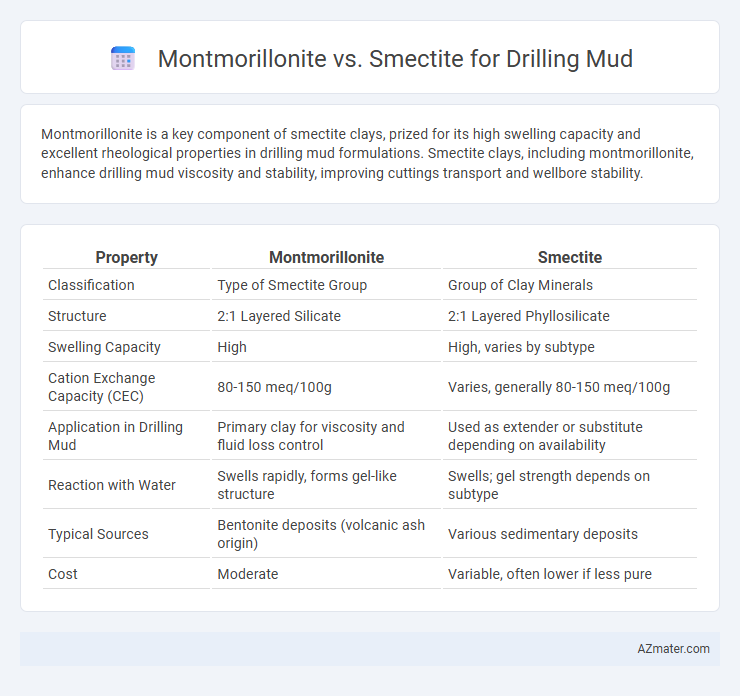
Montmorillonite is a key component of smectite clays, prized for its high swelling capacity and excellent rheological properties in drilling mud formulations. Smectite clays, including montmorillonite, enhance drilling mud viscosity and stability, improving cuttings transport and wellbore stability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Montmorillonite | Smectite |
|---|---|---|
| Classification | Type of Smectite Group | Group of Clay Minerals |
| Structure | 2:1 Layered Silicate | 2:1 Layered Phyllosilicate |
| Swelling Capacity | High | High, varies by subtype |
| Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) | 80-150 meq/100g | Varies, generally 80-150 meq/100g |
| Application in Drilling Mud | Primary clay for viscosity and fluid loss control | Used as extender or substitute depending on availability |
| Reaction with Water | Swells rapidly, forms gel-like structure | Swells; gel strength depends on subtype |
| Typical Sources | Bentonite deposits (volcanic ash origin) | Various sedimentary deposits |
| Cost | Moderate | Variable, often lower if less pure |
Introduction to Drilling Mud Minerals
Montmorillonite and smectite are essential clay minerals in drilling mud formulations due to their unique swelling and adsorption properties. Montmorillonite, a dominant component of the smectite group, provides superior rheological control and enhances the viscosity and stability of drilling fluids under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions. These minerals improve cuttings suspension, reduce fluid loss, and maintain wellbore integrity, making them critical for efficient drilling operations.
What is Montmorillonite?
Montmorillonite is a key mineral in the smectite group, known for its exceptional swelling properties and high cation-exchange capacity, making it ideal for drilling mud applications. Its layered structure allows water absorption between sheets, enhancing viscosity and fluid loss control in drilling fluids. This mineral's ability to improve rheological properties and provide thermal stability makes it a preferred choice in formulating efficient and environmentally friendly drilling mud formulations.
Understanding Smectite Clay
Smectite clay, a primary component in drilling mud, is prized for its exceptional swelling capacity and high cation exchange capacity, which enhance the mud's viscosity and filtration control. Montmorillonite, a member of the smectite group, exhibits superior plasticity and water absorption properties crucial for stabilizing boreholes and preventing fluid loss during drilling operations. Understanding the unique characteristics of smectite clays like montmorillonite allows for optimized formulation of drilling fluids, improving wellbore stability and drilling efficiency.
Montmorillonite vs Smectite: Key Differences
Montmorillonite is a specific type of smectite clay mineral predominantly used in drilling mud due to its high swelling capacity and excellent rheological properties. Smectite refers to a group of clay minerals that includes montmorillonite, characterized by their layered structure and ability to absorb water, but montmorillonite exhibits superior plasticity and viscosity control essential for maintaining borehole stability. Key differences lie in montmorillonite's enhanced cation exchange capacity and finer particle size, making it more effective in optimizing drilling fluid performance and minimizing fluid loss.
Physical Properties Relevant to Drilling Muds
Montmorillonite and Smectite are both types of clay minerals commonly used in drilling muds due to their high swelling capacity and excellent rheological properties. Montmorillonite exhibits a layered structure with high cation exchange capacity (CEC), enhancing viscosity and fluid loss control, while Smectite shares similar swelling behavior but often has a slightly lower plasticity index. The particle size distribution and mineral purity influence penetration resistance and filtration properties, making Montmorillonite generally preferred for high-performance drilling fluid formulations.
Swelling Capacity and Fluid Loss Control
Montmorillonite, a primary component of smectite clays, exhibits superior swelling capacity due to its high cation exchange capacity and layered silicate structure, making it highly effective in drilling mud formulations. Smectite clays, including montmorillonite, excel in fluid loss control by forming a thin, impermeable filter cake that minimizes filtrate invasion into formations. Optimizing the montmorillonite-to-smectite ratio enhances drilling mud performance, balancing maximum swelling for viscosity and effective fluid loss reduction.
Rheological Behavior in Mud Formulation
Montmorillonite, a primary component of smectite group clays, significantly influences the rheological behavior of drilling mud by enhancing viscosity and gel strength, crucial for efficient cuttings suspension and hole cleaning. Differences in basal spacing and cation exchange capacity between Montmorillonite and other smectites affect the swelling properties and thixotropy of the mud, impacting its flow properties under shear stress. Optimizing the proportion of Montmorillonite in mud formulation improves yield point and plastic viscosity, essential for maintaining wellbore stability and minimizing fluid loss in challenging drilling environments.
Cost and Availability of Montmorillonite and Smectite
Montmorillonite and smectite are both key clay minerals used in drilling muds for their swelling and rheological properties, but Montmorillonite typically commands a higher cost due to its superior purity and performance characteristics. Smectite, often sourced from broader sedimentary deposits, is generally more abundant and less expensive, making it a cost-effective option for large-scale drilling operations. Availability of Montmorillonite can be limited based on geographic location, whereas smectite's widespread occurrence ensures more consistent supply and better logistical advantages.
Performance in Various Drilling Conditions
Montmorillonite and smectite exhibit distinct performance characteristics in drilling mud applications, with montmorillonite offering superior swelling capacity and rheological control under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions. Smectite, a group of minerals including montmorillonite, provides excellent fluid loss control and viscosity stability in low-salinity and low-temperature drilling environments. Optimizing drilling mud formulations with montmorillonite enhances borehole stability and minimizes formation damage during deep well drilling, while smectite's flexibility supports diverse hydrocarbon extraction scenarios.
Choosing the Right Clay for Optimal Drilling Mud Performance
Montmorillonite, a primary component of smectite clays, offers superior swelling and rheological properties critical for drilling mud performance, delivering excellent viscosity and filtration control. Smectite clays, characterized by their high cation exchange capacity and water absorption, enhance mud stability and cutoff formation damage during drilling operations. Selecting montmorillonite-rich smectite over other clay minerals ensures improved wellbore stability, reduced torque, and optimal cuttings suspension in complex drilling environments.
Infographic: Montmorillonite vs Smectite for Drilling Mud
 azmater.com
azmater.com