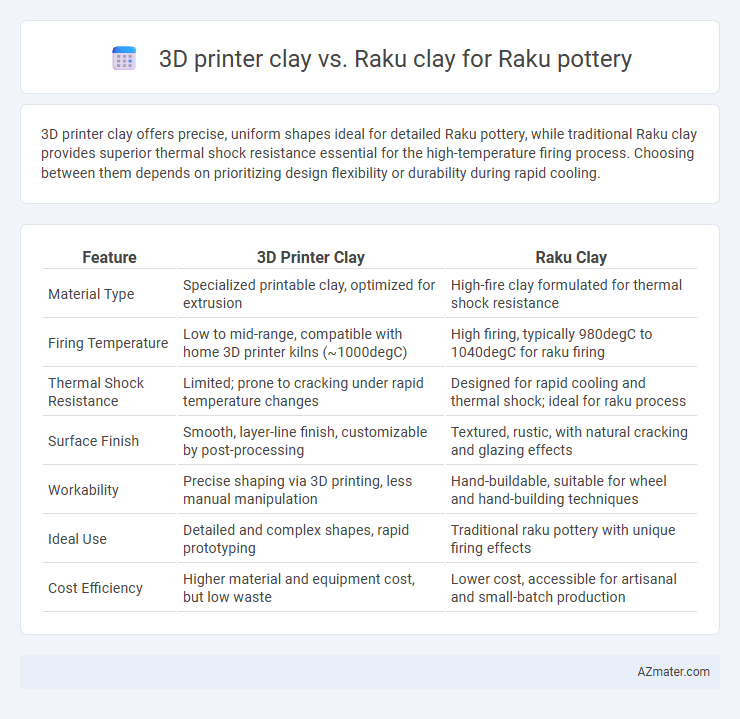
3D printer clay offers precise, uniform shapes ideal for detailed Raku pottery, while traditional Raku clay provides superior thermal shock resistance essential for the high-temperature firing process. Choosing between them depends on prioritizing design flexibility or durability during rapid cooling.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 3D Printer Clay | Raku Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Specialized printable clay, optimized for extrusion | High-fire clay formulated for thermal shock resistance |
| Firing Temperature | Low to mid-range, compatible with home 3D printer kilns (~1000degC) | High firing, typically 980degC to 1040degC for raku firing |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Limited; prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes | Designed for rapid cooling and thermal shock; ideal for raku process |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, layer-line finish, customizable by post-processing | Textured, rustic, with natural cracking and glazing effects |
| Workability | Precise shaping via 3D printing, less manual manipulation | Hand-buildable, suitable for wheel and hand-building techniques |
| Ideal Use | Detailed and complex shapes, rapid prototyping | Traditional raku pottery with unique firing effects |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher material and equipment cost, but low waste | Lower cost, accessible for artisanal and small-batch production |
Introduction to Raku Pottery and Clay Selection
Raku pottery involves a unique firing process characterized by rapid heating and cooling, which demands clay that can withstand thermal shock. Raku clay, specifically formulated with grog and high refractory properties, offers the necessary durability and flexibility for the unpredictable Raku firing cycle. In contrast, 3D printer clay lacks the specialized composition and thermal resistance essential for successful Raku pottery, making traditional Raku clay the preferred choice for artisans aiming for optimal results.
What Is 3D Printer Clay?
3D printer clay is a specialized, printable material designed for use in ceramic 3D printers, allowing artists to create precise and intricate pottery shapes with fine detail and consistency. Unlike traditional Raku clay, which is formulated for rapid firing and thermal shock resistance during the Raku firing process, 3D printer clay often requires post-print drying and firing to achieve durability and the characteristic textures of Raku pottery. This innovative clay bridges digital fabrication and traditional ceramic techniques, enabling artists to explore complex designs while still embracing the unpredictable surface effects unique to Raku firing.
Understanding Raku Clay: Key Properties
Raku clay is specially formulated for rapid thermal shock resistance, featuring a high grog content that minimizes warping and cracking during the quick firing and cooling process unique to Raku pottery. In contrast, 3D printer clay typically lacks the necessary thermal stability and grog composition, making it less suitable for the intense firing cycles of Raku techniques. Understanding these key properties--thermal shock resistance, grog content, and firing temperature tolerance--is essential for selecting the appropriate clay to achieve the desired durability and finish in Raku pottery.
Compatibility of 3D Printer Clay with Raku Firing
3D printer clay designed for Raku pottery exhibits specific formulations that enhance compatibility with rapid thermal shock during Raku firing, unlike traditional Raku clay which contains grog to resist cracking. The silica and alumina content in 3D printer clay ensures better thermal expansion control, reducing warping and fractures in open-air firing cycles. Optimizing clay chemistry for Raku firing conditions improves the final ceramic piece's surface quality and structural integrity.
Thermal Shock Resistance: 3D Printer Clay vs. Raku Clay
Raku clay is specifically formulated to withstand rapid temperature changes during the raku firing process, exhibiting excellent thermal shock resistance due to its grog content and high firing temperature tolerance. In contrast, 3D printer clay, often designed for precision and smooth extrusion, typically lacks the robust thermal shock resistance needed for traditional raku firing cycles. Therefore, raku clay is superior for pottery subjected to the intense thermal shocks characteristic of raku firing.
Workability in Sculpture: Moldability and Surface Texture
3D printer clay offers precise moldability with smooth, consistent surface texture ideal for detailed Raku pottery sculptures, allowing intricate designs and uniform layers. Raku clay, traditionally hand-formed, provides exceptional workability with natural plasticity, enabling tactile shaping and unique textures through manual manipulation and firing effects. Sculptors benefit from 3D printer clay's digital accuracy for complex forms, while Raku clay enhances organic surface variations essential to authentic Raku pottery aesthetics.
Firing Results: Color, Texture, and Cracking
3D printer clay for Raku pottery often yields more consistent color and smoother texture due to its uniform composition, while traditional Raku clay develops rich, unpredictable hues and organic textures from the rapid thermal shocks during firing. Raku clay is prone to intentional cracking and crazing, enhancing its distinctive character, whereas 3D printer clay tends to minimize cracks, providing a more controlled finish. Fire results highlight Raku clay's ability to produce dramatic surface effects and vibrant color variations, contrasting with 3D clay's reliability and precision in delicate designs.
Durability and Finished Pottery Longevity
3D printer clay designed for Raku pottery offers precise layering and intricate detailing but generally lacks the durability of traditional Raku clay, which is formulated to withstand the rapid thermal shocks of the Raku firing process. Raku clay typically contains grog or other refractory materials that enhance its thermal resistance and reduce cracking during cooling, resulting in finished pieces with greater longevity and structural integrity. The durability and longevity of the finished pottery are superior in Raku clay due to its tailored composition for rapid heating and cooling cycles inherent in Raku firing.
Cost and Availability Considerations
3D printer clay for Raku pottery offers lower initial costs due to its compatibility with affordable desktop 3D printers, while traditional Raku clay typically requires specialized materials that can be pricier and less accessible. Availability of 3D printer clay is growing steadily through online retailers and specialty suppliers, providing greater convenience and supply consistency. In contrast, Raku clay is often sourced from local ceramic suppliers or specialized markets, which may limit options but ensures material quality tailored for high-temperature firing and thermal shock resistance.
Which Clay Is Best for Raku Pottery?
Raku clay is specifically formulated to withstand the rapid heating and cooling cycles of Raku firing, making it the ideal choice for Raku pottery due to its thermal shock resistance and durability. While 3D printer clay can offer precision and ease of shaping, it often lacks the necessary refractory properties and plasticity required for traditional Raku techniques. Selecting Raku clay ensures better structural integrity and desired surface effects after the dramatic firing process characteristic of Raku pottery.
Infographic: 3D printer clay vs Raku clay for Raku Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com