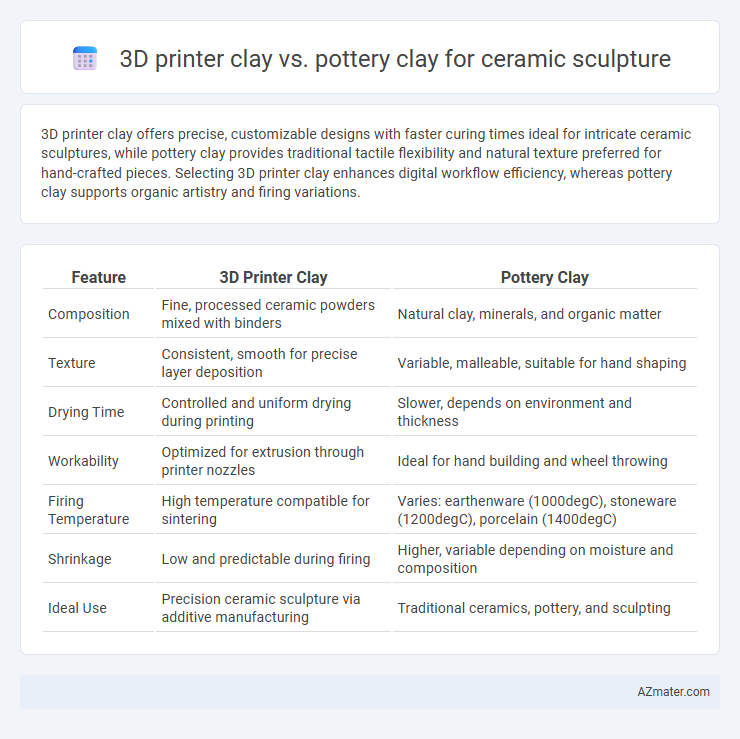
3D printer clay offers precise, customizable designs with faster curing times ideal for intricate ceramic sculptures, while pottery clay provides traditional tactile flexibility and natural texture preferred for hand-crafted pieces. Selecting 3D printer clay enhances digital workflow efficiency, whereas pottery clay supports organic artistry and firing variations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 3D Printer Clay | Pottery Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fine, processed ceramic powders mixed with binders | Natural clay, minerals, and organic matter |
| Texture | Consistent, smooth for precise layer deposition | Variable, malleable, suitable for hand shaping |
| Drying Time | Controlled and uniform drying during printing | Slower, depends on environment and thickness |
| Workability | Optimized for extrusion through printer nozzles | Ideal for hand building and wheel throwing |
| Firing Temperature | High temperature compatible for sintering | Varies: earthenware (1000degC), stoneware (1200degC), porcelain (1400degC) |
| Shrinkage | Low and predictable during firing | Higher, variable depending on moisture and composition |
| Ideal Use | Precision ceramic sculpture via additive manufacturing | Traditional ceramics, pottery, and sculpting |
Introduction to 3D Printer Clay and Pottery Clay
3D printer clay is a specialized, printable material designed for precise layering in ceramic sculpture, allowing for intricate designs and rapid prototyping. Pottery clay, traditionally sourced from natural deposits, offers superior plasticity and workability suited for hand-building and wheel-throwing techniques. While 3D printer clay integrates digital fabrication advancements, pottery clay remains favored for its organic texture and traditional crafting versatility.
Key Material Properties Compared
3D printer clay, typically made from a blend of fine ceramic powders and binders, offers enhanced precision and consistency, ideal for complex ceramic sculptures with intricate details. Pottery clay, such as earthenware or stoneware, provides better plasticity and moisture retention, enabling greater flexibility for hand-building and wheel-throwing techniques. Key differences include drying shrinkage rates, firing temperature ranges, and tensile strength, with 3D printer clay optimized for controlled layer adhesion and pottery clay suited for traditional sculpting and glazing methods.
Preparation and Handling Differences
3D printer clay for ceramic sculpture requires precise moisture control and typically needs to be loaded into specific printer cartridges or extruders designed for additive manufacturing, enabling detailed layer-by-layer construction with minimal manual intervention. Pottery clay demands more hands-on preparation, involving wedging to remove air bubbles and achieve consistent texture before hand-building or wheel-throwing, which allows for larger, more traditional sculptural forms but with less precision. Handling 3D printer clay involves managing its rheological properties to maintain flow through the nozzle, while pottery clay handling emphasizes pliability and plasticity to shape and join pieces by hand.
Forming Techniques for Sculpture
3D printer clay offers precise, layer-by-layer shaping ideal for complex, detailed ceramic sculptures, using additive manufacturing techniques like extrusion or selective laser sintering. Pottery clay relies on traditional forming methods such as hand-building, coiling, slab construction, and wheel throwing to create organic shapes with tactile texture. The choice between 3D printer clay and pottery clay affects the control over surface detail, structural integrity, and the ability to experiment with intricate geometries in ceramic sculpture.
Design Flexibility and Complexity
3D printer clay offers superior design flexibility and complexity by enabling intricate, precise shapes through digital modeling and additive layering, which traditional pottery clay cannot easily achieve. Pottery clay, while versatile for hand-building and wheel-throwing, is limited by manual shaping techniques and drying constraints that affect fine detail and complex structures. The digital nature of 3D printer clay allows for rapid prototyping and replication of highly detailed ceramic sculptures with consistent quality.
Surface Texture and Finish
3D printer clay offers a more uniform surface texture with smoother finishes due to its layer-by-layer additive process, ideal for intricate and detailed ceramic sculptures requiring precision. Pottery clay, by contrast, delivers a more organic and tactile surface texture, with natural variations that add character and depth after hand-forming and firing. The finish of pottery clay often includes a range of glaze options enhancing texture, while 3D printed clay may require additional post-processing to achieve similar surface refinement.
Firing and Sintering Considerations
3D printer clay designed for ceramic sculpture typically contains binders that burn off cleanly during firing, allowing for precise sintering and stronger final pieces without excessive shrinkage. Pottery clay, made from natural minerals and organic matter, requires slower firing schedules to prevent cracking and maintain structural integrity due to higher organic content and moisture retention. Understanding the thermal properties and adjustments in kiln temperature ramps is crucial for both materials to achieve optimal densification and durability in the finished ceramic sculpture.
Strength and Durability of the Sculptures
3D printer clay designed for ceramic sculptures typically offers consistent density and uniform drying, resulting in fewer cracks and higher tensile strength compared to traditional pottery clay. Pottery clay, while versatile and often preferred for hand-building, can have variable moisture content that affects the sculpture's durability and makes it more prone to warping or cracking during firing. The engineered composition of 3D printer clay enhances structural integrity, making it a superior choice for sculptures requiring high strength and long-term durability.
Cost and Accessibility Analysis
3D printer clay for ceramic sculpture offers higher initial costs due to specialized equipment and materials but provides precise, repeatable designs suitable for intricate projects. Pottery clay remains more cost-effective and widely accessible, with lower entry barriers for artists relying on traditional hand-building or wheel-throwing techniques. Accessibility to pottery clay is enhanced by widespread availability in art stores and community studios, while 3D printer clay requires investment in technology and technical skills, impacting overall affordability.
Choosing the Best Clay for Ceramic Sculpture
Choosing the best clay for ceramic sculpture depends on the desired texture, durability, and ease of shaping. 3D printer clay offers precision and consistency ideal for detailed and repetitive designs, while pottery clay provides a natural, traditional medium with superior plasticity and workability for hand-crafted textures. Artists seeking a balance between fine detail and organic feel often opt for pottery clay, whereas those prioritizing accuracy and repeatability may prefer 3D printer clay.
Infographic: 3D printer clay vs Pottery clay for Ceramic Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com