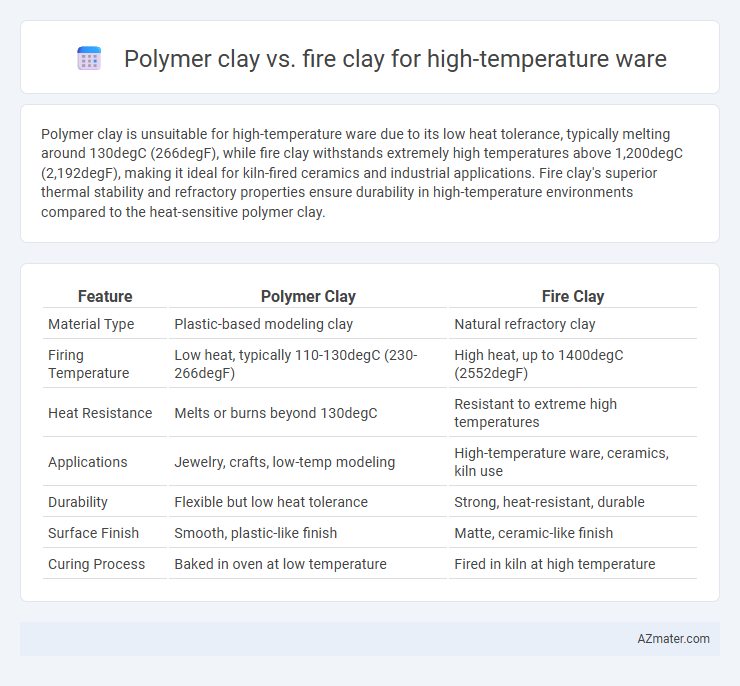
Polymer clay is unsuitable for high-temperature ware due to its low heat tolerance, typically melting around 130degC (266degF), while fire clay withstands extremely high temperatures above 1,200degC (2,192degF), making it ideal for kiln-fired ceramics and industrial applications. Fire clay's superior thermal stability and refractory properties ensure durability in high-temperature environments compared to the heat-sensitive polymer clay.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polymer Clay | Fire Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Plastic-based modeling clay | Natural refractory clay |
| Firing Temperature | Low heat, typically 110-130degC (230-266degF) | High heat, up to 1400degC (2552degF) |
| Heat Resistance | Melts or burns beyond 130degC | Resistant to extreme high temperatures |
| Applications | Jewelry, crafts, low-temp modeling | High-temperature ware, ceramics, kiln use |
| Durability | Flexible but low heat tolerance | Strong, heat-resistant, durable |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, plastic-like finish | Matte, ceramic-like finish |
| Curing Process | Baked in oven at low temperature | Fired in kiln at high temperature |
Introduction to High Temperature Clays
High temperature clays such as fire clay are specifically formulated to withstand extreme thermal conditions, making them ideal for creating durable ceramic ware used in kiln firing and industrial applications. Polymer clay, on the other hand, is composed of synthetic materials that harden at low temperatures and cannot endure the intense heat required for high temperature ware. Fire clay contains a high concentration of alumina and silica, granting superior resistance to thermal shock and structural integrity in high heat environments.
What is Polymer Clay?
Polymer clay is a synthetic modeling material composed of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) particles mixed with plasticizers, allowing it to be moldable at room temperature and hardened by baking at relatively low temperatures around 130degC to 150degC. Unlike fire clay, which is a natural ceramic material designed to withstand extremely high temperatures exceeding 1200degC, polymer clay is not suitable for high-temperature ware or functional pottery subjected to heat stress. Its primary use lies in creating decorative items, jewelry, and art objects rather than durable heat-resistant cookware or kiln-fired ceramics.
What is Fire Clay?
Fire clay is a type of refractory clay composed primarily of kaolinite, prized for its high melting point and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for high-temperature ware such as kiln linings and firebricks. Unlike polymer clay, which hardens through curing and contains synthetic polymers, fire clay withstands extreme heat without deforming or melting, ensuring durability in industrial and ceramic applications. Its heat retention and structural integrity enable the creation of pottery, bricks, and other items subject to intense thermal conditions.
Composition and Material Differences
Polymer clay consists mainly of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) combined with plasticizers and fillers, making it suitable for low-temperature curing but not for high-temperature applications. Fire clay is primarily composed of refractory alumina silicate minerals with high refractory properties that can withstand temperatures above 1,200degC, making it ideal for high-temperature ware like kiln bricks and ceramic molds. The key material difference lies in polymer clay's synthetic organic composition versus fire clay's inorganic refractory mineral composition, dictating their respective temperature tolerances and functional uses.
Temperature Resistance: Polymer vs Fire Clay
Polymer clay typically withstands temperatures up to 130degC (266degF) before softening or deforming, making it unsuitable for high-temperature applications. Fire clay, a type of refractory ceramic, can endure temperatures exceeding 1,200degC (2,192degF) without structural damage, making it ideal for high-temperature ware such as kiln linings and cookware. The vast difference in temperature resistance positions fire clay as the preferred material for any application requiring sustained exposure to extreme heat.
Workability and Sculpting Characteristics
Polymer clay offers exceptional workability with a soft, pliable texture ideal for detailed sculpting and fine textures, hardening only after baking at relatively low temperatures (typically around 265degF to 275degF). Fire clay, designed for high-temperature ware, exhibits a dense, coarse texture requiring more effort to shape but withstands extremely high firing temperatures (up to 2500degF), making it suitable for functional ceramics and durable sculptures. Sculptors favor polymer clay for intricate models and precision work, while fire clay is preferred for heat-resistant, robust pieces needing structural integrity during fiery kiln processes.
Firing and Curing Processes
Polymer clay requires baking at relatively low temperatures, typically between 230degF to 275degF (110degC to 135degC), for curing without combustion, making it suitable for small craft projects rather than high-temperature ware. Fire clay withstands extreme firing temperatures above 2300degF (1260degC), enabling its use in high-temperature ceramics and kiln-fired pottery, where it undergoes vitrification to develop durability and heat resistance. The firing process for fire clay involves controlled temperature ramps and soak times in a kiln to achieve optimal structural strength, unlike polymer clay's simpler, low-heat curing process.
Durability Under High Temperatures
Fire clay exhibits superior durability under high temperatures, maintaining structural integrity well above 1200degC, making it ideal for industrial kilns and refractory applications. Polymer clay, by contrast, is designed for lower temperature curing, typically hardening around 110degC, and degrades when exposed to high heat, limiting its use in high-temperature ware. The refractory properties of fire clay ensure long-lasting performance and resistance to thermal shock, which polymer clay cannot withstand.
Applications in High Temperature Ware
Polymer clay is unsuitable for high temperature ware due to its low heat tolerance and tendency to degrade above 130degC, making it ideal only for decorative or low-heat applications. Fire clay, composed of refractory materials, withstands temperatures exceeding 1,200degC and is widely used in manufacturing kiln bricks, fireproof insulation, and high-temperature cookware. Its thermal durability and resistance to thermal shock make fire clay the preferred choice in industrial and artisanal high temperature ware production.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Project
Polymer clay offers ease of use and vibrant colors, making it ideal for low to moderate temperature crafts, but it is unsuitable for high-temperature applications due to its plastic composition. Fire clay, composed of refractory minerals, withstands temperatures above 1,400degC, making it the preferred choice for functional ceramics like cookware, kiln furniture, and industrial ware. Selecting the right clay depends on the required thermal resistance, durability, and final use of the product to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Infographic: Polymer clay vs Fire clay for High temperature ware
 azmater.com
azmater.com