Ultra-thin glass offers enhanced light transmission and delicate detail for stained glass art, while colored glass provides vibrant hues and traditional opacity. Artists prefer ultra-thin glass for intricate designs requiring luminosity and colored glass for bold, saturated color effects.
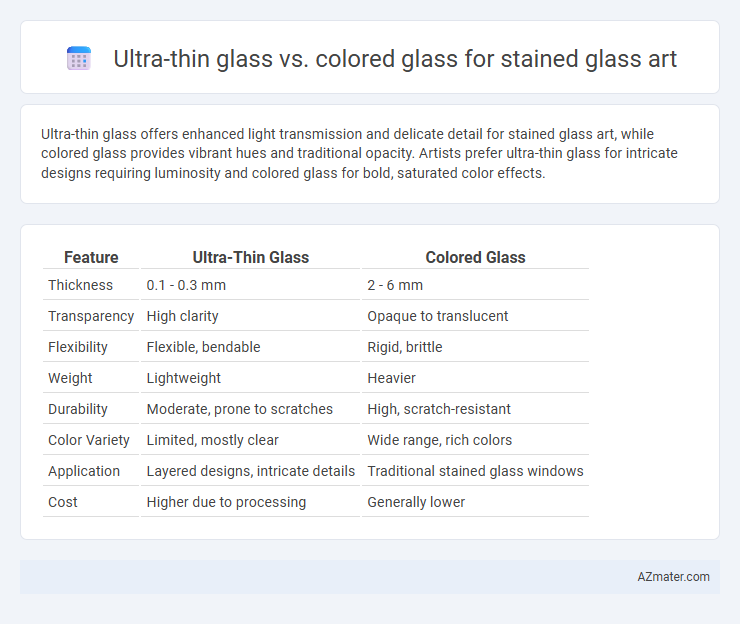
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ultra-Thin Glass | Colored Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.1 - 0.3 mm | 2 - 6 mm |
| Transparency | High clarity | Opaque to translucent |
| Flexibility | Flexible, bendable | Rigid, brittle |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to scratches | High, scratch-resistant |
| Color Variety | Limited, mostly clear | Wide range, rich colors |
| Application | Layered designs, intricate details | Traditional stained glass windows |
| Cost | Higher due to processing | Generally lower |
Introduction to Stained Glass Art
Stained glass art utilizes various types of glass to create vibrant, light-filled designs, with ultra-thin glass offering exceptional translucency and delicate detail, enhancing luminosity and intricate patterns. Colored glass remains a traditional choice, boasting rich hues and durability that preserve the historical essence of stained glass windows. Selecting between ultra-thin and colored glass depends on the desired visual effect, structural needs, and artistic style within stained glass craftsmanship.
Overview of Ultra-thin Glass
Ultra-thin glass offers exceptional flexibility and high transparency, making it ideal for intricate stained glass art requiring delicate detailing. Its minimal thickness enhances light transmission and color vibrancy, surpassing traditional colored glass in visual clarity. Artisans favor ultra-thin glass for contemporary designs that demand lightweight yet durable materials with precise cutting capabilities.
Overview of Colored Glass
Colored glass for stained glass art offers a vibrant spectrum of hues achieved through metallic oxide additives during production, resulting in rich, translucent panels that enhance light interplay. Unlike ultra-thin glass, colored glass typically has greater thickness and weight, providing structural durability and deeper visual texture. This glass type is prized for its ability to convey intricate designs with bold coloration, making it a staple in traditional and contemporary stained glass artworks.
Key Differences: Ultra-thin vs Colored Glass
Ultra-thin glass in stained glass art offers exceptional flexibility and translucency, allowing intricate patterns and light diffusion, whereas colored glass provides vibrant, rich hues essential for traditional stained glass designs. Ultra-thin glass is significantly lighter and less prone to breakage, enabling more delicate and detailed artistic techniques compared to the sturdier, thicker colored glass. The manufacturing process differs, with ultra-thin glass often made by advanced float or pellet fusion methods, while colored glass relies on metal oxide infusions during production to achieve its vivid pigmentation.
Aesthetic Impact on Stained Glass Art
Ultra-thin glass offers a delicate translucency and refined light diffusion that enhances the intricate details of stained glass art, creating a subtle glow and depth. Colored glass provides bold, vibrant hues that deliver immediate visual impact and rich contrasts, intensifying the emotional expression within the artwork. The choice between ultra-thin and colored glass significantly influences the aesthetic dynamics, either emphasizing softness and nuance or vibrancy and drama in stained glass creations.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Ultra-thin glass in stained glass art offers exceptional flexibility and lightweight properties but generally exhibits lower durability compared to traditional colored glass, making it more prone to cracking under stress. Colored glass, typically thicker and more robust, provides superior resistance to environmental factors and mechanical impact, ensuring longer-lasting vibrancy and structural integrity. Artists seeking longevity and resilience in their stained glass projects often prefer colored glass for its proven durability and enduring color retention.
Flexibility and Workability in Art Design
Ultra-thin glass offers superior flexibility and ease of cutting, enabling intricate designs and delicate details in stained glass art, while colored glass, often thicker and less pliable, requires more careful handling and limits intricate manipulation. The lightweight nature of ultra-thin glass reduces stress on lead came or copper foil, enhancing durability and allowing for more complex, dynamic compositions. Artists benefit from ultra-thin glass's smooth surface and consistent thickness, which improve soldering precision and overall workability compared to traditional colored glass varieties.
Cost and Accessibility of Materials
Ultra-thin glass reduces overall costs by using less raw material and enabling easier cutting, making it accessible for artists on tight budgets. Colored glass often demands higher expenses due to specialized manufacturing processes and limited suppliers, which can restrict availability for some creators. Choosing ultra-thin glass enhances material accessibility while maintaining visual appeal and lowering project expenses.
Applications and Suitability for Various Projects
Ultra-thin glass offers exceptional flexibility and delicacy for intricate stained glass projects, making it ideal for detailed designs and small-scale artworks. Colored glass, with its robust durability and vibrant hues, suits larger installations and outdoor applications where strength and light transmission are critical. Selecting the appropriate material depends on project scale, desired detail level, and environmental exposure.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Stained Glass Art
Ultra-thin glass offers delicate transparency and finer detail ideal for intricate stained glass art, while colored glass provides bold vibrancy and durability essential for traditional designs. Selecting the right glass depends on the artwork's complexity, desired light transmission, and color intensity. Consider factors like thickness, texture, and how they enhance both visual impact and structural integrity in stained glass projects.
Infographic: Ultra-thin glass vs Colored glass for Stained glass art
 azmater.com
azmater.com