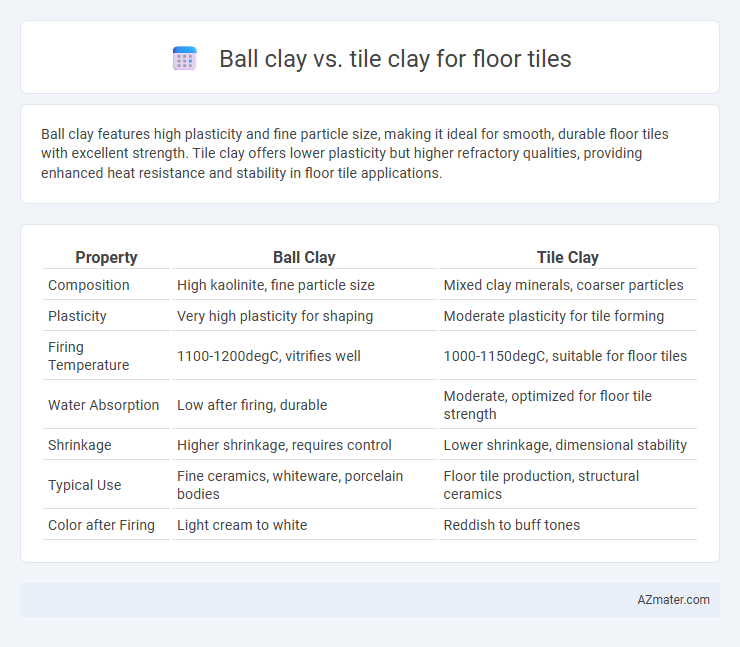
Ball clay features high plasticity and fine particle size, making it ideal for smooth, durable floor tiles with excellent strength. Tile clay offers lower plasticity but higher refractory qualities, providing enhanced heat resistance and stability in floor tile applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ball Clay | Tile Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High kaolinite, fine particle size | Mixed clay minerals, coarser particles |
| Plasticity | Very high plasticity for shaping | Moderate plasticity for tile forming |
| Firing Temperature | 1100-1200degC, vitrifies well | 1000-1150degC, suitable for floor tiles |
| Water Absorption | Low after firing, durable | Moderate, optimized for floor tile strength |
| Shrinkage | Higher shrinkage, requires control | Lower shrinkage, dimensional stability |
| Typical Use | Fine ceramics, whiteware, porcelain bodies | Floor tile production, structural ceramics |
| Color after Firing | Light cream to white | Reddish to buff tones |
Introduction to Ball Clay and Tile Clay
Ball clay is a fine-grained, highly plastic sedimentary clay known for its excellent binding properties and white firing characteristics, making it ideal for enhancing strength and workability in ceramic floor tiles. Tile clay, specifically formulated for floor tile production, contains balanced proportions of kaolin, ball clay, and other minerals to achieve optimal durability, color, and texture. Understanding the distinct composition and firing behavior of ball clay versus tile clay is essential for selecting materials that ensure long-lasting, aesthetically pleasing floor tiles.
Key Properties of Ball Clay
Ball clay features fine particle size, high plasticity, and excellent binding properties, making it ideal for producing smooth, durable floor tiles with superior shape retention. Its high kaolin content enhances whiteness and strength while minimizing shrinkage during firing, crucial for tile stability and lifespan. Compared to tile clay, ball clay's superior workability and firing characteristics result in higher quality floor tiles with improved mechanical strength and surface finish.
Key Properties of Tile Clay
Tile clay used for floor tiles exhibits high plasticity and excellent workability, ensuring precise shaping and detailed designs. Its low shrinkage and good firing properties provide durability and resistance to cracking under pressure. Unlike ball clay, tile clay often contains higher alumina content, enhancing hardness and wear resistance critical for floor tile applications.
Differences in Mineral Composition
Ball clay contains high amounts of kaolinite, mica, and quartz, resulting in excellent plasticity and strength, making it suitable for smooth, durable ceramic floor tiles. Tile clay typically has lower plasticity with higher proportions of feldspar and silica, contributing to improved vitrification and hardness in fired floor tiles. These differences in mineral composition directly influence the workability, firing temperature, and final durability of floor tiles made from each clay type.
Plasticity and Workability Compared
Ball clay exhibits high plasticity, making it highly moldable and ideal for producing thin, intricate floor tiles with fine detail and minimal cracking during drying. In contrast, tile clay typically has lower plasticity but offers better workability for larger, thicker floor tiles, ensuring structural integrity and reducing warping risks. The superior plasticity of ball clay enhances shape retention and surface smoothness, while tile clay's firmer consistency improves handling during pressing and shaping processes.
Impact on Tile Strength and Durability
Ball clay enhances tile strength due to its high plasticity and fine particle size, resulting in denser, more durable floor tiles that resist cracking under stress. Tile clay, often less plastic and coarser, may produce tiles with lower mechanical strength and reduced impact resistance, making them more prone to chipping and wear over time. Therefore, selecting ball clay in the ceramic formula significantly improves floor tile robustness and longevity, crucial for high-traffic areas.
Firing Temperatures and Shrinkage Rates
Ball clay typically fires at higher temperatures ranging from 1100degC to 1250degC and exhibits higher shrinkage rates around 12-15%, making it suitable for dense, durable floor tiles. Tile clay usually fires at lower temperatures between 950degC and 1150degC with lower shrinkage rates of about 5-9%, resulting in lighter, more porous tiles ideal for traditional floor coverings. Selecting the right clay depends on balancing firing temperature capabilities with desired tile durability and dimensional stability during the firing process.
Surface Finish and Color Outcomes
Ball clay produces a smooth, plastic surface ideal for achieving a fine, polished finish on floor tiles, enhancing gloss and uniformity in color. Tile clay, with its coarser texture, results in a more rustic or matte surface, offering varied color shades due to its higher impurity content. The choice between ball clay and tile clay significantly impacts the final tile's surface quality and color consistency.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Ball clay, known for its plasticity and smooth texture, typically costs more than tile clay due to its higher quality and strength, which enhances the durability of floor tiles. Tile clay, often sourced locally, tends to be more readily available and less expensive, making it a cost-effective option for large-scale flooring projects. Availability of ball clay can be limited and region-specific, whereas tile clay is generally abundant, influencing overall project budget and procurement timelines.
Choosing the Right Clay for Floor Tiles
Ball clay offers superior plasticity and strength, making it ideal for durable and finely detailed floor tiles, while tile clay provides more natural texture and color variation for aesthetic appeal. Choosing the right clay depends on the desired balance between strength, workability, and surface finish, with ball clay preferred for high-impact resistance and tile clay favored for decorative flooring. Understanding the specific properties of each clay type ensures optimal performance and longevity of floor tiles in various environments.
Infographic: Ball clay vs Tile clay for Floor tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com