China clay, also known as kaolin, offers high purity and low reactivity, making it ideal for foundry sand binders with excellent thermal stability. Montmorillonite clay provides superior plasticity and water absorption, enhancing sand cohesion but may introduce challenges in controlling moisture content during casting.
Table of Comparison
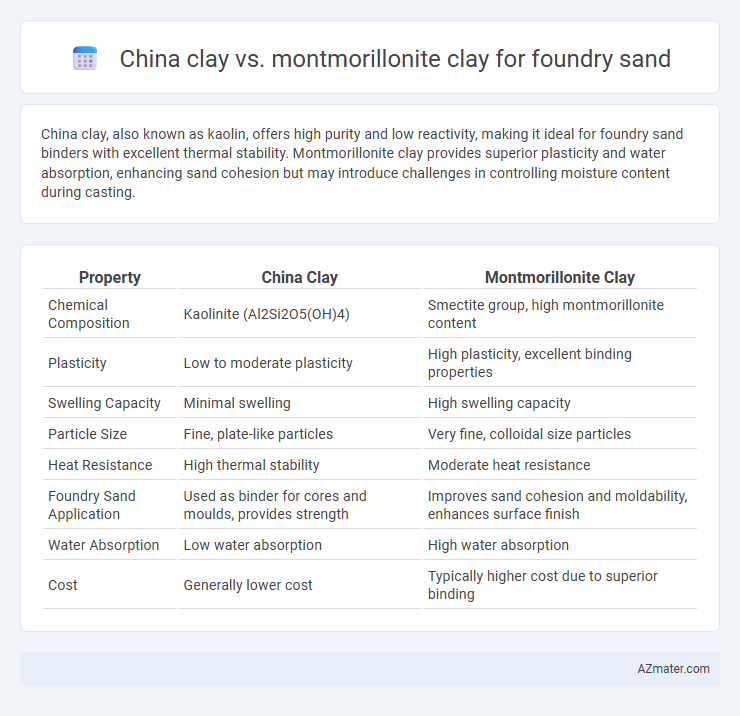
| Property | China Clay | Montmorillonite Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4) | Smectite group, high montmorillonite content |
| Plasticity | Low to moderate plasticity | High plasticity, excellent binding properties |
| Swelling Capacity | Minimal swelling | High swelling capacity |
| Particle Size | Fine, plate-like particles | Very fine, colloidal size particles |
| Heat Resistance | High thermal stability | Moderate heat resistance |
| Foundry Sand Application | Used as binder for cores and moulds, provides strength | Improves sand cohesion and moldability, enhances surface finish |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption | High water absorption |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost due to superior binding |
Introduction to Foundry Sand Clays
Foundry sand clays, such as China clay (kaolin) and Montmorillonite clay, play crucial roles in molding and core-making processes due to their binding properties and thermal stability. China clay offers high refractory strength and plasticity, making it ideal for precision casting and detailed mold shapes, while Montmorillonite clay provides superior swelling capacity and moisture retention, enhancing the sand's cohesiveness and green strength. Selection between these clays depends on the specific foundry requirements, balancing mold strength, permeability, and surface finish quality.
Overview of China Clay: Properties and Uses
China clay, also known as kaolin, exhibits fine particle size, high purity, and excellent refractory properties, making it ideal for foundry sand applications where thermal resistance and mold strength are critical. Its high alumina content enhances the durability and binding capacity of the sand molds, improving casting quality and surface finish. Widely used in precision casting, China clay's low impurities minimize defects and contribute to consistent mold performance in metal casting processes.
Montmorillonite Clay: Characteristics and Applications
Montmorillonite clay, a key component in foundry sand, is highly valued for its exceptional plasticity, swelling capacity, and strong bonding properties that enhance mold strength and surface finish in metal casting. Its fine particle size and high cation exchange capacity improve refractory performance and gas permeability, making it ideal for precision casting applications. Compared to China clay, Montmorillonite clay provides superior moisture retention and moldability, which reduces defects and increases dimensional accuracy in foundry molds.
Chemical Composition Comparison
China clay, primarily composed of kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4), features high alumina and silica content with low impurities, making it ideal for foundry sand binders due to its plasticity and thermal stability. Montmorillonite clay, rich in smectite minerals with a chemical formula of (Na,Ca)0.33(Al,Mg)2Si4O10(OH)2*nH2O, contains higher amounts of magnesium and iron oxides, imparting greater swelling capacity and moisture retention. The lower alumina and higher exchangeable cations in montmorillonite affect its binding properties and permeability compared to the chemically more inert china clay preferred in high-quality foundry applications.
Particle Size and Shape Influence
China clay, primarily composed of kaolinite, features larger, plate-like particles that enhance the refractory properties and permeability of foundry sand molds. Montmorillonite clay, with finer, more irregularly shaped particles, contributes higher plasticity and cohesion, improving mold strength but potentially reducing permeability. Optimal particle size and shape balance in foundry sand blends directly impacts thermal stability, gas permeability, and mold surface finish quality.
Binding Strength in Foundry Sand
China clay, primarily composed of kaolinite, exhibits moderate binding strength in foundry sand applications due to its relatively low plasticity and particle shape, which allows for adequate mold cohesion but limited flexibility. Montmorillonite clay, characterized by its high swelling capacity and layered structure, offers superior binding strength in foundry sand by enhancing green sand mold toughness and moisture retention. The superior binding performance of montmorillonite improves the dimensional stability and surface finish of castings compared to china clay-based molds.
Moisture Retention and Permeability
China clay (kaolin) in foundry sand exhibits moderate moisture retention and good permeability, supporting effective mold stability and gas escape during metal casting. Montmorillonite clay, known for its high moisture retention due to its swelling properties, can reduce sand permeability, potentially causing defects in casting processes. Optimizing clay content balances moisture control and permeability, critical for maintaining mold strength and casting quality.
Thermal Stability and Refractoriness
China clay, also known as kaolin, exhibits high thermal stability and refractoriness, making it suitable for molds and cores in foundry sand applications where consistent heat resistance is crucial. Montmorillonite clay has lower thermal stability due to its layered structure, which can cause swelling and reduced refractoriness under high temperatures, limiting its use in high-temperature foundry processes. The superior refractoriness of China clay helps maintain mold integrity and surface finish during metal casting in foundries.
Environmental and Cost Considerations
China clay, primarily composed of kaolinite, offers moderate environmental benefits due to its natural abundance and lower processing requirements, reducing energy consumption and emissions in foundry sand applications. Montmorillonite clay, with its higher swelling capacity and greater water retention, often requires more intensive mining and purification, leading to increased environmental impacts and higher operational costs. Cost considerations favor China clay for its widespread availability and lower processing expenses, whereas Montmorillonite's enhanced binding properties can justify higher costs in specialized foundry uses despite its environmental footprint.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Clay for Foundry Sand
China clay offers high whiteness and purity, making it suitable for molds requiring smooth surface finishes and minimal impurities. Montmorillonite clay provides superior plasticity and binding strength, enhancing green sand mold stability and moisture retention. Selecting between China clay and Montmorillonite depends on the specific foundry application needs, with China clay preferred for fine surface detail and Montmorillonite favored for robust mold integrity.
Infographic: China clay vs Montmorillonite clay for Foundry sand
 azmater.com
azmater.com