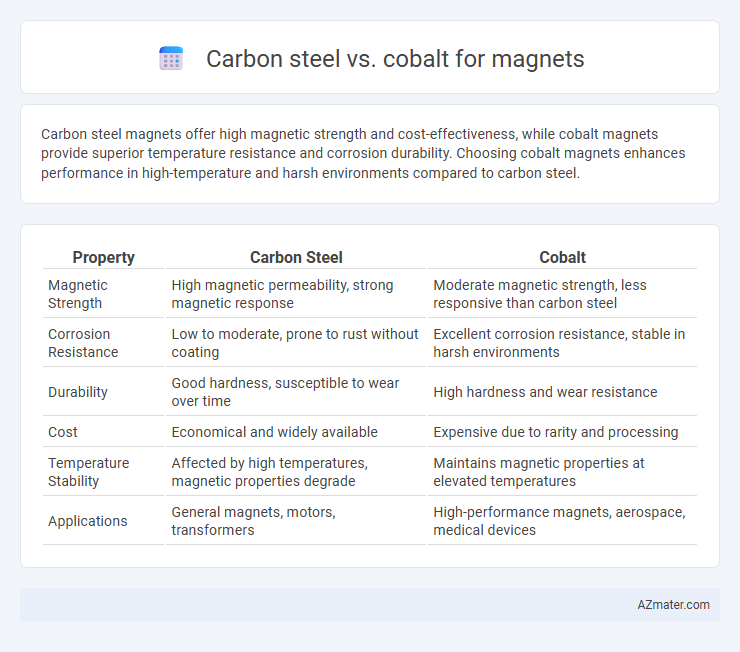
Carbon steel magnets offer high magnetic strength and cost-effectiveness, while cobalt magnets provide superior temperature resistance and corrosion durability. Choosing cobalt magnets enhances performance in high-temperature and harsh environments compared to carbon steel.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Steel | Cobalt |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Strength | High magnetic permeability, strong magnetic response | Moderate magnetic strength, less responsive than carbon steel |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low to moderate, prone to rust without coating | Excellent corrosion resistance, stable in harsh environments |
| Durability | Good hardness, susceptible to wear over time | High hardness and wear resistance |
| Cost | Economical and widely available | Expensive due to rarity and processing |
| Temperature Stability | Affected by high temperatures, magnetic properties degrade | Maintains magnetic properties at elevated temperatures |
| Applications | General magnets, motors, transformers | High-performance magnets, aerospace, medical devices |
Introduction to Magnetic Materials
Carbon steel and cobalt are pivotal materials in the realm of magnetic applications, each offering distinct magnetic properties. Carbon steel exhibits high magnetic permeability and strong magnetic retention, making it ideal for electromagnets and transformer cores, whereas cobalt stands out with superior coercivity and thermal stability, suited for permanent magnets such as Alnico alloys. Understanding the microstructural differences and magnetic domain behavior between carbon steel and cobalt enhances the selection process for efficient and specialized magnetic devices.
Overview of Carbon Steel as a Magnet Material
Carbon steel is a popular magnet material due to its high iron content and excellent magnetic permeability, which allows it to produce strong, durable magnets ideal for industrial and electronic applications. Its alloy composition, primarily iron mixed with 0.05% to 2% carbon, enhances hardness and tensile strength while maintaining good magnetic properties. Carbon steel magnets are cost-effective, easily machinable, and exhibit strong coercivity, making them suitable for permanent magnet applications where moderate magnetic strength and durability are required.
Cobalt-Based Magnets: Properties and Applications
Cobalt-based magnets exhibit high magnetic strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and superior thermal stability compared to carbon steel magnets, making them ideal for high-performance applications. These magnets are commonly used in aerospace, medical devices, and electric motors where durability under extreme conditions is critical. Their ability to maintain magnetic properties at elevated temperatures up to 600degC sets cobalt magnets apart from carbon steel counterparts, which typically degrade faster.
Magnetic Strength Comparison: Carbon Steel vs. Cobalt
Cobalt magnets exhibit higher magnetic strength and thermal stability compared to carbon steel magnets, making them ideal for high-performance applications. Carbon steel magnets, while cost-effective, have lower coercivity and magnetic retention, leading to faster demagnetization under stress. The intrinsic magnetic properties of cobalt allow for stronger magnetic flux density and improved resistance to corrosion compared to carbon steel alternatives.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Carbon steel magnets offer high durability due to their strong structural properties, but they are prone to rust and corrosion without proper coating or maintenance. Cobalt magnets exhibit superior corrosion resistance and maintain magnetic strength in harsh environments, making them ideal for applications requiring both durability and longevity. The choice between carbon steel and cobalt hinges on balancing mechanical strength with environmental resilience for optimal magnet performance.
Cost and Availability
Carbon steel magnets tend to be more cost-effective and widely available due to the abundance of iron and carbon materials, making them a budget-friendly option for large-scale use. Cobalt magnets, in contrast, are significantly more expensive because cobalt is a rarer and more costly metal, limiting their widespread availability. The higher price and limited supply of cobalt impact its feasibility for mass production despite its superior magnetic properties.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Cobalt magnets exhibit superior performance in high-temperature environments, maintaining magnetic strength up to 400degC, whereas carbon steel magnets typically begin to lose magnetism above 200degC. The Curie temperature of cobalt alloys is significantly higher than that of carbon steel, enabling better thermal stability and resistance to demagnetization. This makes cobalt a preferred choice for applications requiring consistent magnetic properties under elevated temperatures.
Common Uses in Industry
Carbon steel magnets are widely used in industrial applications such as automotive manufacturing, electrical motors, and heavy machinery due to their high magnetic strength and cost-effectiveness. Cobalt magnets, including Alnico alloys, are preferred in aerospace, medical devices, and high-performance sensors for their excellent temperature stability and corrosion resistance. Both materials serve critical roles, with carbon steel dominating mass production needs and cobalt excelling in specialized environments requiring durability under extreme conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon steel magnets exhibit a lower environmental impact due to their abundance and recyclability, reducing the need for intensive mining activities compared to cobalt. Cobalt mining poses significant sustainability challenges, including habitat destruction and ethical concerns related to labor practices in cobalt-rich regions. Utilizing carbon steel helps minimize ecological disruption and supports circular economy principles, whereas cobalt's scarcity and extraction issues complicate its sustainable use in magnet production.
Choosing the Right Material: Key Considerations
Choosing between carbon steel and cobalt for magnets involves evaluating magnetic strength, corrosion resistance, and temperature stability. Carbon steel offers high magnetic permeability and affordability but is prone to rust and lower temperature tolerance. Cobalt magnets provide superior corrosion resistance and maintain magnetic properties at elevated temperatures, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications.
Infographic: Carbon steel vs Cobalt for Magnet
 azmater.com
azmater.com