Brass coins offer superior corrosion resistance and a warm golden appearance, making them ideal for long-term durability and aesthetic appeal. Nickel coins provide higher hardness and wear resistance, ensuring longevity and maintaining detailed designs under heavy circulation.
Table of Comparison
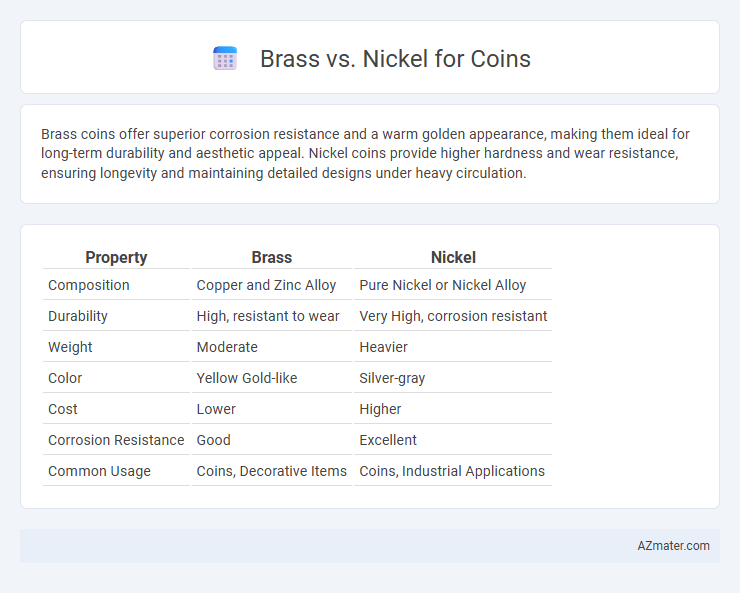
| Property | Brass | Nickel |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper and Zinc Alloy | Pure Nickel or Nickel Alloy |
| Durability | High, resistant to wear | Very High, corrosion resistant |
| Weight | Moderate | Heavier |
| Color | Yellow Gold-like | Silver-gray |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Common Usage | Coins, Decorative Items | Coins, Industrial Applications |
Introduction to Coin Material Selection
Brass and nickel are widely used materials in coin production due to their durability and resistance to corrosion. Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, offers affordability and distinct coloration, making it popular for commemorative and lower-value coins. Nickel, known for its hardness and brightness, provides superior wear resistance and is often favored for circulating coins requiring longevity.
Overview of Brass and Nickel in Coinage
Brass, an alloy primarily composed of copper and zinc, offers excellent corrosion resistance and a warm golden color, making it a popular choice for coinage requiring durability and aesthetic appeal. Nickel, a silvery-white metal known for its hardness and resistance to wear, is commonly used in coin production to enhance strength and extend circulation life. Both metals provide distinct advantages in coinage, with brass favored for its visual appeal and nickel for its robustness in high-traffic currency.
Physical Properties: Brass vs Nickel
Brass coins exhibit high malleability and excellent corrosion resistance due to their copper and zinc composition, making them durable in various environments. Nickel coins demonstrate superior hardness and wear resistance, attributed to their dense, silvery-white metal structure, which helps maintain coin detail over time. The density of nickel (8.90 g/cm3) surpasses that of brass (approximately 8.4-8.7 g/cm3), contributing to a heavier coin that resists deformation more effectively.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Brass coins exhibit excellent durability and superior wear resistance due to their copper-zinc alloy composition, which resists corrosion and maintains surface detail over time. Nickel coins offer enhanced hardness and abrasion resistance, making them highly resistant to scratches and deformation under heavy circulation. While brass provides better corrosion resistance in humid environments, nickel ensures longer-lasting luster and structural integrity in high-traffic coin usage.
Corrosion and Tarnish Resistance
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, offers superior corrosion resistance compared to nickel, making it less prone to rust and degradation in moist environments. Nickel provides excellent tarnish resistance due to its natural oxidation layer, which protects the coin's surface from discoloration over time. Selecting brass or nickel for coins depends on balancing corrosion durability with desired aesthetic longevity and maintenance needs.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Brass coins generally cost less to produce than nickel coins due to the lower price of copper and zinc alloys compared to pure nickel, impacting minting expenses significantly. The fluctuating market prices of nickel, often influenced by global demand and mining constraints, can lead to higher and less predictable costs for coin production. Choosing brass over nickel for currency reduces long-term economic volatility and enhances cost-efficiency for governments and mints managing large-scale coin circulation.
Aesthetic Appeal and Visual Characteristics
Brass coins exhibit a warm, golden-yellow hue with a subtle shine that enhances their visual richness, making them highly appealing for collectors and currency users seeking a classic look. Nickel coins feature a cooler, silver-gray tone with a reflective, polished surface that conveys a modern, sleek aesthetic often associated with durability and sophistication. The choice between brass and nickel significantly influences a coin's visual impact, with brass offering a vintage charm and nickel providing a contemporary brilliance.
Minting Process and Workability
Brass offers excellent workability in the minting process due to its high malleability and corrosion resistance, allowing for detailed coin designs and easier stamping without cracking. Nickel, while harder and more durable, requires higher pressure during striking, which can increase wear on minting dies but provides greater resistance to wear and tarnish on the finished coin. The choice between brass and nickel impacts die longevity, production speed, and the final coin's surface quality, with brass favored for intricate designs and nickel for enhanced durability in circulation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Brass coins, composed primarily of copper and zinc, generally have a lower environmental footprint than nickel due to easier recycling processes and less energy-intensive extraction methods. Nickel mining often involves significant ecological disturbance and higher greenhouse gas emissions, making it less sustainable compared to brass alloys. Sustainable coin production increasingly favors brass for its recyclability and reduced environmental impact throughout the lifecycle.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Brass and Nickel for Coins
Brass offers superior corrosion resistance and a warm golden appearance, making it ideal for commemorative or collectible coins, while nickel provides excellent durability and a bright silver finish suited for high-circulation currency. Cost differences also influence the choice, as brass tends to be less expensive than nickel, impacting large-scale production budgets. The decision ultimately depends on balancing aesthetic preferences, wear resistance, and budget considerations for the intended coin use.
Infographic: Brass vs Nickel for Coin
 azmater.com
azmater.com