability to form a uniform, durable coating with good adhesion enhances the longevity of steel parts exposed to moisture and harsh environments. Compared to tin plating, zinc offers superior protection against corrosion at a lower cost, while also contributing to environmental sustainability through its recyclability.
Key Chemical Properties: Tin vs Zinc
Tin plating offers excellent corrosion resistance and a low melting point of 232degC, making it ideal for soldering applications, while zinc plating provides superior sacrificial protection due to its higher reactivity and melting point of 420degC. Tin's chemical stability in various environments contrasts with zinc's ability to form a protective oxide layer that prevents rust on steel substrates. Both metals exhibit distinct electrochemical potentials, with zinc acting as an anode to protect underlying metals, whereas tin serves primarily as a barrier coating.
Corrosion Resistance: Tin Compared to Zinc
Tin exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to zinc due to its ability to form a stable, non-porous oxide layer that protects underlying metals from environmental factors. Zinc provides sacrificial protection by corroding preferentially, but it is more susceptible to white rust in humid conditions. Tin plating is preferred for applications requiring long-term resistance to oxidation and moisture without frequent maintenance.
Cost Analysis: Tin Plating vs Zinc Plating
Tin plating generally costs more than zinc plating due to the higher price of raw tin and more complex processing requirements. Zinc plating offers a more economical solution for large-scale industrial applications, with lower material costs and faster deposition rates. However, tin plating provides superior corrosion resistance and solderability, which may justify the higher expense in specialized uses.
Environmental Impact of Tin and Zinc Plating
Tin plating produces less toxic waste compared to zinc plating, as tin is more environmentally benign and does not leach harmful heavy metals into soil or water. Zinc plating, while offering excellent corrosion resistance, can release zinc ions that may accumulate and disrupt aquatic ecosystems. The energy consumption for both processes is comparable, but proper recycling and waste treatment are critical to minimizing environmental impact for both materials.
Industrial Applications: Best Uses for Each Metal
Tin plating is widely favored in the electronics industry due to its excellent solderability, corrosion resistance, and low toxicity, making it ideal for protecting delicate components and circuit boards. Zinc plating is predominantly used in automotive and construction industries because of its superior sacrificial corrosion protection, durability, and cost-effectiveness for steel parts and fasteners exposed to harsh environments. Choosing between tin and zinc depends on specific industrial requirements such as exposure conditions, mechanical wear, and desired lifespan of the coated materials.
Longevity and Maintenance Considerations
Zinc plating offers superior corrosion resistance and longer-lasting protection in outdoor or industrial environments compared to tin plating, which is more prone to wear and oxidation. Tin plating requires more frequent maintenance to preserve its conductivity and appearance, especially in high-humidity or corrosive settings. Zinc coatings generally provide durable, low-maintenance protection suitable for automotive and construction applications where longevity is critical.
Choosing the Right Plating: Factors to Consider
Tin plating offers excellent corrosion resistance and solderability, making it ideal for electronic components, while zinc plating provides superior protection against rust and abrasion, preferred in automotive and construction applications. Factors to consider when choosing between tin and zinc plating include the operating environment, required corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and cost constraints. Evaluating these parameters ensures optimal performance and longevity of the plated parts.
Infographic: Tin vs Zinc for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com