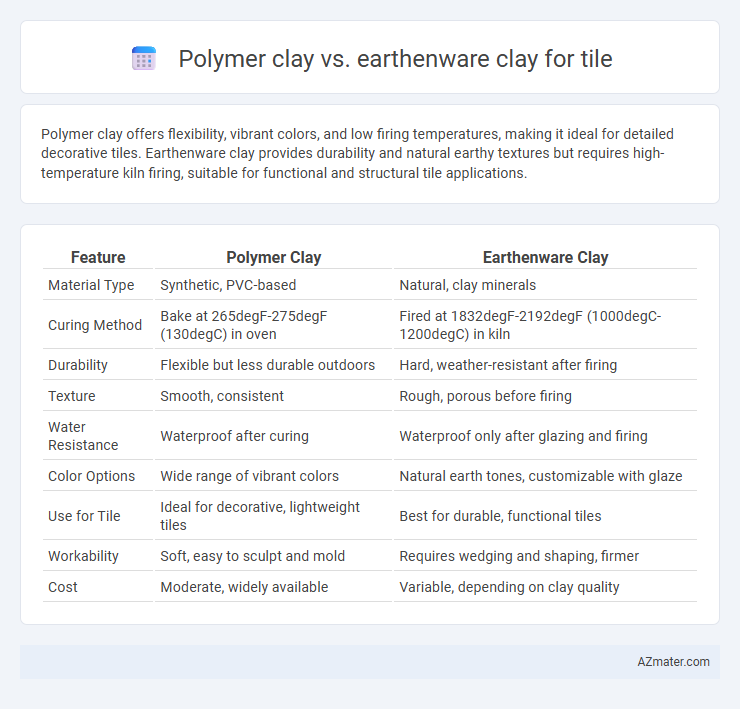
Polymer clay offers flexibility, vibrant colors, and low firing temperatures, making it ideal for detailed decorative tiles. Earthenware clay provides durability and natural earthy textures but requires high-temperature kiln firing, suitable for functional and structural tile applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polymer Clay | Earthenware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic, PVC-based | Natural, clay minerals |
| Curing Method | Bake at 265degF-275degF (130degC) in oven | Fired at 1832degF-2192degF (1000degC-1200degC) in kiln |
| Durability | Flexible but less durable outdoors | Hard, weather-resistant after firing |
| Texture | Smooth, consistent | Rough, porous before firing |
| Water Resistance | Waterproof after curing | Waterproof only after glazing and firing |
| Color Options | Wide range of vibrant colors | Natural earth tones, customizable with glaze |
| Use for Tile | Ideal for decorative, lightweight tiles | Best for durable, functional tiles |
| Workability | Soft, easy to sculpt and mold | Requires wedging and shaping, firmer |
| Cost | Moderate, widely available | Variable, depending on clay quality |
Introduction to Polymer Clay and Earthenware Clay
Polymer clay is a synthetic modeling material made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) that stays pliable until baked in a home oven, offering fine detail and vibrant color options ideal for lightweight, decorative tiles. Earthenware clay, a natural porous ceramic material fired at lower kiln temperatures (typically between 1,000degC and 1,150degC), provides sturdy, traditional tiles with a rustic, textured finish that absorbs glazes well. Choosing between polymer clay and earthenware clay depends on the desired tile durability, finish, firing method, and the intended use environment.
Composition and Properties Comparison
Polymer clay, composed mainly of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) along with plasticizers, remains flexible and cures at low temperatures, making it ideal for detailed, small-scale tile designs. Earthenware clay consists primarily of natural clay minerals rich in kaolinite, quartz, and feldspar, requiring high-temperature kiln firing to harden, which results in a porous, durable tile surface suitable for functional applications. The differing compositions influence their properties: polymer clay offers lightweight, waterproof, and vibrant color options without firing, while earthenware clay provides structural strength, heat resistance, and breathability after firing.
Workability: Handling and Shaping Differences
Polymer clay offers superior flexibility and ease of manipulation at room temperature, making it ideal for intricate tile designs and detailed shaping. Earthenware clay requires moisture control and periodic kneading to prevent cracking or drying, requiring more skill during handling and longer working times. The drying and firing process for earthenware also demands careful timing, whereas polymer clay cures quickly with consistent heat from a standard oven.
Tile Making Techniques: Polymer vs Earthenware
Polymer clay offers precise shaping and fine detail retention for tile making due to its pliability and low firing temperature, making it ideal for intricate designs and small-scale projects. Earthenware clay requires higher firing temperatures, providing durability and a natural, textured finish suited for traditional tile techniques such as hand-building and slip decoration. While polymer clay cures quickly without a kiln, earthenware demands careful kiln firing to achieve strength and water resistance, impacting tile production time and final usability.
Firing and Curing Processes Explained
Polymer clay requires curing by baking at a low temperature, typically between 265degF and 275degF (130degC to 135degC), for about 15-30 minutes depending on thickness, without the need for traditional kiln firing. Earthenware clay demands firing in a kiln at high temperatures around 1,800degF (982degC) to achieve proper hardness and durability, undergoing a chemical transformation called vitrification. The curing process of polymer clay solidifies through heat-activated polymerization, whereas earthenware clay undergoes physical and chemical changes during firing that strengthen the tile structurally.
Durability and Longevity of Tiles
Polymer clay offers excellent durability for decorative tiles, resisting cracking and moisture over time due to its synthetic composition and flexibility. Earthenware clay, while traditional and aesthetically pleasing, is more porous and prone to chipping or deterioration if not properly glazed and fired at high temperatures. For long-lasting tile projects, polymer clay provides superior longevity in moisture-rich environments, whereas earthenware requires careful sealing to maintain its durability.
Design Flexibility and Color Options
Polymer clay offers exceptional design flexibility with its ability to be molded into intricate shapes and blended with various pigments for a wide spectrum of vibrant colors, making it ideal for detailed and colorful tile designs. Earthenware clay provides a more traditional pottery feel but has limited color options, primarily relying on natural earthy tones and glazes applied after firing to achieve color variations. The choice between polymer and earthenware clay impacts the final aesthetic, with polymer clay excelling in versatility and brightness, while earthenware clay emphasizes rustic, organic finishes.
Safety and Toxicity Considerations
Polymer clay is a non-toxic synthetic material that hardens at low temperatures, making it safe for indoor use and handling without the need for a kiln, while earthenware clay requires firing at high temperatures, producing potentially harmful fumes if not properly ventilated. Earthenware clay can contain natural minerals and additives that release dust and toxins during sanding or firing, necessitating the use of respiratory protection and proper kiln safety measures. Polymer clay offers greater safety for hobbyists and indoor crafting due to its stable chemical composition and lower risk of toxic exposure compared to the traditional handling hazards of earthenware clay.
Cost and Accessibility Analysis
Polymer clay is generally more affordable upfront, with prices ranging from $10 to $20 per pound, making it accessible for hobbyists and small projects, while earthenware clay costs about $0.50 to $2 per pound but often requires additional expenses such as kiln firing and glazing materials. Polymer clay's availability in craft stores and online platforms offers greater convenience compared to earthenware clay, which is typically sourced from specialized ceramic suppliers. The need for a kiln and longer curing time increases the overall cost and limits earthenware clay's accessibility for beginners or casual tile makers.
Best Use Cases for Each Clay Type
Polymer clay excels for intricate, lightweight tile designs requiring detailed textures and vibrant colors, ideal for miniature or decorative tile projects due to its flexibility and low-temperature curing. Earthenware clay is best suited for functional, durable tiles exposed to weather or wear, as it withstands high firing temperatures and provides a porous, traditional ceramic finish. Selecting between polymer and earthenware clay depends on whether the tile's purpose emphasizes artistic detail and indoor use or structural strength and outdoor durability.
Infographic: Polymer clay vs Earthenware clay for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com