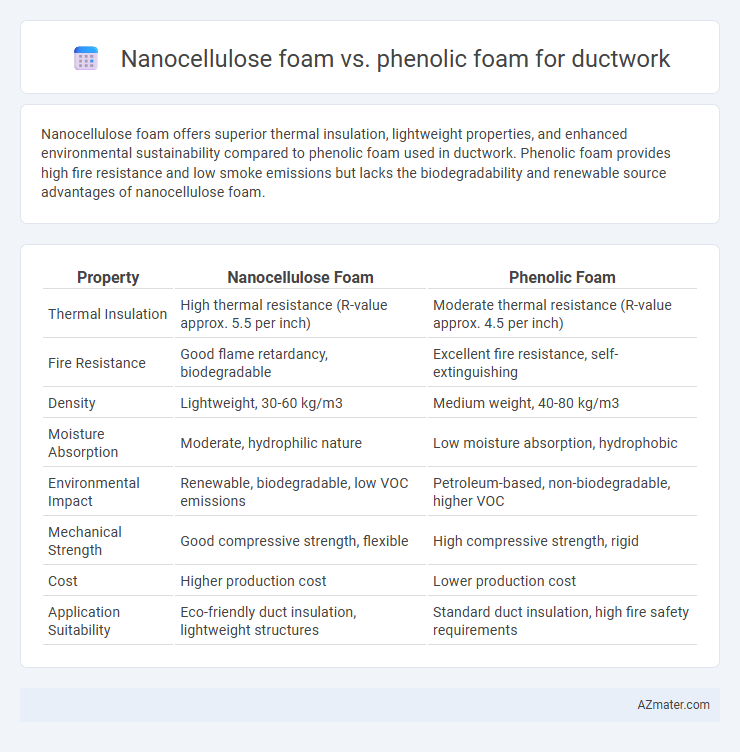
Nanocellulose foam offers superior thermal insulation, lightweight properties, and enhanced environmental sustainability compared to phenolic foam used in ductwork. Phenolic foam provides high fire resistance and low smoke emissions but lacks the biodegradability and renewable source advantages of nanocellulose foam.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nanocellulose Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High thermal resistance (R-value approx. 5.5 per inch) | Moderate thermal resistance (R-value approx. 4.5 per inch) |
| Fire Resistance | Good flame retardancy, biodegradable | Excellent fire resistance, self-extinguishing |
| Density | Lightweight, 30-60 kg/m3 | Medium weight, 40-80 kg/m3 |
| Moisture Absorption | Moderate, hydrophilic nature | Low moisture absorption, hydrophobic |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, biodegradable, low VOC emissions | Petroleum-based, non-biodegradable, higher VOC |
| Mechanical Strength | Good compressive strength, flexible | High compressive strength, rigid |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost |
| Application Suitability | Eco-friendly duct insulation, lightweight structures | Standard duct insulation, high fire safety requirements |
Introduction to Foam Materials in Ductwork
Nanocellulose foam and phenolic foam are advanced insulation materials commonly used in ductwork for HVAC systems due to their thermal performance and fire resistance. Nanocellulose foam offers superior biodegradability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and excellent thermal insulation properties, making it a sustainable alternative. Phenolic foam provides low smoke emission, high flame retardancy, and dimensional stability, which are critical for maintaining duct integrity and safety in commercial and industrial applications.
Overview of Nanocellulose Foam
Nanocellulose foam, derived from renewable cellulose fibers, offers superior thermal insulation and mechanical strength compared to traditional phenolic foam used in ductwork. This eco-friendly material provides excellent moisture resistance and fire retardancy, enhancing the durability and safety of HVAC systems. Nanocellulose foam's lightweight structure and biodegradability make it an innovative alternative that reduces environmental impact while maintaining high-performance standards in duct insulation.
Overview of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam is a rigid, closed-cell insulating material known for its excellent fire resistance, low smoke emission, and high thermal performance, making it a preferred choice for ductwork insulation. Its dense structure provides superior moisture resistance and dimensional stability compared to other foam types. Phenolic foam's low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.020 W/m*K, enhances energy efficiency in HVAC systems while ensuring compliance with stringent fire safety standards.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Nanocellulose foam exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to phenolic foam in ductwork applications, offering higher tensile strength and better flexibility due to its nanofibril network structure. Phenolic foam, while providing excellent thermal insulation and fire resistance, tends to be more brittle and prone to cracking under mechanical stress. The enhanced durability and impact resistance of nanocellulose foam contribute to longer-lasting duct systems with reduced maintenance requirements.
Thermal Insulation Efficiency
Nanocellulose foam offers superior thermal insulation efficiency compared to phenolic foam due to its high porosity and low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.025 W/m*K, which enhances energy savings in ductwork applications. Phenolic foam, while effective with thermal conductivity values near 0.02 W/m*K, often lacks the biodegradability and mechanical flexibility presented by nanocellulose foam. The advanced nanostructure in nanocellulose foam ensures better thermal resistance and durability under varying temperature conditions, making it an innovative material for sustainable HVAC insulation solutions.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Nanocellulose foam offers superior fire resistance compared to phenolic foam in ductwork applications due to its natural thermal stability and lower smoke emission under high temperatures. Phenolic foam, although possessing inherent fire-retardant properties, tends to release toxic gases like formaldehyde during combustion, posing significant safety risks. Choosing nanocellulose foam enhances overall fire safety compliance and reduces hazardous emissions, making it a preferable material for safer duct insulation solutions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nanocellulose foam offers superior environmental benefits compared to phenolic foam, as it is derived from renewable plant fibers, resulting in lower carbon footprint and enhanced biodegradability. Phenolic foam, while effective in insulation, relies on petrochemical-based resins that contribute to toxic emissions and present challenges in recycling. Choosing nanocellulose foam for ductwork supports sustainable building practices by reducing reliance on non-renewable resources and minimizing hazardous waste generation.
Cost Effectiveness and Economic Considerations
Nanocellulose foam offers superior cost effectiveness for ductwork due to its renewable sourcing and lower environmental impact, translating to potential savings in disposal and regulatory compliance. Phenolic foam, while traditionally less expensive per unit, incurs higher long-term costs associated with health hazards and more complex installation processes. Economic considerations favor nanocellulose foam as innovations reduce production costs and improve its thermal performance, making it a sustainable and financially viable alternative in HVAC applications.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Nanocellulose foam offers lightweight handling and easy cutting, reducing installation time and labor compared to phenolic foam, which requires more precise fitting due to its rigid structure. Maintenance of nanocellulose foam is simplified by its higher resistance to mechanical damage and moisture, lowering the need for frequent repairs in ductwork applications. Phenolic foam, while fire-resistant, demands careful inspection and replacement if compromised, increasing long-term maintenance complexity.
Future Trends and Recommendations
Nanocellulose foam, derived from renewable biomass, offers enhanced biodegradability, superior thermal insulation, and lower environmental impact compared to traditional phenolic foam used in ductwork. Future trends indicate a growing shift towards nanocellulose foam driven by stricter green building regulations and increased demand for sustainable, non-toxic materials in HVAC systems. Industry recommendations emphasize investing in scalable production methods for nanocellulose foam and developing comprehensive fire resistance standards to accelerate its adoption in commercial and residential ductwork applications.
Infographic: Nanocellulose foam vs Phenolic foam for Ductwork
 azmater.com
azmater.com