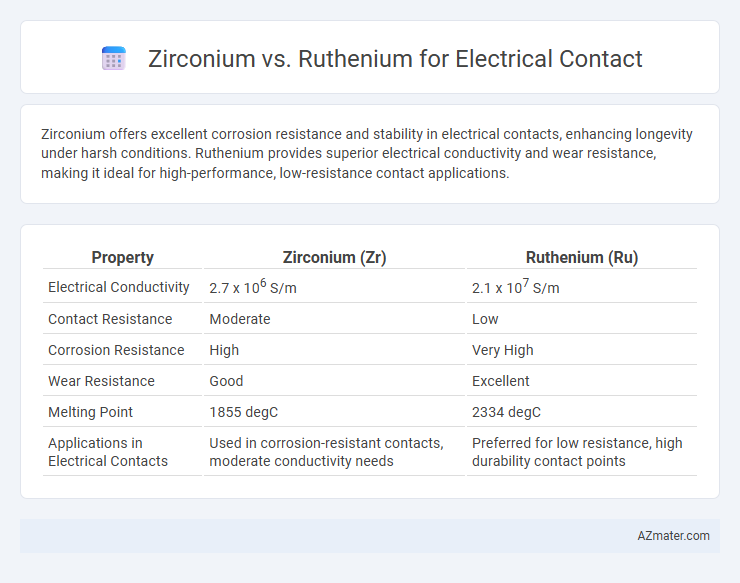
Zirconium offers excellent corrosion resistance and stability in electrical contacts, enhancing longevity under harsh conditions. Ruthenium provides superior electrical conductivity and wear resistance, making it ideal for high-performance, low-resistance contact applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zirconium (Zr) | Ruthenium (Ru) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 2.7 x 106 S/m | 2.1 x 107 S/m |
| Contact Resistance | Moderate | Low |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Very High |
| Wear Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Melting Point | 1855 degC | 2334 degC |
| Applications in Electrical Contacts | Used in corrosion-resistant contacts, moderate conductivity needs | Preferred for low resistance, high durability contact points |
Overview of Zirconium and Ruthenium in Electrical Contacts
Zirconium and ruthenium are both valuable in electrical contacts due to their excellent corrosion resistance and stability under high temperatures. Zirconium offers superior oxidation resistance and mechanical strength, making it suitable for harsh environments and prolonged contact life. Ruthenium excels in electrical conductivity and wear resistance, often used as a thin plating to enhance contact durability and minimize electrical resistance.
Material Properties Comparison: Zirconium vs Ruthenium
Zirconium offers excellent corrosion resistance and good electrical conductivity, making it suitable for electrical contacts in harsh environments, whereas Ruthenium provides superior hardness and wear resistance alongside high electrical conductivity, enhancing contact durability. Zirconium's lower electrical resistivity (approximately 42 nO*m) compares to Ruthenium's slightly higher resistivity (around 71 nO*m), impacting efficiency in electrical transmission. The choice between Zirconium and Ruthenium depends on prioritizing corrosion resistance and ductility versus mechanical strength and contact longevity in electrical applications.
Electrical Conductivity: Which Metal Performs Better?
Ruthenium offers superior electrical conductivity compared to zirconium, making it a preferred choice for electrical contacts requiring efficient current flow. While zirconium provides good corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, its lower electrical conductivity can limit performance in high-conductivity applications. Ruthenium's excellent conductivity combined with high wear resistance ensures reliable and long-lasting electrical connections in demanding environments.
Wear Resistance and Durability of Zirconium and Ruthenium Contacts
Zirconium electrical contacts exhibit exceptional wear resistance due to their strong oxide layer, enhancing durability under high-load and harsh environmental conditions. Ruthenium contacts demonstrate superior hardness and corrosion resistance, resulting in longer service life and stable performance in low-voltage switching applications. Both metals provide reliable wear resistance, but zirconium excels in high-temperature environments, while ruthenium is preferred for its durability in fine, low-wear contacts.
Oxidation and Corrosion Resistance in Electrical Environments
Zirconium exhibits excellent oxidation resistance due to the formation of a stable, dense oxide layer, making it highly effective in preventing corrosion in electrical contacts exposed to harsh environments. Ruthenium, a platinum-group metal, offers superior corrosion resistance and maintains electrical conductivity under oxidative stress, making it ideal for long-term, high-reliability electrical contacts. Both metals are valued in electrical applications, but ruthenium's robustness against oxidation and corrosion often provides enhanced durability in demanding electrical environments.
Cost Analysis: Zirconium vs Ruthenium for Electrical Applications
Zirconium offers a more cost-effective solution for electrical contacts compared to ruthenium, primarily due to its greater abundance and lower raw material price, making it attractive for large-scale industrial use. Ruthenium, though more expensive, provides superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, which can justify higher initial costs in high-performance or specialized applications. Evaluating total lifecycle costs, including maintenance and replacement frequency, often reveals zirconium as the economical choice for most standard electrical contact requirements.
Suitability for High-Temperature Operations
Zirconium offers excellent resistance to oxidation and maintains structural integrity at temperatures up to 1800degC, making it suitable for high-temperature electrical contacts. Ruthenium features exceptional electrical conductivity and strong corrosion resistance but typically operates effectively below 1200degC. For electrical contacts in extreme heat environments, zirconium is generally preferred due to its superior thermal stability and oxidation resistance.
Environmental Impact and Material Sustainability
Zirconium offers excellent corrosion resistance and is abundant, making it a sustainable choice for electrical contacts with minimal environmental impact during extraction and processing. Ruthenium, though highly durable and providing superior electrical conductivity, is a rare platinum-group metal with a limited supply and higher ecological footprint due to intensive mining activities. Selecting zirconium supports eco-friendly manufacturing and long-term resource availability, whereas ruthenium demands careful consideration of sustainability and environmental costs.
Industry Applications: Where Each Metal Excels
Zirconium excels in electrical contact applications within the aerospace and nuclear industries due to its exceptional corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability, ensuring reliable performance under extreme conditions. Ruthenium is favored in the electronics industry for its outstanding conductivity, hardness, and wear resistance, making it ideal for microelectronic contacts and thin-film resistors. Both metals find critical roles in specific sectors, with zirconium suited for harsh environments and ruthenium optimized for precision electrical components.
Choosing the Right Metal for Electrical Contact Needs
Zirconium offers excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for electrical contacts in harsh environments. Ruthenium provides superior electrical conductivity and wear resistance, enhancing contact reliability in low-voltage, high-cycle applications. Selecting the right metal depends on balancing environmental conditions, conductivity requirements, and mechanical durability for optimal electrical contact performance.
Infographic: Zirconium vs Ruthenium for Electrical Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com