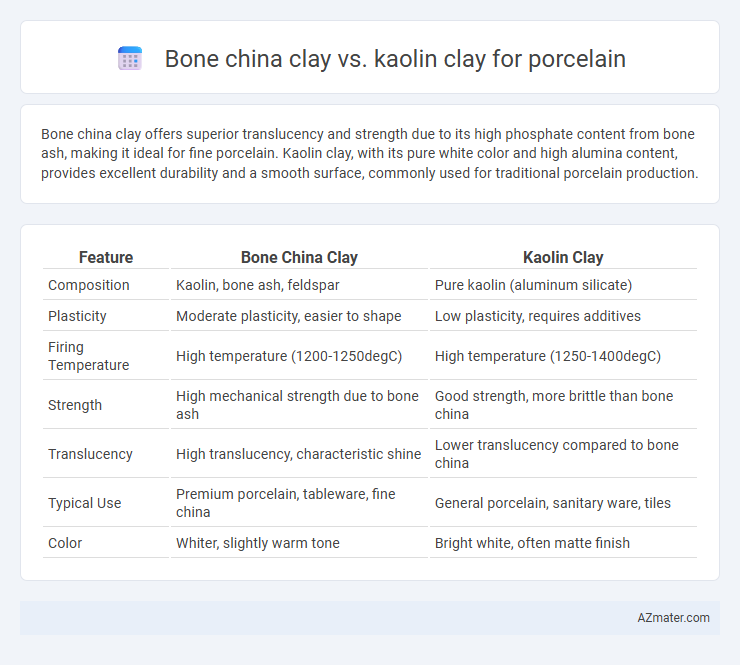
Bone china clay offers superior translucency and strength due to its high phosphate content from bone ash, making it ideal for fine porcelain. Kaolin clay, with its pure white color and high alumina content, provides excellent durability and a smooth surface, commonly used for traditional porcelain production.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bone China Clay | Kaolin Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Kaolin, bone ash, feldspar | Pure kaolin (aluminum silicate) |
| Plasticity | Moderate plasticity, easier to shape | Low plasticity, requires additives |
| Firing Temperature | High temperature (1200-1250degC) | High temperature (1250-1400degC) |
| Strength | High mechanical strength due to bone ash | Good strength, more brittle than bone china |
| Translucency | High translucency, characteristic shine | Lower translucency compared to bone china |
| Typical Use | Premium porcelain, tableware, fine china | General porcelain, sanitary ware, tiles |
| Color | Whiter, slightly warm tone | Bright white, often matte finish |
Introduction to Bone China Clay and Kaolin Clay
Bone china clay is a unique blend of fine-grained kaolin clay, feldspar, and bone ash, resulting in a highly translucent and durable porcelain. Kaolin clay, often referred to as china clay, is a primary ingredient in porcelain production known for its purity, whiteness, and plasticity, providing the essential structure for both traditional and bone china. The addition of bone ash in bone china clay enhances its strength and translucency, distinguishing it from kaolin clay used in standard hard-paste porcelain.
Origin and Composition of Bone China Clay
Bone china clay originates primarily from England and contains a unique blend of bone ash, feldspar, and kaolin, which contributes to its high translucency and strength. Kaolin clay, derived from the decomposition of feldspar-rich rocks, is a key ingredient but lacks the bone ash component, resulting in a denser, less translucent porcelain. The calcium phosphate in bone ash enhances the vitrification process, setting bone china apart in durability and whiteness compared to traditional kaolin-based porcelain.
Origin and Composition of Kaolin Clay
Kaolin clay, originating primarily from weathered granite in regions such as China, Georgia (USA), and Cornwall (UK), is a key ingredient in porcelain due to its high purity and fine particle size. Composed mainly of the mineral kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4), kaolin clay provides whiteness and plasticity essential for shaping delicate porcelain pieces. Bone china clay incorporates kaolin but also includes bone ash, which enhances translucency and strength compared to pure kaolin-based porcelain.
Physical Properties Comparison
Bone china clay typically contains bone ash, which enhances its strength and translucency, making it more durable and less prone to chipping compared to kaolin clay. Kaolin clay, known for its high purity and fine particle size, provides superior whiteness and is crucial for producing hard-paste porcelain with excellent thermal resistance. While bone china exhibits a lower firing temperature and higher plasticity, kaolin's higher refractory qualities contribute to better resistance against deformation and chemical wear in porcelain production.
Differences in Porcelain-Making Techniques
Bone china clay contains bone ash, which enhances translucency and strength, allowing for thinner, more delicate porcelain pieces through lower firing temperatures and quick cooling processes. Kaolin clay, known as the primary ingredient in traditional porcelain, requires higher firing temperatures and longer kiln times to achieve its characteristic hardness, resulting in denser, less translucent ware. Porcelain-making with bone china emphasizes controlled, lower-temperature firings to maintain its delicate properties, while kaolin-based porcelain demands precise, high-temperature firings to attain its durability and white, opaque finish.
Strength and Durability: Bone China vs Kaolin
Bone china clay is renowned for its exceptional strength and durability due to the incorporation of bone ash, which enhances its translucency and reduces brittleness compared to traditional kaolin clay. Kaolin clay, while fundamental in porcelain production, results in a more porous and less resilient material without the reinforcement provided by bone ash. Therefore, bone china porcelain typically offers superior mechanical strength and resistance to chipping, making it more durable in everyday use.
Aesthetic Qualities: Transparency and Whiteness
Bone china clay exhibits superior transparency compared to kaolin clay, creating a delicately translucent porcelain that allows light to subtly pass through its thin walls. The incorporation of bone ash enhances the whiteness of bone china, resulting in a warm, creamy hue that contrasts with the cooler, often chalkier white produced by pure kaolin clay. Kaolin clay, prized for its pure white base, provides a sturdier but less translucent porcelain, emphasizing brightness and opacity over translucency.
Cost and Accessibility of Raw Materials
Bone china clay contains bone ash, which increases its cost due to the additional processing and sourcing of animal-derived materials, making it less accessible than kaolin clay. Kaolin clay, a natural white clay primarily composed of kaolinite, is more widely available and cost-effective, making it the preferred choice for many porcelain manufacturers. The scarcity and ethical considerations associated with bone ash further limit bone china clay's raw material accessibility compared to kaolin-based porcelain.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bone china clay, composed primarily of bone ash, kaolin, and feldspar, tends to have a higher environmental impact due to the ethical concerns and resource intensity involved in sourcing animal bone ash. Kaolin clay, a naturally occurring mineral, is more sustainable as it requires minimal processing and has lower carbon emissions during extraction, making it a preferable choice for eco-friendly porcelain production. Sustainable practices in kaolin mining, such as land rehabilitation and water recycling, further enhance its environmental advantages over bone china clay.
Choosing the Right Clay for Porcelain Production
Bone china clay contains bone ash, feldspar, and kaolin, offering high whiteness, translucency, and mechanical strength ideal for fine porcelain. Kaolin clay, a primary ingredient in porcelain, provides excellent plasticity and high firing temperature resistance, essential for durability and shape retention. Selecting the right clay depends on the desired end product characteristics, with bone china preferred for delicate, translucent wares and kaolin favored for traditional, robust porcelain items.
Infographic: Bone china clay vs Kaolin clay for Porcelain
 azmater.com
azmater.com