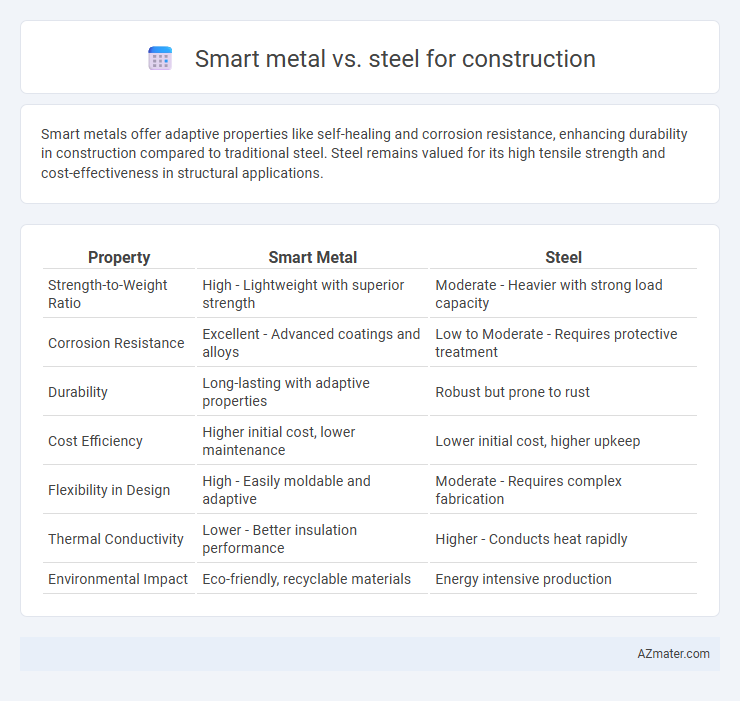
Smart metals offer adaptive properties like self-healing and corrosion resistance, enhancing durability in construction compared to traditional steel. Steel remains valued for its high tensile strength and cost-effectiveness in structural applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Smart Metal | Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | High - Lightweight with superior strength | Moderate - Heavier with strong load capacity |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent - Advanced coatings and alloys | Low to Moderate - Requires protective treatment |
| Durability | Long-lasting with adaptive properties | Robust but prone to rust |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial cost, lower maintenance | Lower initial cost, higher upkeep |
| Flexibility in Design | High - Easily moldable and adaptive | Moderate - Requires complex fabrication |
| Thermal Conductivity | Lower - Better insulation performance | Higher - Conducts heat rapidly |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, recyclable materials | Energy intensive production |
Introduction to Smart Metal and Steel in Modern Construction
Smart metal in construction refers to advanced materials embedded with sensors or designed to adapt to environmental changes, enhancing durability and structural performance. Steel remains a fundamental material due to its strength, versatility, and cost-effectiveness, widely used in frameworks and reinforcements. Integrating smart metals with traditional steel structures offers innovative solutions for real-time monitoring and adaptive responses in modern construction projects.
Defining Smart Metal: Features and Innovations
Smart metal in construction refers to advanced metallic materials embedded with sensors or designed with adaptive properties that respond to environmental changes such as temperature, stress, or corrosion. These metals incorporate features like self-healing capabilities, shape memory effects, and real-time structural health monitoring, enhancing durability and safety compared to traditional steel. Innovations in smart metal technology enable proactive maintenance, improved energy efficiency, and extended lifespan of construction frameworks, revolutionizing modern building practices.
Traditional Steel: Properties and Common Uses
Traditional steel, characterized by its high tensile strength and durability, remains a cornerstone in construction for structural frameworks, beams, and reinforcement bars. Its versatility supports heavy load-bearing applications and offers excellent weldability, making it ideal for skyscrapers, bridges, and industrial buildings. The material's resistance to deformation and cost-effectiveness contribute to its widespread use in foundational and support elements across diverse construction projects.
Mechanical Strength Comparison: Smart Metal vs Steel
Smart metal exhibits enhanced mechanical strength through advanced alloying and microstructural engineering, offering superior tensile strength and fatigue resistance compared to traditional steel grades. Steel remains widely used due to its balanced strength, ductility, and cost-effectiveness, but smart metals like shape-memory alloys and high-entropy alloys provide improved load-bearing capacity and deformation recovery. Mechanical strength comparisons highlight smart metals' potential for higher durability and resilience in dynamic construction environments where performance under cyclic stress is critical.
Durability and Lifespan: Which Material Lasts Longer?
Smart metal, engineered with advanced alloys and coatings, often exhibits superior corrosion resistance and enhanced durability compared to traditional steel, making it well-suited for harsh construction environments. Steel, particularly high-grade structural steel, offers robust strength and longevity but may require frequent maintenance to prevent rust and degradation in exposed settings. Overall, smart metal tends to last longer in demanding applications due to its innovative composition and protective treatments, reducing lifecycle costs and extending structural lifespan.
Cost Analysis: Smart Metal vs Conventional Steel
Smart metal offers a competitive cost advantage over conventional steel due to its enhanced durability and reduced maintenance expenses, leading to lower lifecycle costs in construction projects. Although the initial investment in smart metal can be higher, savings from energy efficiency, corrosion resistance, and longer service life contribute to overall cost-effectiveness. In contrast, conventional steel often incurs additional expenses related to frequent repairs, protective coatings, and shorter replacement cycles, increasing total project costs over time.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Smart metal alloys, engineered for enhanced strength and durability, reduce material usage and waste during construction, offering significant environmental benefits compared to traditional steel. Steel production is energy-intensive and emits substantial CO2, whereas smart metals often incorporate recycled elements and require less energy for fabrication. Choosing smart metals promotes sustainability by lowering carbon footprints and supporting circular economy principles in construction projects.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Construction Projects
Smart metal offers superior flexibility and adaptability in construction projects compared to traditional steel due to its ability to change shape, self-heal, and respond to environmental stimuli. Its shape memory and superelastic properties enable dynamic structural adjustments, reducing the need for extensive retrofitting and enhancing the longevity of constructions. This advanced adaptability makes smart metal ideal for innovative architectural designs and seismic-resistant structures, outperforming conventional steel in modern construction applications.
Safety and Maintenance Requirements
Smart metal offers enhanced safety features compared to traditional steel due to its advanced corrosion resistance and self-healing properties, reducing structural failure risks over time. Steel requires regular maintenance, such as coatings and inspections to prevent rust and deterioration, increasing long-term costs and safety concerns. The reduced maintenance demands of smart metals improve overall durability and ensure safer construction environments.
Future Trends: The Role of Smart Metals in Construction
Smart metals in construction are revolutionizing building efficiency by integrating sensors and self-healing properties, unlike traditional steel which lacks these advanced features. These metals enhance structural health monitoring, enabling real-time data collection that predicts maintenance needs and extends building lifespan. Future trends emphasize the growing adoption of smart metals for sustainable, resilient infrastructure that adapts to environmental conditions and reduces long-term costs.
Infographic: Smart metal vs Steel for Construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com