Bamboo fiber offers superior moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties compared to cotton fiber, enhancing textile breathability and odor resistance. Cotton fiber provides natural softness and durability, making it a traditional choice for comfortable and long-lasting textiles.
Table of Comparison
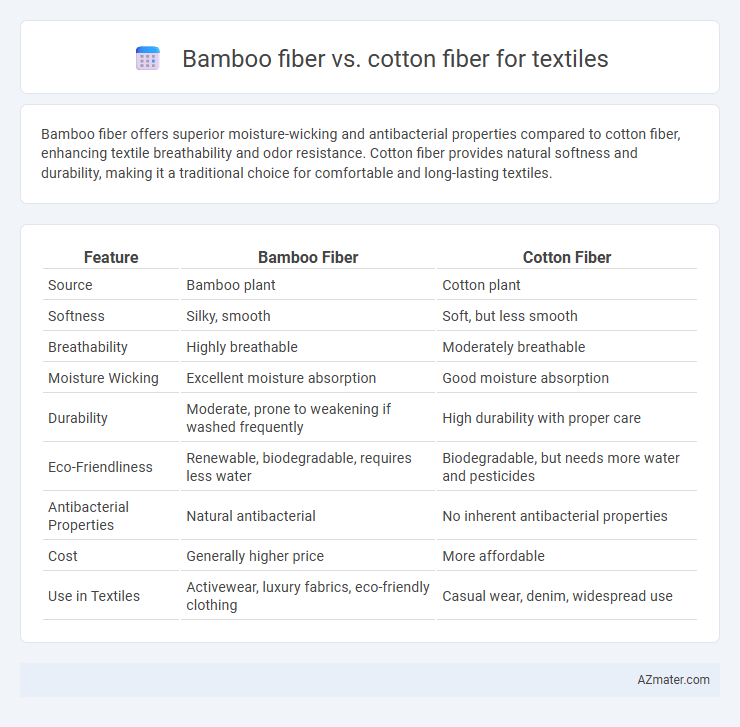
| Feature | Bamboo Fiber | Cotton Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Bamboo plant | Cotton plant |
| Softness | Silky, smooth | Soft, but less smooth |
| Breathability | Highly breathable | Moderately breathable |
| Moisture Wicking | Excellent moisture absorption | Good moisture absorption |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to weakening if washed frequently | High durability with proper care |
| Eco-Friendliness | Renewable, biodegradable, requires less water | Biodegradable, but needs more water and pesticides |
| Antibacterial Properties | Natural antibacterial | No inherent antibacterial properties |
| Cost | Generally higher price | More affordable |
| Use in Textiles | Activewear, luxury fabrics, eco-friendly clothing | Casual wear, denim, widespread use |
Introduction to Bamboo Fiber and Cotton Fiber
Bamboo fiber, derived from the cellulose of bamboo plants, offers exceptional softness, moisture-wicking properties, and natural antibacterial qualities, making it a sustainable alternative in textile production. Cotton fiber, sourced from the seed hairs of the cotton plant, is renowned for its breathability, durability, and widespread use in apparel manufacturing worldwide. Both fibers present unique environmental footprints, with bamboo often highlighted for its rapid growth and lower water consumption compared to traditional cotton.
Origins and Production Processes
Bamboo fiber originates from the pulp of bamboo plants, using a mechanical or chemical process to extract cellulose, while cotton fiber comes directly from the seed hairs of cotton plants after harvesting. The production of bamboo fiber often involves eco-friendly methods such as mechanical crushing and natural enzyme degumming, though some processes use chemical solvents like sodium hydroxide. Cotton fiber production entails picking, ginning to separate seeds, cleaning, and spinning, with organic cotton emphasizing minimal chemical use to reduce environmental impact.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Bamboo fiber production requires significantly less water and pesticides compared to cotton, reducing environmental strain and chemical runoff. Cotton cultivation consumes about 20,000 liters of water per kilogram, whereas bamboo grows with minimal irrigation, making it a more sustainable textile resource. Bamboo fibers are also biodegradable and renewable, offering a lower carbon footprint throughout their lifecycle compared to conventional cotton fibers.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
Bamboo fiber is highly sustainable due to its rapid growth rate, requiring minimal water and no pesticides, making it an eco-friendly alternative to conventional cotton. Cotton cultivation demands significant water usage and extensive chemical inputs, contributing to soil degradation and pollution. Bamboo's biodegradability and natural antibacterial properties further enhance its appeal in sustainable textile production.
Texture, Softness, and Comfort
Bamboo fiber offers a silky texture that feels smoother and more luxurious compared to the coarser, denser weave of cotton fiber. Bamboo's natural moisture-wicking properties enhance breathability and softness, resulting in superior comfort for sensitive skin and all-day wear. Cotton fibers, while durable and breathable, often lack the hypoallergenic qualities and silky finish found in bamboo textiles.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Bamboo fiber exhibits superior breathability compared to cotton fiber, allowing air to circulate freely and keeping the fabric cooler and fresher during wear. Its microscopic structure facilitates efficient moisture-wicking, quickly drawing sweat away from the skin and enhancing overall comfort. Cotton fiber, while breathable, tends to retain moisture longer, making bamboo a preferred choice for activewear and humid climates.
Durability and Longevity
Bamboo fiber exhibits superior durability in textile applications due to its natural strength and resistance to wear, often lasting longer than cotton under similar conditions. Cotton fiber, while soft and breathable, tends to degrade faster with frequent washing and exposure to elements, reducing its longevity in textiles. The antibacterial and moisture-wicking properties of bamboo fiber further contribute to its sustained integrity and prolonged lifespan compared to traditional cotton fabrics.
Allergenicity and Skin Sensitivity
Bamboo fiber is naturally hypoallergenic and contains antibacterial properties, making it ideal for sensitive skin and reducing the risk of irritations compared to cotton fiber. Cotton, while breathable and soft, can sometimes retain allergens like dust mites and chemicals from pesticides, potentially causing skin sensitivities. Textile products made from bamboo fiber are increasingly preferred for individuals prone to eczema and contact dermatitis due to their moisture-wicking and gentle texture.
Cost and Market Availability
Bamboo fiber is generally more expensive than cotton fiber due to its complex processing and lower cultivation scale, impacting overall textile production costs. Cotton fiber dominates the market with widespread availability and established supply chains, making it more accessible for large-scale manufacturing. The emerging demand for sustainable textiles drives niche growth in bamboo fiber, but cotton remains cost-effective and readily available for mass-market use.
Final Verdict: Which Fiber is Better for Textiles?
Bamboo fiber offers superior moisture-wicking, antibacterial properties, and sustainability compared to conventional cotton, making it ideal for eco-friendly textiles. Cotton fibers provide softness, breathability, and durability, preferred in traditional textile applications and widespread consumer acceptance. Considering environmental impact and functional benefits, bamboo fiber emerges as a better choice for innovative and sustainable textile manufacturing.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber vs Cotton fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com