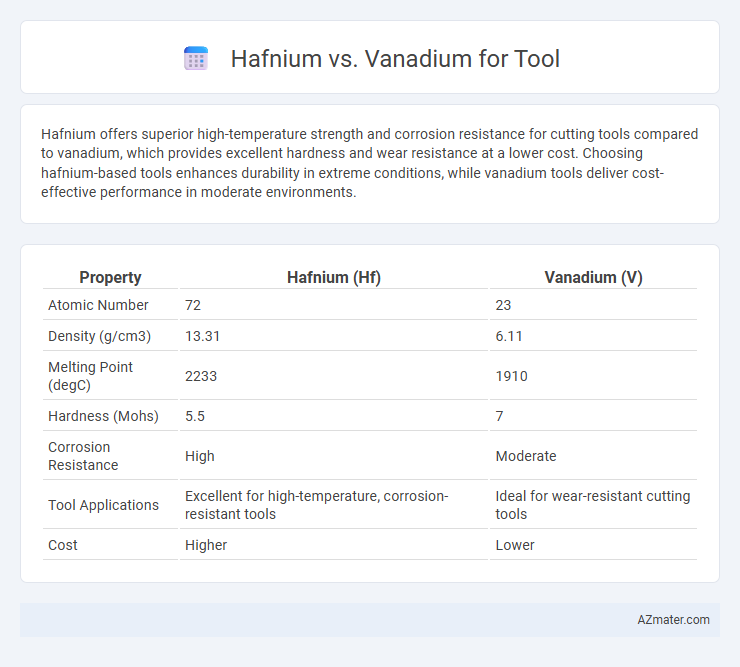
Hafnium offers superior high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance for cutting tools compared to vanadium, which provides excellent hardness and wear resistance at a lower cost. Choosing hafnium-based tools enhances durability in extreme conditions, while vanadium tools deliver cost-effective performance in moderate environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hafnium (Hf) | Vanadium (V) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 72 | 23 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 13.31 | 6.11 |
| Melting Point (degC) | 2233 | 1910 |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 5.5 | 7 |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Tool Applications | Excellent for high-temperature, corrosion-resistant tools | Ideal for wear-resistant cutting tools |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Hafnium and Vanadium in Toolmaking
Hafnium and vanadium are critical alloys used in toolmaking due to their unique mechanical properties. Hafnium offers excellent ductility and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for high-precision cutting tools and aerospace applications. Vanadium enhances tool steel hardness and wear resistance, improving the durability and performance of industrial cutting and machining tools.
Chemical and Physical Properties Comparison
Hafnium exhibits superior corrosion resistance and higher melting point (2233degC) compared to vanadium's melting point of 1910degC, making it ideal for high-temperature tool applications. Its density (13.31 g/cm3) significantly exceeds that of vanadium (6.0 g/cm3), contributing to enhanced durability and wear resistance in cutting and drilling tools. Vanadium's notable hardness and ability to form stable carbides improve tool strength and toughness, whereas hafnium's chemical inertness provides exceptional oxidation resistance in extreme environments.
Mechanical Strength and Hardness
Hafnium exhibits superior mechanical strength and hardness compared to vanadium, making it highly suitable for high-performance cutting tools. Its high melting point of 2233degC and excellent tensile strength enhance tool durability under extreme conditions. Vanadium, while valued for improving steel hardness through alloying, generally offers lower intrinsic strength and hardness than hafnium in pure form.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Hafnium exhibits superior corrosion and oxidation resistance compared to vanadium, making it highly suitable for high-temperature and corrosive environments in tooling applications. Its stable oxide layer forms a protective barrier that prevents further degradation, enhancing tool longevity and performance under harsh conditions. Vanadium, while offering good wear resistance, is more prone to oxidation and corrosion, limiting its effectiveness in aggressive environments.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Hafnium outperforms vanadium in tool applications due to its superior thermal stability, maintaining strength and hardness at temperatures above 1500degC, while vanadium typically degrades above 1000degC. Hafnium alloys exhibit enhanced resistance to thermal softening and oxidation, which extends tool life under high-temperature machining conditions. Vanadium, though beneficial for toughness and wear resistance, cannot match hafnium's thermal endurance in demanding thermal performance scenarios.
Machinability and Fabrication Ease
Hafnium offers superior machinability due to its fine grain structure and excellent thermal stability, making it ideal for precision tooling in high-temperature environments. Vanadium, while tougher and more abrasion-resistant, presents greater challenges in fabrication because of its higher hardness and propensity for work hardening. Toolmakers favor hafnium for ease of machining and moderate strength, whereas vanadium is preferred when durability and wear resistance are critical despite more complex machining processes.
Industrial Applications in Tool Manufacturing
Hafnium exhibits exceptional high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for cutting tools used in aerospace and nuclear industries where thermal stability is critical. Vanadium is prized for its ability to improve steel hardness, wear resistance, and toughness, which enhances the performance and lifespan of industrial tools such as drills, saw blades, and dies. In tool manufacturing, the combination of vanadium's alloying benefits with hafnium's thermal properties supports advanced tooling solutions for metalworking and heavy machinery applications.
Cost and Material Availability
Hafnium tools are significantly more expensive than vanadium due to the rarity and complex extraction process of hafnium, which is primarily obtained as a byproduct of zirconium refinement. Vanadium, more abundant in Earth's crust, offers cost-effective availability and widespread use in tool alloys, especially high-strength steels. The limited supply and higher price of hafnium restrict its applications mainly to specialized high-temperature tools, while vanadium's ample availability ensures its dominance in cost-sensitive industrial tooling.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Hafnium exhibits superior corrosion resistance and higher melting points compared to vanadium, making it safer for high-temperature tool applications with reduced risk of material degradation and environmental contamination. Vanadium's extraction and processing involve toxic byproducts, posing greater environmental hazards and necessitating stringent safety protocols. Choosing hafnium can minimize ecological impact and enhance worker safety due to less hazardous exposure during manufacturing and use.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Metal for Tools
Hafnium offers superior heat resistance and corrosion durability, making it ideal for high-temperature tool applications in industries like aerospace and nuclear. Vanadium excels in enhancing steel hardness and wear resistance, providing cost-effective strength for general cutting and drilling tools. Choosing between hafnium and vanadium depends on specific performance requirements, with hafnium favored for extreme environments and vanadium preferred for robust, everyday tool manufacturing.
Infographic: Hafnium vs Vanadium for Tool
 azmater.com
azmater.com