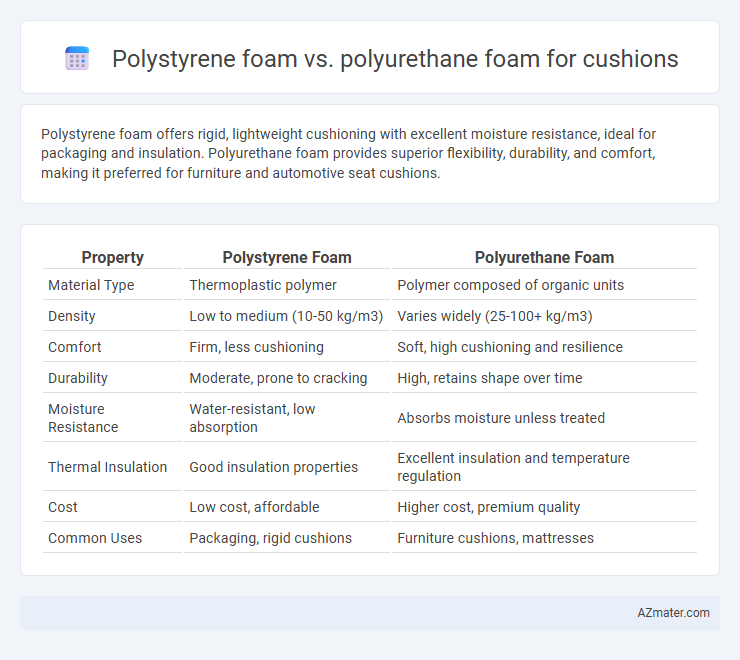
Polystyrene foam offers rigid, lightweight cushioning with excellent moisture resistance, ideal for packaging and insulation. Polyurethane foam provides superior flexibility, durability, and comfort, making it preferred for furniture and automotive seat cushions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polystyrene Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Polymer composed of organic units |
| Density | Low to medium (10-50 kg/m3) | Varies widely (25-100+ kg/m3) |
| Comfort | Firm, less cushioning | Soft, high cushioning and resilience |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to cracking | High, retains shape over time |
| Moisture Resistance | Water-resistant, low absorption | Absorbs moisture unless treated |
| Thermal Insulation | Good insulation properties | Excellent insulation and temperature regulation |
| Cost | Low cost, affordable | Higher cost, premium quality |
| Common Uses | Packaging, rigid cushions | Furniture cushions, mattresses |
Introduction to Foam Materials Used in Cushions
Polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam are widely used materials in cushion manufacturing, each offering distinct properties suited for various applications. Polystyrene foam provides rigid support and excellent insulation, making it ideal for structural cushioning, while polyurethane foam delivers superior flexibility, durability, and comfort due to its open-cell structure. Understanding these material characteristics helps in selecting the appropriate foam type for cushioning needs in furniture, automotive seating, and packaging.
What is Polystyrene Foam?
Polystyrene foam is a lightweight, rigid plastic material commonly used in cushioning due to its excellent impact resistance and thermal insulation properties. Unlike polyurethane foam, polystyrene foam offers superior structural support and is less prone to compression over time, making it ideal for protective packaging and insulation applications. Its closed-cell structure enhances durability and moisture resistance, contributing to its wide use in both industrial and consumer cushioning products.
What is Polyurethane Foam?
Polyurethane foam is a versatile, high-resilience material widely used in cushions for its excellent support and durability compared to polystyrene foam. It offers superior comfort due to its open-cell structure, allowing better breathability and pressure distribution. Polyurethane foam's adaptability to various densities and firmness levels makes it ideal for customized cushioning solutions in furniture and automotive seating.
Density and Comfort Comparison
Polystyrene foam typically has a higher density range of 1.0 to 2.0 lb/ft3, offering firm support but limited cushioning, making it less comfortable for prolonged seating applications compared to polyurethane foam. Polyurethane foam density varies widely from 1.5 to 3.5 lb/ft3 and provides superior comfort due to its flexible cell structure that adapts to pressure, enhancing cushioning and durability. The lower density polystyrene foam is rigid and prone to crumbling, while higher density polyurethane foam balances resilience and softness, ideal for ergonomic cushions.
Durability and Longevity
Polystyrene foam offers moderate durability and is resistant to moisture, making it suitable for short-term cushion applications but prone to cracking under prolonged stress. Polyurethane foam provides superior durability with enhanced resilience and flexibility, maintaining structural integrity and comfort over extended periods. Its ability to withstand repeated compression and resist degradation significantly extends the longevity of cushions compared to polystyrene foam.
Insulation and Breathability
Polystyrene foam offers excellent thermal insulation due to its closed-cell structure, effectively reducing heat transfer in cushions. Polyurethane foam provides superior breathability with an open-cell design, allowing better air circulation and moisture dissipation. For applications requiring both insulation and comfort, polyurethane foam is often preferred, while polystyrene foam excels in maintaining consistent temperature control.
Environmental Impact of Polystyrene and Polyurethane
Polystyrene foam, widely used for cushioning, poses significant environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature and persistence in landfills and oceans, often contributing to microplastic pollution. Polyurethane foam, while also not biodegradable, typically has a more complex chemical composition, making it less prone to fragmentation but raising concerns about toxic emissions during production and disposal. Recycling options for both foams remain limited, intensifying the environmental impact through resource consumption and waste generation.
Cost Effectiveness Analysis
Polystyrene foam offers a lower initial cost compared to polyurethane foam, making it a budget-friendly option for cushion manufacturing. However, polyurethane foam provides superior durability and resilience, which reduces replacement frequency and long-term expenses. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, polyurethane foam often delivers better value through extended lifespan and enhanced comfort despite higher upfront investment.
Common Applications for Each Foam Type
Polystyrene foam is commonly used in packaging, insulation, and disposable food containers due to its lightweight and rigid structure, making it ideal for protecting goods and providing thermal insulation. Polyurethane foam finds extensive application in furniture cushions, automotive seating, and bedding because of its superior flexibility, durability, and comfort-enhancing properties. Both foam types serve distinct purposes in cushioning, with polystyrene favored for structural support and polyurethane preferred for soft, resilient padding.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Cushion Needs
Polystyrene foam offers excellent rigidity and durability, making it ideal for cushions that require firm support and shape retention, such as seat cushions and outdoor furniture. Polyurethane foam provides superior softness, flexibility, and pressure relief, making it suitable for cushions prioritizing comfort and cushioning, like sofa and mattress toppers. Evaluating factors such as desired firmness, durability, and intended use ensures choosing the right foam material tailored to specific cushion needs.
Infographic: Polystyrene foam vs Polyurethane foam for Cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com