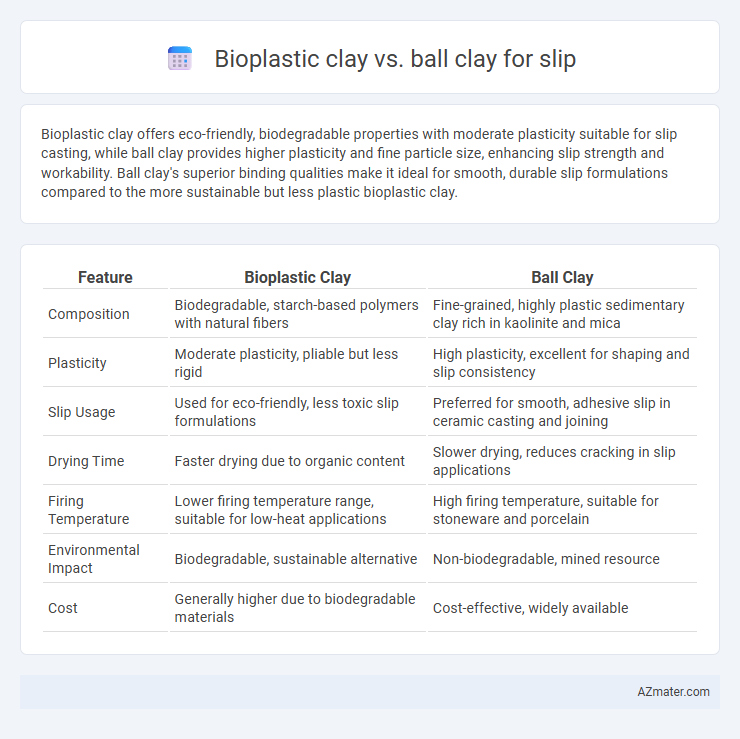
Bioplastic clay offers eco-friendly, biodegradable properties with moderate plasticity suitable for slip casting, while ball clay provides higher plasticity and fine particle size, enhancing slip strength and workability. Ball clay's superior binding qualities make it ideal for smooth, durable slip formulations compared to the more sustainable but less plastic bioplastic clay.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bioplastic Clay | Ball Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Biodegradable, starch-based polymers with natural fibers | Fine-grained, highly plastic sedimentary clay rich in kaolinite and mica |
| Plasticity | Moderate plasticity, pliable but less rigid | High plasticity, excellent for shaping and slip consistency |
| Slip Usage | Used for eco-friendly, less toxic slip formulations | Preferred for smooth, adhesive slip in ceramic casting and joining |
| Drying Time | Faster drying due to organic content | Slower drying, reduces cracking in slip applications |
| Firing Temperature | Lower firing temperature range, suitable for low-heat applications | High firing temperature, suitable for stoneware and porcelain |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, sustainable alternative | Non-biodegradable, mined resource |
| Cost | Generally higher due to biodegradable materials | Cost-effective, widely available |
Introduction to Bioplastic Clay and Ball Clay
Bioplastic clay is a biodegradable, eco-friendly material composed primarily of natural polymers like cornstarch, making it ideal for sustainable ceramics and slip applications where environmental impact is a concern. Ball clay, a highly plastic, fine-grained sedimentary clay rich in kaolinite, possesses excellent binding properties and plasticity, making it the preferred choice for slip casting, pottery, and ceramic production. The fundamental difference lies in bioplastic clay's biodegradability and renewability compared to ball clay's traditional mineral composition and superior workability in wet ceramic processes.
Defining Slip: Purpose and Characteristics
Slip, a fluid suspension of clay and water, serves as a versatile medium for joining and decorating ceramics. Bioplastic clay slip offers enhanced plasticity and flexibility, making it ideal for intricate designs and fine detail work, while ball clay slip provides superior plasticity and strength due to its high kaolinite and mica content, ensuring durability in ceramic construction. Both types of slip excel in adhesion and workability, but the choice depends on the specific ceramic application and desired finish quality.
Composition Comparison: Bioplastic Clay vs Ball Clay
Bioplastic clay primarily consists of biodegradable polymers such as polylactic acid combined with natural fillers, enabling eco-friendly and malleable slip formulations. Ball clay is composed mainly of kaolinite, mica, and quartz, providing excellent plasticity and strength to ceramic slips due to its high alumina content and fine particle size. The differing compositions lead to bioplastic clay offering sustainable, flexible slip options, while ball clay delivers superior workability and structural integrity for traditional ceramics.
Workability and Plasticity in Slip Formulations
Bioplastic clay offers enhanced workability and superior plasticity compared to ball clay in slip formulations, facilitating smoother shaping and reduced cracking during drying. Ball clay provides strong bonding properties but tends to require higher water content, which can impact slip consistency and drying times. Optimizing plasticity through bioplastic clay results in improved green strength and flexibility, essential for complex slip casting processes.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability of Bioplastic Clay
Bioplastic clay offers enhanced sustainability compared to ball clay due to its biodegradable composition derived from renewable plant-based materials, reducing reliance on non-renewable resources. Ball clay mining contributes to environmental degradation through habitat disruption and increased carbon emissions from extraction processes. The use of bioplastic clay in slip applications significantly lowers ecological footprints by minimizing waste accumulation and promoting circular economy principles.
Firing Properties and Performance Differences
Bioplastic clay exhibits lower shrinkage rates during firing compared to ball clay, enhancing dimensional stability in ceramic slip applications. Ball clay offers superior plasticity and workability, but its higher flux content leads to increased vitrification and potential warping at elevated firing temperatures. Performance differences are evident as bioplastic clay produces more consistent fired surfaces with reduced cracking risk, while ball clay's higher organic material content can cause increased porosity and variability in the final fired piece.
Color and Texture Outcomes in Final Products
Bioplastic clay offers vibrant color retention and smooth, elastic texture, making it ideal for slip casting with intricate details and consistent finishes. Ball clay provides superior plasticity and firing strength but tends to yield duller colors and a coarser texture in slip applications. The choice between bioplastic and ball clay significantly impacts the final product's visual appeal and surface quality, with bioplastic clay excelling in bright, uniform color and fine texture.
Cost and Availability: Market Considerations
Bioplastic clay generally incurs higher costs due to its sustainable sourcing and limited production scale compared to ball clay, which is widely available and economically priced owing to extensive mining operations worldwide. Ball clay's abundant reserves ensure consistent supply and lower market price volatility, making it a preferred choice for large-scale slip production in ceramics. Manufacturers must weigh the premium of bioplastic clay's eco-friendly benefits against ball clay's cost efficiency and accessibility when selecting raw materials for slip formulations.
User Experiences and Expert Recommendations
Bioplastic clay offers superior plasticity and less shrinkage compared to ball clay, making it a preferred choice for slip casting among artists seeking smooth, consistent textures and reduced cracking. Users report easier shaping and faster drying times with bioplastic clay, while experts emphasize its eco-friendly composition as an advantage in sustainable ceramics production. Ball clay remains favored for its high plasticity and binding properties in traditional slip formulas, but it may require longer drying times and careful moisture control to prevent defects.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Clay for Slip Applications
Bioplastic clay offers superior flexibility and easier shaping for slip applications, reducing cracking and improving detail retention compared to the denser, more plastic ball clay. Ball clay provides excellent plasticity and firing strength, making it ideal for slips requiring durability and smooth surface finish. Selecting the right clay depends on balancing the desired slip characteristics, with bioplastic clay favored for intricate designs and ball clay preferred for structural stability.
Infographic: Bioplastic clay vs Ball clay for Slip
 azmater.com
azmater.com