Montmorillonite offers superior thermal shock resistance and higher adsorption capacity compared to Fire clay, making it ideal for advanced refractory linings. Fire clay provides excellent mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness, suitable for moderate temperature applications in refractory construction.
Table of Comparison
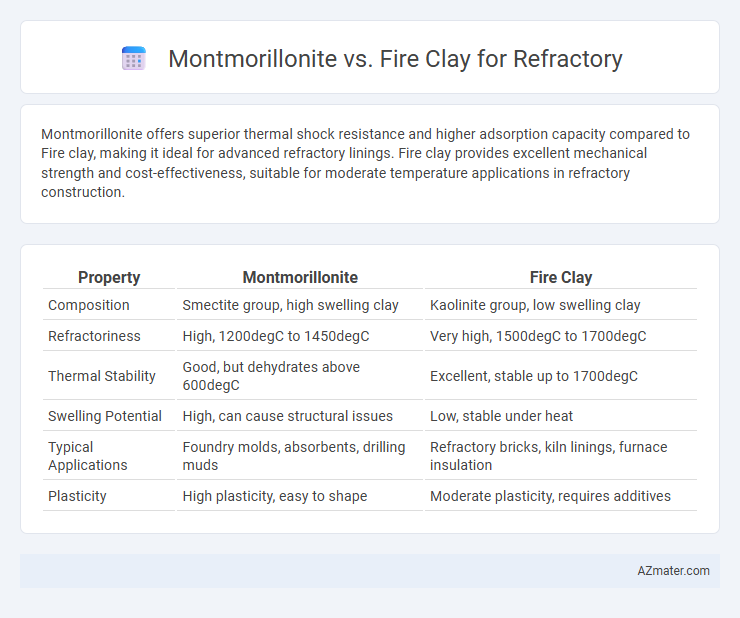
| Property | Montmorillonite | Fire Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Smectite group, high swelling clay | Kaolinite group, low swelling clay |
| Refractoriness | High, 1200degC to 1450degC | Very high, 1500degC to 1700degC |
| Thermal Stability | Good, but dehydrates above 600degC | Excellent, stable up to 1700degC |
| Swelling Potential | High, can cause structural issues | Low, stable under heat |
| Typical Applications | Foundry molds, absorbents, drilling muds | Refractory bricks, kiln linings, furnace insulation |
| Plasticity | High plasticity, easy to shape | Moderate plasticity, requires additives |
Introduction to Refractory Materials
Montmorillonite and fire clay are key refractory materials distinguished by their mineral composition and thermal properties. Montmorillonite, a type of smectite clay, offers high swelling capacity and thermal stability up to 1200degC, making it suitable for lightweight insulating refractories. Fire clay, composed primarily of kaolinite and other aluminosilicates, provides excellent heat resistance and structural strength at temperatures exceeding 1500degC, ideal for heavy-duty furnace linings and firebricks.
What is Montmorillonite Clay?
Montmorillonite clay is a smectite group mineral characterized by its layered structure and high cation exchange capacity, making it highly effective in refractory applications due to its excellent thermal stability and swelling properties. It contains predominantly montmorillonite minerals that enhance the plasticity and bonding strength of fire clay when used in refractory bricks or linings. Fire clay, although rich in alumina and silica, lacks the unique swelling and adsorption features of montmorillonite, which improves refractory performance by providing better thermal shock resistance and structural integrity at high temperatures.
What is Fire Clay?
Fire clay is a type of refractory clay known for its high alumina content, typically ranging between 25% and 40%, which provides excellent heat resistance and thermal stability. It is commonly used in the manufacture of firebricks, kiln linings, and crucibles due to its ability to withstand temperatures up to 1,500degC without deforming. Unlike montmorillonite, which has a swelling property and lower refractory range, fire clay offers superior durability and strength in high-temperature industrial applications.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Montmorillonite primarily consists of hydrous aluminum silicates with a high content of silica (SiO2) and alumina (Al2O3), typically around 60-65% SiO2 and 15-20% Al2O3, offering excellent swelling properties and thermal stability. Fire clay features a higher alumina content, usually 30-40% Al2O3, combined with approximately 45-55% silica, contributing to superior heat resistance and structural strength in refractory applications. The distinct chemical composition differences influence their thermal behavior, with montmorillonite being more suitable for insulation due to its low thermal conductivity, while fire clay is preferred for linings requiring higher mechanical strength and heat endurance.
Thermal Properties and Heat Resistance
Montmorillonite exhibits excellent thermal stability with a melting point above 1500degC, making it highly resistant to thermal shock and suitable for high-temperature refractory applications. Fire clay typically has a slightly lower refractoriness, around 1300degC to 1500degC, but offers good heat resistance and thermal insulation due to its alumina and silica content. Both materials provide durable heat resistance, but montmorillonite's superior thermal conductivity and expansion properties make it preferable in environments requiring rapid temperature changes.
Workability and Molding Characteristics
Montmorillonite clay offers superior plasticity and workability compared to fire clay, making it easier to mold into complex shapes for refractory applications. Fire clay, while less plastic, provides better dimensional stability and resistance to deformation at high temperatures during firing. The enhanced swelling properties of montmorillonite improve green strength but may require careful water content control to prevent cracking in molded refractory components.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Montmorillonite clay offers high plasticity and excellent thermal shock resistance, making it suitable for refractory applications requiring flexibility and resilience. Fire clay, rich in alumina and kaolinite, provides superior mechanical strength and long-term durability under high-temperature conditions. The choice between Montmorillonite and Fire clay depends on the specific refractory requirements, with Fire clay favored for load-bearing structures and Montmorillonite preferred for insulation linings.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Montmorillonite offers a cost-effective option for refractory applications due to its abundant natural deposits and lower extraction expenses, while fire clay typically incurs higher costs because of more limited availability and extensive processing requirements. Availability of Montmorillonite is widespread, especially in regions like the United States and India, ensuring steady supply chains compared to fire clay, which is often region-specific, limiting consistent procurement. Fire clay's superior thermal stability may justify its higher price in specialized refractories, but for general use, Montmorillonite's affordability and accessibility make it preferable.
Applications in Industrial Refractories
Montmorillonite and fire clay both serve critical roles in industrial refractory applications with distinct properties. Montmorillonite is prized for its superior swelling capacity and excellent binding properties, making it ideal for use in castables, ceramic filters, and as a binder in refractories that require high thermal shock resistance. Fire clay, rich in alumina and silica, provides excellent heat resistance and mechanical strength, commonly utilized in brick linings, kiln furniture, and furnace walls exposed to extreme temperatures.
Choosing the Right Clay: Montmorillonite vs Fire Clay
Montmorillonite offers superior plasticity and higher thermal stability, making it ideal for applications requiring excellent refractory bonding and resistance to thermal shock. Fire clay is distinguished by its high alumina content and durability, providing enhanced strength and resistance to chemical attack at elevated temperatures. Selecting between Montmorillonite and Fire clay depends on balancing the need for plasticity and bonding versus mechanical strength and chemical resistance in refractory formulations.
Infographic: Montmorillonite vs Fire clay for Refractory
 azmater.com
azmater.com