Rhodium offers superior reflectivity and corrosion resistance compared to iron, making it ideal for high-quality mirror coatings. Iron mirrors, while more affordable, are prone to rust and provide lower optical clarity.
Table of Comparison
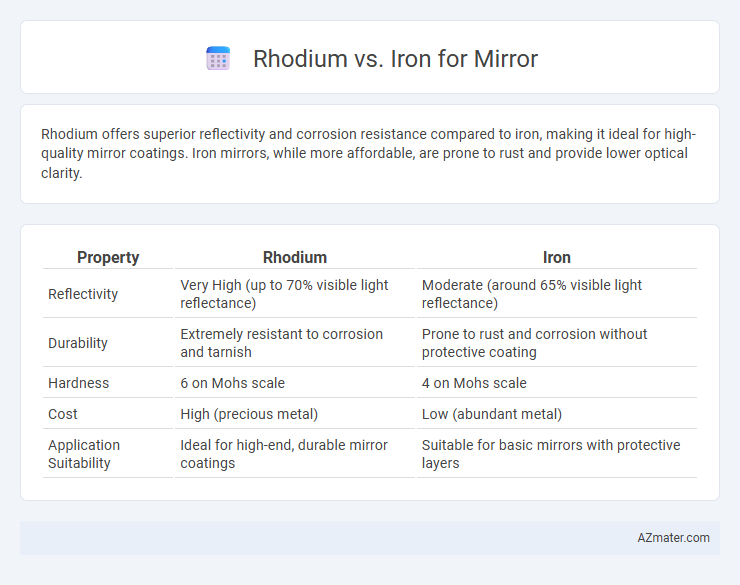
| Property | Rhodium | Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Reflectivity | Very High (up to 70% visible light reflectance) | Moderate (around 65% visible light reflectance) |
| Durability | Extremely resistant to corrosion and tarnish | Prone to rust and corrosion without protective coating |
| Hardness | 6 on Mohs scale | 4 on Mohs scale |
| Cost | High (precious metal) | Low (abundant metal) |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for high-end, durable mirror coatings | Suitable for basic mirrors with protective layers |
Introduction to Rhodium and Iron Mirrors
Rhodium mirrors, known for their exceptional reflectivity and corrosion resistance, offer superior durability and brightness compared to traditional iron mirrors. Iron mirrors, often coated with silver or aluminum, provide cost-effective reflective surfaces but lack the enhanced longevity and tarnish resistance of rhodium coatings. The choice between rhodium and iron mirrors depends on requirements for reflectance quality, environmental resistance, and budget considerations.
Chemical Properties: Rhodium vs Iron
Rhodium exhibits superior chemical stability compared to iron, resisting oxidation and corrosion even at high temperatures, making it ideal for mirror coatings. Iron, prone to rust and tarnish due to its reactivity with oxygen and moisture, requires protective layers to maintain mirror reflectivity. Rhodium's inertness and high reflectance enhance mirror durability and clarity, contrasting with iron's susceptibility to chemical degradation.
Reflectivity and Optical Performance
Rhodium coating offers superior reflectivity compared to iron, with reflectance levels exceeding 85%, making it ideal for high-performance mirrors in optical applications. Iron mirrors exhibit lower reflectivity, around 60-70%, which can result in diminished image brightness and contrast in precision instruments. The high optical performance of rhodium mirrors enhances resolution and clarity, crucial for advanced microscopy and laser systems.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Rhodium offers superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to iron, making it an ideal choice for mirror coatings exposed to harsh environments. Its inert nature prevents tarnishing and oxidation, ensuring long-lasting reflectivity and minimal maintenance. In contrast, iron is prone to rust and degradation when exposed to moisture and air, reducing the mirror's lifespan and optical clarity.
Aesthetic Qualities: Shine and Finish
Rhodium offers a superior aesthetic advantage for mirrors due to its brilliant, reflective shine and durable, tarnish-resistant finish that maintains clarity over time. In contrast, iron exhibits a more subdued luster with a matte or slightly oxidized surface prone to rust, which can dull the mirror's appearance. Rhodium plating enhances visual depth and smoothness, making it the preferred choice for high-end, decorative mirror frames and surfaces.
Cost Comparison: Rhodium vs Iron Mirrors
Rhodium mirrors command a significantly higher price than iron mirrors due to rhodium's rarity and superior corrosion resistance, often costing several hundred dollars per square foot compared to iron's more affordable range. Iron mirrors are budget-friendly but require protective coatings to prevent rust and degradation over time, which can add maintenance costs. Choosing between rhodium and iron mirrors depends on balancing upfront investment against long-term durability and upkeep expenses.
Applications in Industry and Daily Life
Rhodium's exceptional reflectivity and corrosion resistance make it ideal for high-quality mirrors used in precision instruments, luxury automotive trims, and jewelry coatings. Iron mirrors, while more affordable, are prone to oxidation and are typically used in decorative applications or basic household mirrors where durability is less critical. Industrial sectors prioritize rhodium-coated mirrors for laser systems and scientific equipment due to their superior durability and brightness.
Maintenance and Longevity
Rhodium plating on mirrors offers superior corrosion resistance and maintains its reflective luster longer than iron, reducing the frequency of maintenance. Iron mirrors are prone to oxidation and rust, necessitating regular cleaning and protective coatings to preserve clarity. Rhodium's durability under humid or chemical exposure ensures extended longevity, making it a preferred choice for high-quality, low-maintenance mirror applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Rhodium plating on mirrors offers superior corrosion resistance and reflects light more efficiently than iron, but its mining and refining involve significant environmental challenges, including high energy consumption and toxic waste generation. Iron, being abundant and easier to recycle, has a lower environmental footprint despite its susceptibility to rust and lower reflectivity. Sustainable mirror production increasingly favors iron-based coatings combined with protective layers to balance ecological impact and performance.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Mirror
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and a brilliant reflective surface, making it ideal for high-end mirrors requiring durability and a bright, clear reflection. Iron, while more cost-effective, tends to oxidize and tarnish over time, resulting in a duller mirror surface that requires regular maintenance. Selecting rhodium for your mirror ensures long-lasting shine and minimal upkeep, whereas iron suits budget-conscious projects where occasional refinishing is acceptable.
Infographic: Rhodium vs Iron for Mirror
 azmater.com
azmater.com