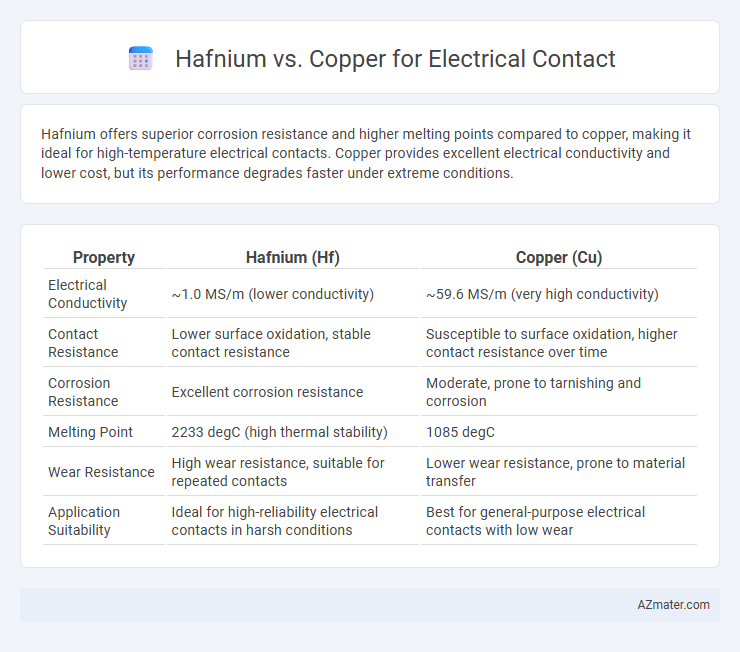
Hafnium offers superior corrosion resistance and higher melting points compared to copper, making it ideal for high-temperature electrical contacts. Copper provides excellent electrical conductivity and lower cost, but its performance degrades faster under extreme conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hafnium (Hf) | Copper (Cu) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | ~1.0 MS/m (lower conductivity) | ~59.6 MS/m (very high conductivity) |
| Contact Resistance | Lower surface oxidation, stable contact resistance | Susceptible to surface oxidation, higher contact resistance over time |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent corrosion resistance | Moderate, prone to tarnishing and corrosion |
| Melting Point | 2233 degC (high thermal stability) | 1085 degC |
| Wear Resistance | High wear resistance, suitable for repeated contacts | Lower wear resistance, prone to material transfer |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for high-reliability electrical contacts in harsh conditions | Best for general-purpose electrical contacts with low wear |
Introduction to Electrical Contact Materials
Hafnium and copper are crucial materials in electrical contact applications due to their distinct electrical and mechanical properties. Copper offers excellent electrical conductivity and thermal performance, making it a standard choice for low-resistance contacts, while hafnium provides superior wear resistance and high melting point, which enhances durability under extreme conditions. The selection between hafnium and copper depends on balancing conductivity with mechanical robustness to optimize contact reliability and longevity.
Overview of Hafnium and Copper
Hafnium and copper exhibit distinct electrical and physical properties that influence their suitability for electrical contacts. Copper is highly valued for its exceptional electrical conductivity (5.96 x 10^7 S/m) and thermal conductivity, making it the standard choice for connectors and circuit components. Hafnium, while having lower conductivity, offers excellent resistance to oxidation, high melting point (2,233degC), and robustness under extreme conditions, making it advantageous for specialized contacts exposed to harsh environments.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Hafnium exhibits significantly lower electrical conductivity compared to copper, with copper's conductivity approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, while hafnium's conductivity is about 2.25 x 10^6 S/m. This difference impacts electrical contact performance, as copper offers superior current-carrying capacity and reduced resistive losses. Despite hafnium's lower conductivity, its high melting point and corrosion resistance make it suitable for specialized electrical contact applications where durability matters more than conductivity.
Thermal Performance of Hafnium vs Copper
Hafnium exhibits superior thermal stability compared to copper, maintaining its structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1500degC, whereas copper's melting point is approximately 1085degC, limiting its thermal endurance in high-temperature applications. Hafnium's thermal conductivity, while lower than copper's 400 W/m*K, remains sufficient for effective heat dissipation in electrical contacts exposed to intense thermal stress. This balance of high melting point and adequate thermal conductivity makes hafnium an excellent material choice for electrical contacts subjected to extreme thermal environments.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Hafnium exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to copper, making it highly suitable for electrical contacts in harsh environments. Its exceptional durability under high temperatures and oxidative conditions ensures longer service life and reduced maintenance. Copper, while offering excellent electrical conductivity, is prone to oxidation and corrosion, which can compromise contact reliability over time.
Mechanical Strength and Wear Resistance
Hafnium exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to copper, making it highly resistant to deformation under mechanical stress in electrical contacts. Its exceptional wear resistance enhances durability in high-load and high-cycle switching environments, reducing material degradation and contact failure. Copper, while excellent for electrical conductivity, is softer and more prone to wear, limiting its lifespan in demanding mechanical applications.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Copper remains the preferred choice for electrical contacts due to its widespread availability and lower cost compared to hafnium. Hafnium, being a rare and costly transition metal, significantly increases material expenses, limiting its practical use in large-scale applications. Cost-effectiveness and supply stability make copper the dominant material for most electrical contact manufacturing despite hafnium's superior corrosion resistance.
Applications in Electrical Engineering
Hafnium is valued in electrical engineering for its high melting point, excellent corrosion resistance, and stable electrical conductivity, making it suitable for high-temperature electrical contact applications such as vacuum interrupters and plasma-facing components in fusion reactors. Copper, widely used in electrical contacts due to its superior electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness, excels in applications like switchgear, connectors, and circuit breakers where lower resistance and efficient current flow are critical. The choice between hafnium and copper hinges on application environments: hafnium is preferred in extreme thermal and oxidative conditions, while copper dominates in standard, cost-sensitive electrical contact uses.
Environmental and Safety Factors
Hafnium offers superior corrosion resistance and higher melting points compared to copper, making it more durable under extreme electrical contact conditions while reducing the risk of toxic metal release. Copper, although highly conductive, is prone to oxidation and wear, which can lead to environmental contamination from copper ions in soil and water. Choosing hafnium minimizes environmental impact and enhances safety by lowering maintenance needs and preventing hazardous material degradation.
Choosing the Right Material for Electrical Contacts
Hafnium offers superior corrosion resistance and higher melting point compared to copper, making it ideal for high-temperature and demanding electrical contact applications. Copper excels in electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness but tends to degrade faster under extreme conditions. Selecting hafnium or copper for electrical contacts depends on balancing conductivity requirements against environmental durability and longevity.
Infographic: Hafnium vs Copper for Electrical Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com