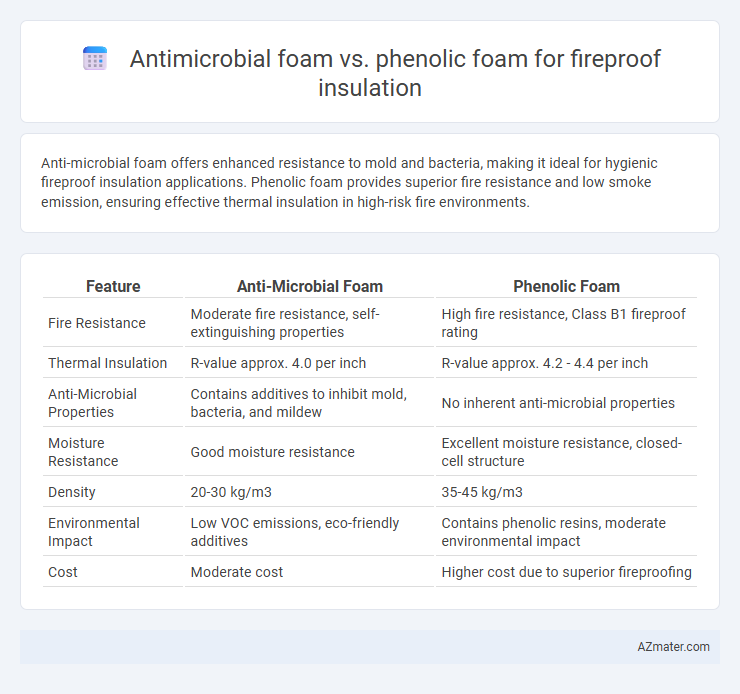
Anti-microbial foam offers enhanced resistance to mold and bacteria, making it ideal for hygienic fireproof insulation applications. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance and low smoke emission, ensuring effective thermal insulation in high-risk fire environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anti-Microbial Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Moderate fire resistance, self-extinguishing properties | High fire resistance, Class B1 fireproof rating |
| Thermal Insulation | R-value approx. 4.0 per inch | R-value approx. 4.2 - 4.4 per inch |
| Anti-Microbial Properties | Contains additives to inhibit mold, bacteria, and mildew | No inherent anti-microbial properties |
| Moisture Resistance | Good moisture resistance | Excellent moisture resistance, closed-cell structure |
| Density | 20-30 kg/m3 | 35-45 kg/m3 |
| Environmental Impact | Low VOC emissions, eco-friendly additives | Contains phenolic resins, moderate environmental impact |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost due to superior fireproofing |
Introduction to Fireproof Insulation Materials
Fireproof insulation materials like anti-microbial foam and phenolic foam play critical roles in enhancing building safety by resisting high temperatures and preventing fire spread. Anti-microbial foam provides dual benefits of fire resistance and inhibition of mold growth, making it suitable for humid environments. Phenolic foam is highly valued for its low smoke emission and excellent thermal insulation properties, offering superior fire retardancy in structural applications.
Overview of Anti-microbial Foam
Anti-microbial foam used in fireproof insulation offers enhanced resistance to mold, bacteria, and fungi, ensuring prolonged material integrity and indoor air quality. Its composition typically includes biocidal agents embedded within the foam matrix, which inhibit microbial growth without compromising fire retardant properties. Compared to phenolic foam, anti-microbial foam provides superior hygiene benefits while maintaining excellent thermal insulation and fire resistance standards.
Overview of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance compared to anti-microbial foam due to its low smoke emission and high thermal stability, making it ideal for fireproof insulation applications. This closed-cell material provides excellent thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity of around 0.020-0.024 W/m*K, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. Phenolic foam also delivers strong fire retardancy by forming a char layer that slows flame propagation, outperforming conventional insulation foams in safety standards compliance.
Fire Resistance Performance Comparison
Phenolic foam exhibits superior fire resistance performance compared to anti-microbial foam, characterized by its low smoke emission, high thermal stability, and slow combustion rate during fire exposure. Anti-microbial foam primarily focuses on inhibiting microbial growth rather than enhancing fire resistance, often demonstrating higher flammability and greater smoke production. The phenolic foam's closed-cell structure and chemical composition contribute significantly to its effectiveness in fireproof insulation applications by preventing flame spread and minimizing toxic gas release.
Thermal Insulation Efficiency
Anti-microbial foam often exhibits enhanced thermal insulation efficiency due to its ability to resist microbial growth that can degrade foam structure and reduce insulating performance over time. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance with low thermal conductivity, making it highly effective in maintaining thermal insulation under high-temperature conditions. When comparing thermal insulation efficiency, phenolic foam tends to offer more stable and reliable performance in fireproof applications, while anti-microbial foam excels in environments prone to biological contamination.
Anti-microbial Properties and Benefits
Anti-microbial foam used for fireproof insulation contains additives that inhibit the growth of mold, mildew, and bacteria, enhancing indoor air quality and maintaining structural integrity over time. In contrast, phenolic foam, while highly fire-resistant with low smoke emission, typically lacks intrinsic anti-microbial properties, which may lead to microbial proliferation in damp conditions. The integration of anti-microbial agents in fireproof foam insulation offers superior protection in humid environments, prolonging insulation lifespan and reducing health risks associated with microbial contamination.
Durability and Longevity in Building Applications
Anti-microbial foam offers enhanced resistance to mold, bacteria, and fungal growth, significantly improving durability in humid or contaminated environments compared to phenolic foam. While phenolic foam provides excellent fireproofing with low smoke emission, its structural integrity may degrade faster under prolonged moisture exposure, impacting longevity. In building applications requiring sustained fire resistance and moisture resilience, anti-microbial foam delivers superior lifespan and maintains insulation performance over time.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Anti-microbial foam and phenolic foam differ significantly in their environmental impact and sustainability profiles for fireproof insulation. Anti-microbial foam often contains chemical additives that may pose environmental and health risks during production and disposal, whereas phenolic foam is typically composed of resins with lower toxicity and better recyclability. Phenolic foam also provides higher thermal efficiency, which contributes to overall energy savings and reduced carbon footprint over the building's lifecycle.
Cost Analysis and Installation Considerations
Anti-microbial foam typically presents a higher upfront cost compared to phenolic foam due to specialized treatment processes that inhibit microbial growth, enhancing longevity in humid environments. Phenolic foam, known for its superior fire resistance and lower thermal conductivity, offers cost-effective fireproof insulation but requires careful handling during installation because of its brittleness and dust generation. Installation of anti-microbial foam demands moisture control measures to maximize effectiveness, while phenolic foam benefits from professional expertise to ensure proper sealing and fire safety compliance, impacting overall labor costs.
Which Foam is Best for Fireproof Insulation?
Phenolic foam offers superior fireproof insulation due to its low smoke emission, high thermal stability, and excellent fire resistance compared to anti-microbial foam, which primarily focuses on inhibiting microbial growth rather than fire safety. Phenolic foam's closed-cell structure significantly reduces flame spread and heat release, making it the preferred choice in fire-critical applications such as industrial and commercial building insulation. While anti-microbial foam may contribute to hygiene, phenolic foam remains the best insulation material where fireproofing performance and safety are paramount.
Infographic: Anti-microbial foam vs Phenolic foam for Fireproof insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com