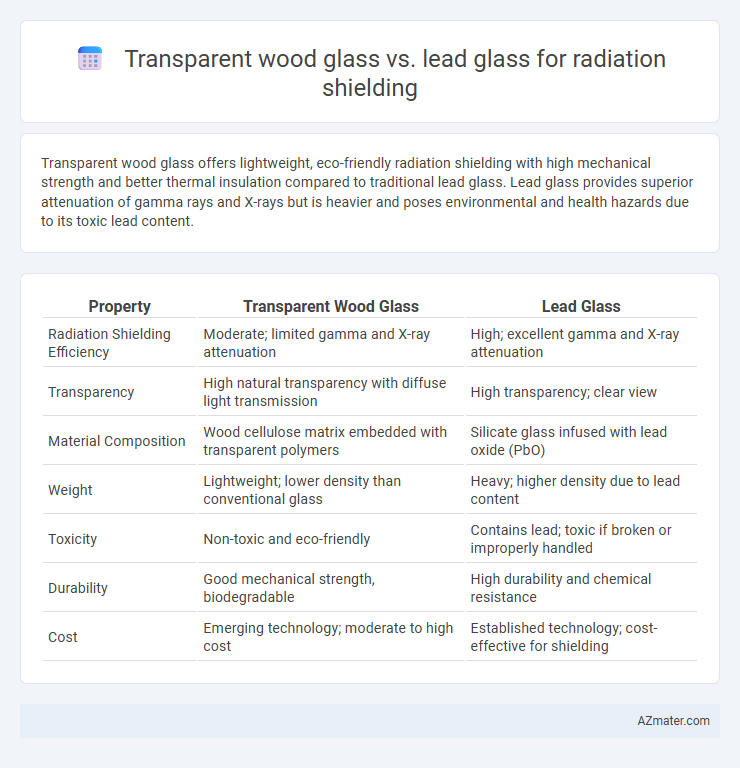
Transparent wood glass offers lightweight, eco-friendly radiation shielding with high mechanical strength and better thermal insulation compared to traditional lead glass. Lead glass provides superior attenuation of gamma rays and X-rays but is heavier and poses environmental and health hazards due to its toxic lead content.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Transparent Wood Glass | Lead Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Radiation Shielding Efficiency | Moderate; limited gamma and X-ray attenuation | High; excellent gamma and X-ray attenuation |
| Transparency | High natural transparency with diffuse light transmission | High transparency; clear view |
| Material Composition | Wood cellulose matrix embedded with transparent polymers | Silicate glass infused with lead oxide (PbO) |
| Weight | Lightweight; lower density than conventional glass | Heavy; higher density due to lead content |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic and eco-friendly | Contains lead; toxic if broken or improperly handled |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength, biodegradable | High durability and chemical resistance |
| Cost | Emerging technology; moderate to high cost | Established technology; cost-effective for shielding |
Introduction to Radiation Shielding Materials
Transparent wood glass offers a lightweight, eco-friendly alternative to traditional lead glass in radiation shielding, combining high mechanical strength with effective radiation attenuation. Lead glass remains a standard for radiation protection due to its high density and excellent shielding properties against X-rays and gamma rays. Innovations in transparent wood composites enhance optical clarity and radiation absorption, presenting promising results for safer and sustainable radiation shielding materials.
Overview of Transparent Wood Glass
Transparent wood glass is an innovative, eco-friendly material composed of chemically treated wood infused with polymer resin to achieve high transparency and mechanical strength. It offers superior UV and near-infrared light blocking capabilities, enhancing energy efficiency compared to traditional lead glass used in radiation shields. Although transparent wood glass exhibits lower density and radiation absorption than lead glass, its renewable origin and better thermal insulation make it a promising alternative for sustainable radiation shielding applications.
Properties of Lead Glass for Radiation Protection
Lead glass for radiation protection features high density and a significant lead oxide content, providing superior attenuation of X-rays and gamma rays compared to transparent wood glass. Its exceptional optical clarity combines with effective shielding, making it ideal for medical and industrial applications requiring reliable radiation protection. Despite heavier weight and fragility, lead glass maintains excellent durability and resistance to radiation-induced degradation, ensuring long-term performance in shielding environments.
Comparative Transparency and Optical Clarity
Transparent wood glass exhibits higher optical clarity and better light transmission compared to traditional lead glass used for radiation shielding, due to its unique cellulose nanofiber structure that minimizes light scattering. Lead glass offers effective radiation attenuation but often compromises on transparency because of its dense, heavy metal content that causes light distortion and yellowing over time. The superior transparency of transparent wood glass enhances visual comfort and color fidelity, making it advantageous for applications requiring clear visibility along with radiation protection.
Radiation Attenuation Capabilities
Transparent wood glass exhibits promising radiation attenuation capabilities due to its composite structure, incorporating cellulose fibers that enhance neutron and gamma-ray absorption compared to traditional lead glass. Lead glass, composed primarily of lead oxide, provides superior attenuation of ionizing radiation, particularly gamma rays, owing to its high atomic number and density. However, transparent wood glass offers a lightweight, eco-friendly alternative with moderate radiation shielding, optimal for applications requiring reduced toxicity and improved structural performance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Transparent wood glass exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to traditional lead glass, boasting higher impact resistance and flexibility due to its nano-cellulose matrix structure. Its enhanced durability under environmental stress such as humidity and temperature fluctuations outperforms lead glass, which is prone to cracking and degradation over time. The eco-friendly composition of transparent wood glass offers a lightweight yet robust alternative for radiation shielding without compromising structural integrity.
Environmental Safety and Toxicity
Transparent wood glass offers a sustainable alternative to traditional lead glass in radiation shielding by utilizing renewable lignocellulosic materials, which significantly reduce environmental impact and promote carbon sequestration. Unlike lead glass, which contains toxic lead oxide posing severe health risks during production, use, and disposal, transparent wood glass is non-toxic and biodegradable, ensuring safer handling and minimal ecological harm. This green innovation not only meets radiation shielding efficacy but also aligns with eco-friendly practices by minimizing hazardous waste generation and enhancing recyclability.
Applications in Medical and Industrial Fields
Transparent wood glass offers lightweight, high-strength radiation shielding suitable for medical imaging rooms and industrial radiography environments, providing visibility with reduced toxicity compared to lead glass. Lead glass remains prevalent for its superior gamma and X-ray attenuation, extensively used in hospitals for protective windows and in nuclear facilities requiring dense radiation barriers. Both materials enhance operational safety with transparent shielding solutions tailored to specific radiation levels and application needs.
Cost-effectiveness and Availability
Transparent wood glass offers a cost-effective alternative to lead glass for radiation shielding due to its lower material and manufacturing expenses. Its availability is increasing as sustainable materials gain traction, making it easier to source compared to lead glass, which relies on rare heavy metals and complex processing. While lead glass provides higher density and superior radiation attenuation, transparent wood glass balances moderate protection with affordability and environmental benefits.
Future Trends in Radiation Shielding Technologies
Transparent wood glass offers a sustainable and lightweight alternative to traditional lead glass for radiation shielding, with improved mechanical strength and environmental benefits driving research focus. Innovations in transparent wood composites incorporate nanomaterials and dopants to enhance radiation attenuation properties, positioning them as a promising material for future medical and industrial shielding applications. Emerging trends emphasize eco-friendly, high-performance radiation shields with tailored optical clarity and reduced toxicity, promoting the gradual shift from lead-based solutions to advanced transparent wood-based shields.
Infographic: Transparent wood glass vs Lead glass for Radiation shield
 azmater.com
azmater.com