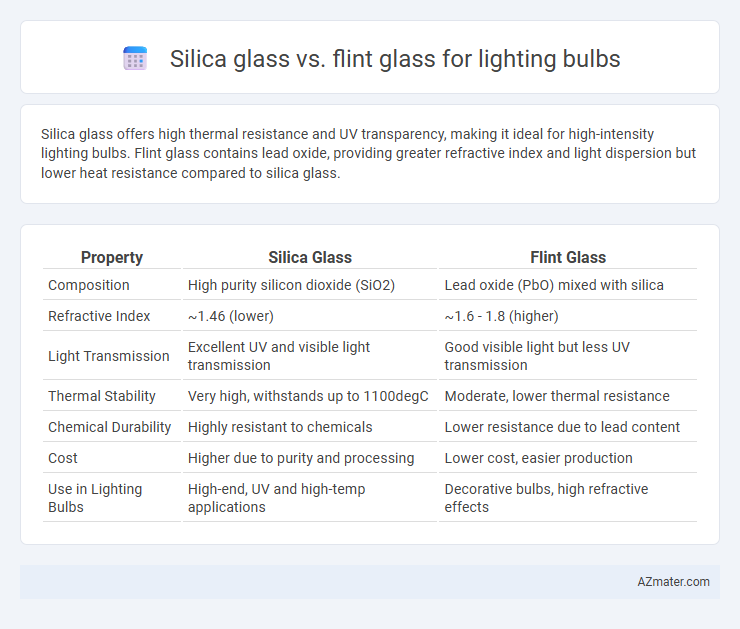
Silica glass offers high thermal resistance and UV transparency, making it ideal for high-intensity lighting bulbs. Flint glass contains lead oxide, providing greater refractive index and light dispersion but lower heat resistance compared to silica glass.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Silica Glass | Flint Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High purity silicon dioxide (SiO2) | Lead oxide (PbO) mixed with silica |
| Refractive Index | ~1.46 (lower) | ~1.6 - 1.8 (higher) |
| Light Transmission | Excellent UV and visible light transmission | Good visible light but less UV transmission |
| Thermal Stability | Very high, withstands up to 1100degC | Moderate, lower thermal resistance |
| Chemical Durability | Highly resistant to chemicals | Lower resistance due to lead content |
| Cost | Higher due to purity and processing | Lower cost, easier production |
| Use in Lighting Bulbs | High-end, UV and high-temp applications | Decorative bulbs, high refractive effects |
Introduction to Silica Glass and Flint Glass
Silica glass, made primarily from silicon dioxide, offers exceptional thermal stability and high-temperature resistance, making it ideal for lighting bulbs exposed to intense heat. Flint glass, composed mainly of lead oxide and silica, provides superior optical clarity and a high refractive index, enhancing light dispersion in bulbs. The choice between silica and flint glass depends on the application's thermal demands and the desired light quality.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Silica glass, primarily composed of high-purity silicon dioxide (SiO2), offers superior thermal stability and resistance to high temperatures, making it ideal for lighting bulbs that operate under extreme heat. Flint glass contains lead oxide (PbO) alongside silica, which increases its refractive index and optical clarity but reduces its thermal resistance compared to silica glass. Manufacturing silica glass involves melting high-purity quartz at temperatures above 1700degC, whereas flint glass production includes adding lead oxide and melting at lower temperatures around 1400degC, resulting in distinct physical and optical properties suited for different lighting applications.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Silica glass offers superior optical clarity and higher light transmission compared to flint glass, making it ideal for lighting bulbs requiring maximum brightness and color accuracy. The low dispersion and high purity of silica glass minimize chromatic aberrations, enhancing the quality of emitted light. Flint glass, with higher refractive index and dispersion, often results in decreased clarity and slight color distortion, reducing overall light efficiency in bulb applications.
Thermal Resistance and Performance
Silica glass offers superior thermal resistance compared to flint glass, withstanding temperatures up to 1200degC, making it ideal for high-performance lighting bulbs that operate under extreme heat. Flint glass, containing lead oxide, has lower thermal resistance, typically up to 500degC, but provides better optical clarity and refractive properties useful in decorative or lower-heat lighting applications. The enhanced thermal stability of silica glass ensures longer bulb lifespan and consistent performance in high-temperature environments.
Chemical Durability and Reactivity
Silica glass exhibits superior chemical durability due to its high purity and strong silicon-oxygen bonds, making it highly resistant to acids, alkalis, and thermal shock in lighting bulb applications. Flint glass, containing lead oxide, has lower chemical resistance and is more prone to corrosion and degradation under harsh environmental conditions. This difference impacts the longevity and stability of bulbs, with silica glass providing enhanced reactivity resistance and maintaining optical clarity over extended use.
Mechanical Strength and Lifespan
Silica glass offers superior mechanical strength compared to flint glass, making it more resistant to thermal shock and mechanical stress in lighting bulbs. Its high purity and excellent thermal stability contribute to a longer lifespan by minimizing devitrification and deformation under prolonged high temperatures. Flint glass, containing lead oxide, has lower mechanical strength and a shorter lifespan due to its susceptibility to heat-induced degradation and brittleness over time.
Cost Efficiency and Scalability
Silica glass offers superior thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-performance lighting bulbs but comes with higher production costs due to energy-intensive manufacturing and raw material expenses. Flint glass, while less heat-resistant and prone to yellowing over time, provides a more cost-efficient and scalable option thanks to lower material costs and simpler fabrication processes. Manufacturers often choose flint glass for mass-produced, budget-friendly bulbs, whereas silica glass suits applications demanding longevity and premium performance despite higher upfront investment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Silica glass offers superior environmental benefits compared to flint glass due to its higher durability and heat resistance, which extend the lifespan of lighting bulbs and reduce waste. The production of silica glass typically involves fewer toxic materials and lower emissions, enhancing its sustainability profile. Flint glass, containing lead oxide, poses significant environmental hazards during manufacturing and disposal, contributing to soil and water contamination.
Application Suitability for Lighting Bulbs
Silica glass offers superior thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-intensity and halogen lighting bulbs that operate at elevated temperatures. Flint glass, with its higher refractive index and optical clarity, is better suited for decorative and precision lighting applications where light dispersion and color rendering are critical. The selection between silica and flint glass directly impacts the bulb's performance, longevity, and light quality in specific lighting environments.
Final Comparison: Choosing the Ideal Glass for Lighting
Silica glass offers superior thermal stability and high transparency in UV and infrared ranges, making it ideal for high-temperature and precision lighting applications. Flint glass, with its higher refractive index and dispersion, provides enhanced brightness and color rendering in decorative and incandescent bulbs. Choosing the ideal glass depends on balancing performance needs: silica glass excels in durability and heat resistance, while flint glass enhances visual appeal through light manipulation.
Infographic: Silica glass vs Flint glass for Lighting bulb
 azmater.com
azmater.com