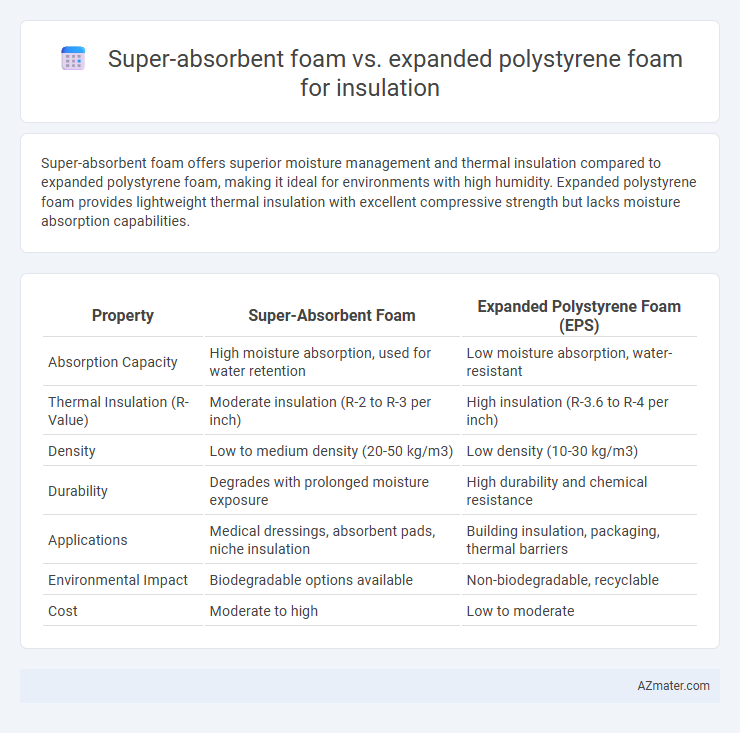
Super-absorbent foam offers superior moisture management and thermal insulation compared to expanded polystyrene foam, making it ideal for environments with high humidity. Expanded polystyrene foam provides lightweight thermal insulation with excellent compressive strength but lacks moisture absorption capabilities.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Super-Absorbent Foam | Expanded Polystyrene Foam (EPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Absorption Capacity | High moisture absorption, used for water retention | Low moisture absorption, water-resistant |
| Thermal Insulation (R-Value) | Moderate insulation (R-2 to R-3 per inch) | High insulation (R-3.6 to R-4 per inch) |
| Density | Low to medium density (20-50 kg/m3) | Low density (10-30 kg/m3) |
| Durability | Degrades with prolonged moisture exposure | High durability and chemical resistance |
| Applications | Medical dressings, absorbent pads, niche insulation | Building insulation, packaging, thermal barriers |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable options available | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Insulation Materials
Super-absorbent foam offers superior moisture retention and thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for environments prone to humidity and temperature fluctuations. Expanded polystyrene foam (EPS) is widely used for its lightweight structure, cost-effectiveness, and excellent thermal resistance in building insulation. Both materials enhance energy efficiency but differ significantly in moisture management and structural versatility within insulation applications.
What is Super-Absorbent Foam?
Super-absorbent foam is a highly porous material designed to absorb and retain large quantities of liquid, making it ideal for moisture control in insulation applications. Unlike expanded polystyrene foam, which primarily provides thermal resistance by trapping air within its closed-cell structure, super-absorbent foam combines insulation with moisture management capabilities to prevent mold and maintain indoor air quality. This unique property makes super-absorbent foam particularly effective in environments prone to humidity and water exposure.
Overview of Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Foam
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) foam is a lightweight, rigid insulation material made from expanded beads of polystyrene, known for its excellent thermal resistance and moisture resistance. EPS offers a high R-value per inch, typically around 4.0 to 4.2, making it a cost-effective option for building insulation, packaging, and protective applications. Its closed-cell structure contributes to durability and resistance to compression, while being environmentally friendly with recyclability options.
Thermal Insulation Properties Comparison
Super-absorbent foam exhibits superior thermal insulation properties due to its closed-cell structure that effectively minimizes heat transfer and retains temperature stability. Expanded polystyrene foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, offers moderate insulation performance with higher thermal conductivity compared to super-absorbent foams. The choice between these materials depends on specific insulation demands, with super-absorbent foam providing enhanced resistance to thermal bridging and moisture absorption.
Moisture Resistance and Water Absorption
Super-absorbent foam excels in moisture resistance by effectively repelling water and preventing absorption, making it ideal for environments prone to high humidity or water exposure. Expanded polystyrene foam offers moderate water absorption resistance but tends to retain some moisture due to its porous structure, which can compromise insulation performance over time. For superior insulation durability and protection against moisture-related damage, super-absorbent foam provides a more reliable solution compared to expanded polystyrene foam.
Durability and Longevity
Super-absorbent foam offers enhanced durability by resisting water absorption and maintaining structural integrity over time, making it ideal for moisture-prone environments. Expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam provides long-lasting insulation with high compressive strength but can degrade faster when exposed to UV light and moisture without proper protective barriers. Choosing between the two depends on application conditions, with super-absorbent foam excelling in durability under wet conditions and EPS offering consistent longevity in dry, controlled settings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Super-absorbent foam offers enhanced moisture resistance and biodegradability compared to expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam, which is non-biodegradable and contributes significantly to landfill waste due to its persistence in the environment. EPS foam's production relies heavily on petroleum-based resources and emits higher levels of greenhouse gases, whereas super-absorbent foam often incorporates bio-based materials, reducing carbon footprint and promoting circular economy principles. The environmental impact of super-absorbent foam is generally lower, supporting sustainable insulation solutions by minimizing pollution and improving end-of-life biodegradability.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Super-absorbent foam typically offers superior insulation performance with higher R-values per inch, but its upfront cost is significantly greater than expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam, making EPS more favorable for budget-conscious projects. EPS foam combines affordability with decent thermal insulation, providing an economical choice for large-scale applications where initial expenditure is a critical factor. Evaluations of life-cycle costs reveal that while super-absorbent foam may reduce long-term energy expenses, EPS foam maintains a competitive advantage in initial investment and widespread availability.
Typical Applications in Construction and Industry
Super-absorbent foam is widely used in construction for moisture control in foundations, roofing, and wall insulation due to its high water retention and vapor barrier properties. Expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam is favored in both construction and industry for thermal insulation in walls, roofs, and packaging because of its lightweight, high thermal resistance (R-value around 4 per inch), and compressive strength. Typical industrial applications of EPS include insulation in refrigerated transport and protective packaging, while super-absorbent foam is primarily applied in water-damage mitigation and controlled moisture environments.
Choosing the Best Foam Insulation for Your Needs
Super-absorbent foam offers superior moisture resistance and thermal insulation by trapping air effectively, making it ideal for environments with high humidity or potential water exposure. Expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam provides excellent structural strength, lightweight properties, and cost-efficiency, suitable for dry conditions and large-scale applications. Evaluating factors such as moisture levels, insulation R-value requirements, and budget constraints helps determine whether super-absorbent or EPS foam insulation best suits your project needs.
Infographic: Super-absorbent foam vs Expanded polystyrene foam for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com