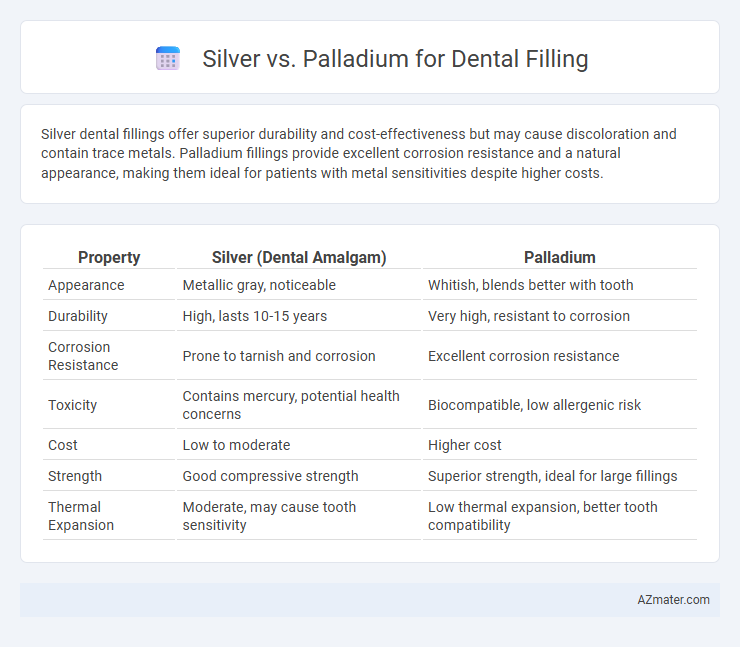
Silver dental fillings offer superior durability and cost-effectiveness but may cause discoloration and contain trace metals. Palladium fillings provide excellent corrosion resistance and a natural appearance, making them ideal for patients with metal sensitivities despite higher costs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Silver (Dental Amalgam) | Palladium |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Metallic gray, noticeable | Whitish, blends better with tooth |
| Durability | High, lasts 10-15 years | Very high, resistant to corrosion |
| Corrosion Resistance | Prone to tarnish and corrosion | Excellent corrosion resistance |
| Toxicity | Contains mercury, potential health concerns | Biocompatible, low allergenic risk |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Higher cost |
| Strength | Good compressive strength | Superior strength, ideal for large fillings |
| Thermal Expansion | Moderate, may cause tooth sensitivity | Low thermal expansion, better tooth compatibility |
Introduction to Dental Filling Materials
Dental filling materials primarily include silver amalgam and palladium alloys, known for their durability and biocompatibility in restorative dentistry. Silver amalgam, composed of a mixture of metals including silver, mercury, tin, and copper, offers strength and wear resistance suitable for posterior teeth. Palladium-based alloys provide enhanced corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, often preferred in cases requiring a metal alloy with reduced tarnishing and improved biocompatibility.
Overview of Silver Fillings (Amalgam)
Silver fillings, commonly known as dental amalgam, are composed of a mixture of metals including silver, mercury, tin, and copper, making them highly durable and resistant to wear. These restorations have been widely used in dentistry for over 150 years due to their strength and cost-effectiveness. Despite their longevity, concerns about mercury content have led to increased interest in alternative materials like palladium-based alloys.
Overview of Palladium Fillings
Palladium fillings are prized in dentistry for their durability, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility, making them a superior alternative to traditional silver amalgams. These fillings provide a natural metallic luster and exhibit minimal wear over time, which contributes to long-lasting dental restorations. Palladium alloys often contain a blend of metals that enhance strength and provide excellent sealing to prevent bacterial infiltration.
Material Composition and Properties
Silver dental fillings, primarily composed of a silver-tin alloy combined with copper and trace metals, offer high durability and resistance to wear, making them suitable for molars subjected to heavy chewing forces. Palladium dental fillings, often part of high-noble or noble alloys including gold and sometimes silver, provide excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, reducing the risk of allergic reactions and enhancing longevity. The differences in thermal expansion rates between silver and palladium alloys influence their marginal integrity and overall performance in dental restorations.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Silver dental fillings, commonly referred to as amalgam, offer exceptional strength and long-lasting durability, often lasting 10-15 years or more under normal biting forces. Palladium, used in some dental alloys, provides superior corrosion resistance and maintains strength over time but is typically more expensive and less commonly used in bulk fillings. Both metals exhibit high wear resistance, yet silver amalgam remains the preferred choice for large restorations due to its proven longevity and cost-effectiveness in dental applications.
Aesthetic Differences: Silver vs Palladium
Silver dental fillings, primarily composed of amalgam, exhibit a metallic, dark gray appearance that contrasts noticeably with natural tooth color, making them less aesthetically appealing. Palladium-infused dental materials offer a more subtle, silver-white tone that blends better with natural teeth, enhancing overall cosmetic appeal. The choice between silver and palladium fillings significantly impacts the visual harmony of dental restorations, with palladium providing a more discreet, tooth-colored finish.
Biocompatibility and Allergic Reactions
Silver and palladium differ significantly in biocompatibility and allergic reactions when used in dental fillings. Silver amalgam contains mercury, which can cause allergic or toxic responses in sensitive patients, whereas palladium alloys generally exhibit higher biocompatibility with fewer allergic reactions reported. Studies indicate that palladium's corrosion resistance enhances safety and reduces the risk of hypersensitivity compared to silver-based materials.
Cost Analysis: Silver vs Palladium Fillings
Silver dental fillings, primarily composed of amalgam, generally cost between $50 to $150 per tooth, making them one of the most affordable options for dental restorations. Palladium fillings, often found in high-noble metal alloys, can range from $250 to $500 or more per tooth due to the metal's rarity and superior corrosion resistance. Cost differences are influenced by material prices, durability, and aesthetic preferences, with silver fillings favored for budget-conscious patients and palladium selected for its longevity and biocompatibility despite higher upfront costs.
Longevity and Maintenance Considerations
Silver dental fillings, commonly made from amalgam, offer superior longevity, often lasting 10 to 15 years or more with minimal maintenance due to their strong resistance to wear and corrosion. Palladium fillings, while more aesthetically pleasing and less prone to tarnish than silver, typically have a shorter lifespan of around 7 to 10 years and may require more careful oral hygiene to prevent discoloration and degradation. Maintenance considerations for silver fillings include monitoring for potential cracks or mercury leakage, whereas palladium fillings demand regular polishing and vigilance against surface erosion to preserve their appearance and functionality.
Choosing the Best Filling Material for Your Needs
Silver amalgam fillings offer durability and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for large cavities and high-bite pressure areas, while palladium-based alloys provide superior corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, reducing allergic reactions and enhancing longevity. Consider factors like cavity size, aesthetic preference, budget, and potential metal sensitivities when selecting between silver and palladium for dental restorations. Consulting a dental professional ensures the chosen material aligns with your oral health requirements and lifestyle.
Infographic: Silver vs Palladium for Dental Filling
 azmater.com
azmater.com