Fire clay offers higher heat resistance and durability compared to red clay, making it ideal for refractory bricks. Red clay is more abundant and cost-effective but is less suitable for high-temperature applications due to its lower thermal stability.
Table of Comparison
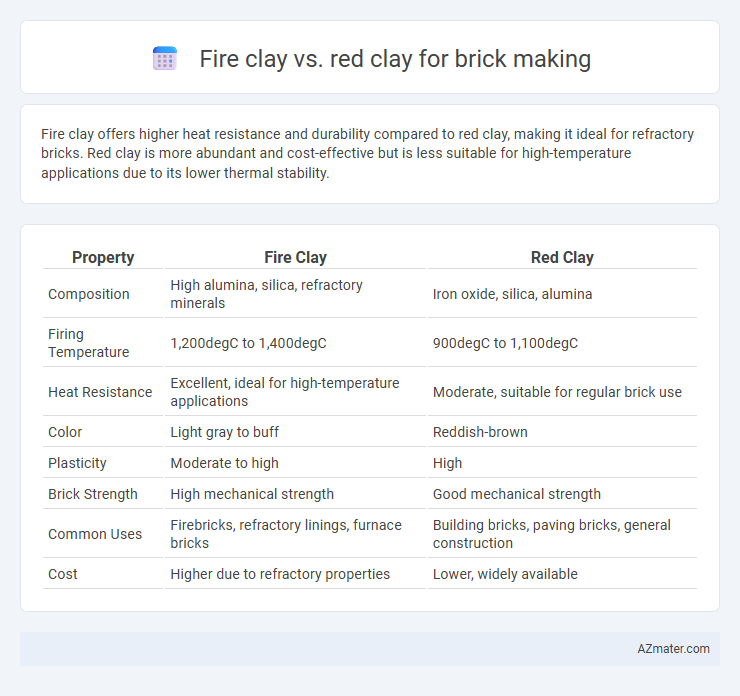
| Property | Fire Clay | Red Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High alumina, silica, refractory minerals | Iron oxide, silica, alumina |
| Firing Temperature | 1,200degC to 1,400degC | 900degC to 1,100degC |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent, ideal for high-temperature applications | Moderate, suitable for regular brick use |
| Color | Light gray to buff | Reddish-brown |
| Plasticity | Moderate to high | High |
| Brick Strength | High mechanical strength | Good mechanical strength |
| Common Uses | Firebricks, refractory linings, furnace bricks | Building bricks, paving bricks, general construction |
| Cost | Higher due to refractory properties | Lower, widely available |
Introduction to Fire Clay and Red Clay
Fire clay is a heat-resistant type of clay primarily composed of kaolinite and other refractory minerals, commonly used in the production of firebricks designed to withstand high temperatures above 1,200degC. Red clay, rich in iron oxide, is widely used in traditional brick making due to its natural reddish color and good plasticity, but it has lower refractory properties compared to fire clay. The distinct mineral compositions of fire clay and red clay determine their specific applications in construction and industrial settings.
Composition Differences Between Fire Clay and Red Clay
Fire clay contains a higher percentage of alumina (Al2O3) typically ranging from 25% to 40%, and has low iron oxide content, which makes it more refractory and suitable for high-temperature applications. Red clay, on the other hand, has a higher iron oxide content (around 5% to 7%), giving it its characteristic red color but lower refractory properties. The silica (SiO2) content in fire clay is usually balanced with high alumina, whereas red clay contains more variable silica and iron content, affecting its plasticity and firing behavior.
Physical Properties Affecting Brick Quality
Fire clay exhibits high refractoriness and excellent plasticity, making it ideal for bricks that withstand intense heat and thermal stress, while red clay generally offers lower heat resistance but good durability due to its iron oxide content. The particle size distribution and moisture retention in fire clay contribute to superior shaping and firing consistency, whereas red clay's coarser texture and higher shrinkage can affect brick uniformity and strength. Understanding these physical properties is crucial for selecting the appropriate clay type to achieve optimal brick quality for specific construction requirements.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Fire clay exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to red clay, withstanding temperatures up to 1,600degC, making it ideal for refractory brick production. Red clay typically endures temperatures only up to 1,000degC, limiting its use to standard construction bricks. The higher alumina content in fire clay enhances its thermal stability and durability under extreme heat conditions.
Shrinkage and Firing Temperature Requirements
Fire clay exhibits lower shrinkage rates compared to red clay due to its higher alumina content, which enhances thermal stability during the firing process. Its required firing temperature typically ranges between 1200degC and 1400degC, enabling the production of durable, refractory bricks. Red clay, conversely, has higher shrinkage, often leading to cracking, with a firing temperature requirement of around 900degC to 1100degC, making it suitable for standard bricks but less resistant to thermal stress.
Workability and Molding Characteristics
Fire clay offers superior workability compared to red clay due to its finer particle size and plasticity, which facilitates easier molding and shaping of bricks. Red clay, although coarser, provides adequate molding characteristics but can be less pliable, requiring more water to achieve the desired consistency. The enhanced plasticity of fire clay results in bricks with a smoother surface and fewer imperfections during the forming process.
Color and Aesthetic Outcomes in Finished Bricks
Fire clay bricks typically exhibit a range of warm tones from light buff to deep reddish-brown, offering a natural, rustic aesthetic ideal for decorative and heritage-style masonry projects. Red clay bricks, rich in iron oxide, consistently produce vibrant red to reddish-orange hues, providing a classic, bold appearance favored in traditional and contemporary architecture. The color variation in fire clay bricks results from their unique mineral content and firing process, creating diverse textures and finishes that enhance visual interest in finished brickwork.
Durability and Longevity in Structures
Fire clay bricks exhibit superior durability and longevity compared to red clay bricks due to their high alumina content and ability to withstand extreme temperatures without cracking or warping. Red clay bricks, while commonly used, have lower thermal resistance and tend to absorb more moisture, which can lead to faster degradation and structural weaknesses over time. Construction projects requiring enhanced structural integrity and fire resistance typically favor fire clay for its robust performance in harsh environmental conditions.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Fire clay, known for its high heat resistance, generally incurs higher costs due to limited sources and complex extraction processes. Red clay is more abundant and widely available, resulting in lower raw material expenses and easier procurement for mass brick production. Cost-efficiency in brick making often favors red clay, while fire clay's premium price reflects its specialized applications and scarcity.
Best Applications for Fire Clay vs. Red Clay Bricks
Fire clay bricks excel in high-temperature applications due to their exceptional heat resistance and durability, making them ideal for furnaces, kilns, and fireplaces. Red clay bricks, prized for their structural strength and aesthetic appeal, are best suited for general construction, including residential buildings, walls, and pavements. Selecting fire clay bricks enhances performance in thermal environments, while red clay bricks provide cost-effective, reliable solutions for load-bearing structures.
Infographic: Fire clay vs Red clay for Brick making
 azmater.com
azmater.com