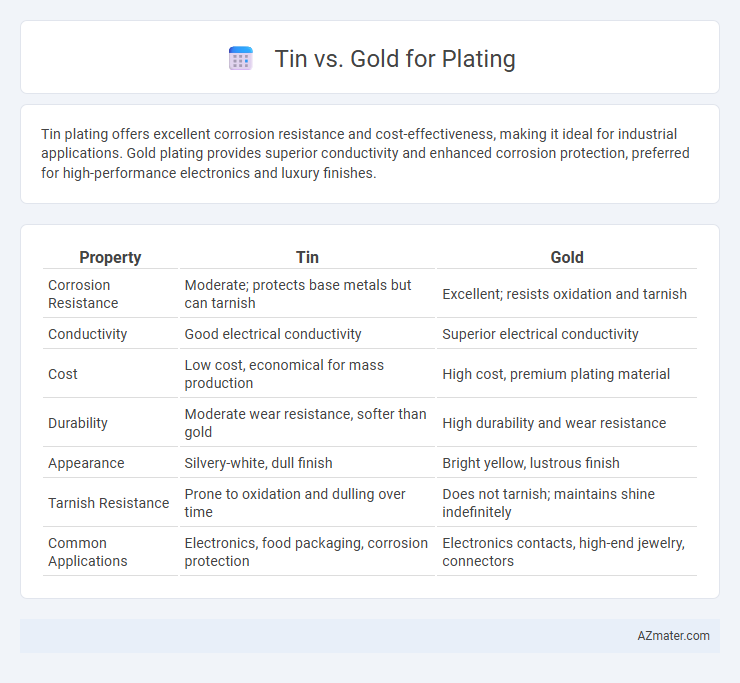
Tin plating offers excellent corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for industrial applications. Gold plating provides superior conductivity and enhanced corrosion protection, preferred for high-performance electronics and luxury finishes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tin | Gold |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate; protects base metals but can tarnish | Excellent; resists oxidation and tarnish |
| Conductivity | Good electrical conductivity | Superior electrical conductivity |
| Cost | Low cost, economical for mass production | High cost, premium plating material |
| Durability | Moderate wear resistance, softer than gold | High durability and wear resistance |
| Appearance | Silvery-white, dull finish | Bright yellow, lustrous finish |
| Tarnish Resistance | Prone to oxidation and dulling over time | Does not tarnish; maintains shine indefinitely |
| Common Applications | Electronics, food packaging, corrosion protection | Electronics contacts, high-end jewelry, connectors |
Introduction to Metal Plating: Tin vs Gold
Tin and gold are widely used metals for plating due to their unique properties and applications. Tin plating offers excellent corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, making it ideal for electronic components and food packaging, while gold plating provides superior corrosion resistance, high conductivity, and an attractive finish, often used in high-performance connectors and jewelry. The choice between tin and gold plating depends on factors such as cost, environmental conditions, and required durability for the specific application.
Key Differences Between Tin and Gold Plating
Tin plating offers excellent corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for electrical components where solderability is crucial, while gold plating provides superior conductivity and exceptional corrosion resistance, especially in high-reliability electronics and harsh environments. Gold plating maintains its luster and conductivity over time, whereas tin can form dull oxide layers that might affect performance. The significant price difference also impacts application choices, with tin favored for budget-sensitive projects and gold preferred for premium, long-lasting finishes.
Electrical Conductivity: Tin vs Gold
Gold offers superior electrical conductivity compared to tin, making it the preferred choice for high-performance electronic connectors and contacts. Tin, while less conductive, is more cost-effective and provides adequate conductivity for many general-purpose applications. The excellent corrosion resistance of gold ensures long-term stable electrical connections, whereas tin may oxidize over time, potentially impacting conductivity.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Gold plating exhibits superior corrosion resistance due to its inertness and resistance to oxidation, making it ideal for harsh environments and electronic components. Tin plating, while less resistant to corrosion, provides adequate protection against oxidation and is more cost-effective for applications requiring moderate corrosion resistance. The choice between tin and gold plating hinges on the desired balance of durability, cost, and environmental exposure.
Cost Analysis: Tin Plating vs Gold Plating
Tin plating offers a cost-effective alternative to gold plating, with tin priced significantly lower per ounce, reducing overall material expenses in mass production. Gold plating provides superior corrosion resistance and enhanced electrical conductivity but entails higher costs due to gold's market value and complex plating processes. For applications where budget constraints and high volume are critical, tin plating delivers adequate performance at a fraction of gold plating's financial investment.
Applications in Electronics and Industry
Tin plating is widely used in electronics due to its excellent solderability, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for connectors, printed circuit boards, and semiconductor packaging. Gold plating offers superior conductivity, oxidation resistance, and reliability, primarily utilized in high-performance connectors, contacts, and critical electronic components where durability is essential. Industrial applications favor tin plating for large-scale, cost-sensitive production, while gold plating is preferred in precision electronics requiring optimal signal clarity and long-term stability.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Tin plating offers moderate durability and corrosion resistance, suitable for applications requiring cost-effective protection against oxidation and mild wear. Gold plating provides superior wear resistance and exceptional durability due to its non-reactive, dense atomic structure, making it ideal for high-performance electronics and connectors. Despite higher cost, gold plating maintains conductivity and aesthetic appeal longer than tin under harsh environmental conditions.
Environmental Impact of Tin and Gold Plating
Tin plating generates significantly less environmental impact compared to gold plating due to its lower toxicity and the abundance of tin resources, which reduces the need for extensive mining operations. Gold plating involves energy-intensive extraction and refining processes that contribute to habitat destruction, water pollution, and high carbon emissions. Recycling tin is more straightforward and eco-friendly, while gold recovery often requires complex chemical treatments with hazardous byproducts.
Maintenance and Longevity
Tin plating offers excellent corrosion resistance but tends to wear faster than gold, requiring more frequent maintenance to preserve its appearance and protective qualities. Gold plating provides superior durability and resistance to tarnish, significantly extending the lifespan of plated components with minimal upkeep. For applications demanding long-term reliability and minimal maintenance, gold plating is the preferred choice despite its higher initial cost.
Choosing the Right Plating for Your Project
Choosing the right plating for your project hinges on the specific requirements for conductivity, corrosion resistance, and cost. Tin plating offers excellent solderability and is cost-effective for applications needing moderate protection, while gold plating provides superior corrosion resistance and reliable conductivity, ideal for high-performance electronics. Consider the operating environment and longevity to determine whether tin's affordability or gold's durability best suits your project needs.
Infographic: Tin vs Gold for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com