China clay offers higher purity and finer texture, ideal for producing smooth, white bricks. Fire clay provides greater heat resistance and durability, making it suitable for refractory bricks exposed to high temperatures.
Table of Comparison
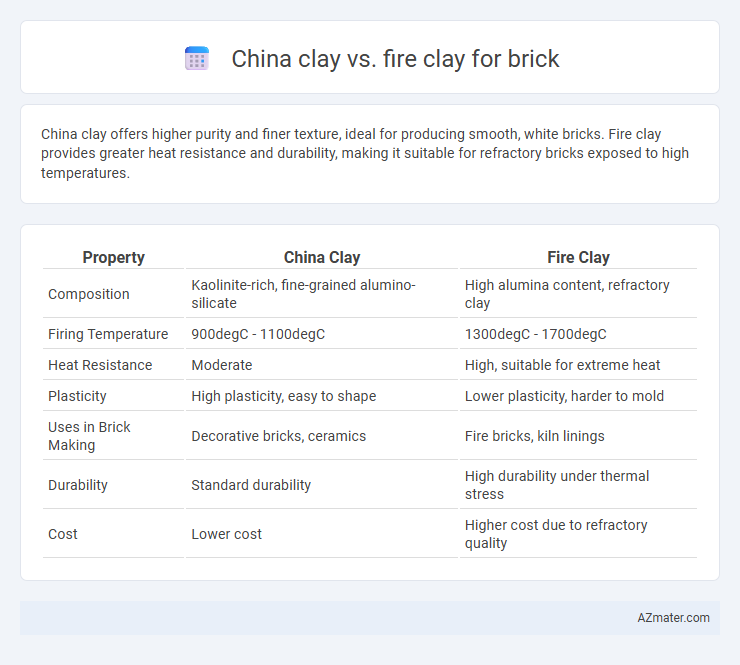
| Property | China Clay | Fire Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Kaolinite-rich, fine-grained alumino-silicate | High alumina content, refractory clay |
| Firing Temperature | 900degC - 1100degC | 1300degC - 1700degC |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate | High, suitable for extreme heat |
| Plasticity | High plasticity, easy to shape | Lower plasticity, harder to mold |
| Uses in Brick Making | Decorative bricks, ceramics | Fire bricks, kiln linings |
| Durability | Standard durability | High durability under thermal stress |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to refractory quality |
Introduction to China Clay and Fire Clay
China clay, also known as kaolin, is a fine white clay primarily composed of the mineral kaolinite, valued for its plasticity, whiteness, and resistance to high temperatures, making it ideal for ceramic and brick manufacturing. Fire clay, containing a higher concentration of alumina and silica, is heat-resistant and capable of withstanding temperatures above 1500degC, making it essential for refractory bricks used in high-temperature applications such as furnaces and kilns. The distinct mineral compositions of China clay and Fire clay influence their thermal properties and specific roles in brick production, with China clay providing smoothness and fire clay offering durability under extreme heat.
Understanding the Composition of China Clay
China clay, also known as kaolin, primarily consists of the mineral kaolinite, which imparts high plasticity and whiteness to bricks, making it ideal for fine ceramic and refractory applications. Fire clay contains a higher proportion of alumina and silica, providing enhanced heat resistance and durability in bricks used for high-temperature environments. Understanding that China clay's pure composition offers superior whiteness and plasticity helps in selecting the right clay type for aesthetic and structural requirements in brick manufacturing.
Chemical and Physical Properties of Fire Clay
Fire clay contains a high percentage of alumina (Al2O3) typically ranging from 25% to 40%, along with silica (SiO2) and minimal iron oxides, which contributes to its superior heat resistance compared to China clay. Its physical properties include high plasticity, refractory temperature above 1500degC, and excellent thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for firebrick manufacturing. In contrast, China clay (kaolin) has lower alumina content and higher amounts of silica and water, resulting in lower refractoriness and less suitability for high-temperature applications.
Manufacturing Process: China Clay Bricks
China clay bricks utilize kaolin, a fine white clay composed primarily of the mineral kaolinite, which undergoes a refining process including washing, blending, and sieving to remove impurities and ensure uniform consistency. The manufacturing process involves molding the refined clay into brick shapes, followed by drying to reduce moisture content and high-temperature firing (typically between 1000degC and 1200degC) to achieve vitrification, resulting in strong, white, and dense bricks. This contrasts with fire clay bricks, which use refractory clays rich in alumina and silica, processed to withstand higher temperatures but with different thermal and mechanical properties suited for industrial applications.
Manufacturing Process: Fire Clay Bricks
Fire clay bricks are manufactured by mining high-quality fire clay, followed by crushing, grinding, and mixing with water to create a plastic mass. This mass is then molded into bricks using extrusion or press molding, dried slowly to prevent cracks, and fired at high temperatures between 1200degC to 1400degC, which enhances their refractory properties. The firing process vitrifies the clay particles, resulting in dense, strong bricks capable of withstanding extreme heat, contrasting with China clay bricks that undergo a lower firing temperature and have different thermal resistance.
Comparative Strength and Durability
China clay bricks exhibit higher plasticity but lower compressive strength compared to fire clay bricks, making them less durable under heavy structural loads. Fire clay bricks possess superior thermal stability and withstand higher temperatures due to their refractory properties, resulting in enhanced strength and longevity in industrial applications. The denser microstructure of fire clay contributes to greater resistance against wear, erosion, and high-pressure environments when compared to china clay-based bricks.
Thermal Resistance and Performance
China clay offers moderate thermal resistance suitable for standard brick applications, providing good insulation properties due to its fine particle size and purity. Fire clay, characterized by its high alumina content and refractory nature, exhibits superior thermal resistance and can withstand higher temperatures, making it ideal for bricks used in furnaces and high-heat environments. The performance of fire clay bricks surpasses China clay bricks in durability and thermal stability under extreme heat conditions.
Applications and Suitability in Construction
China clay, also known as kaolin, is prized for its fine particle size and high refractory properties, making it suitable for producing smooth, white ceramics and bricks that require a high degree of purity and resistance to heat. Fire clay contains a higher alumina content and can withstand extreme temperatures, making it ideal for firebricks used in furnaces, kilns, and other high-temperature construction applications. In construction, fire clay bricks are preferred for structural components exposed to intense heat, while china clay bricks are better suited for aesthetic finishes and moderate temperature environments.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
China clay typically costs less than fire clay due to its abundant availability and lower processing requirements, making it a budget-friendly option for brick manufacturing. Fire clay, characterized by higher refractory properties and durability, incurs greater expenses in mining and refining, leading to increased brick production costs. Choosing between China clay and fire clay for bricks involves balancing initial material costs against the bricks' intended thermal resistance and longevity, impacting long-term economic efficiency.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Clay for Brick Making
China clay, known for its high purity and fine particle size, produces bricks with a smooth surface and good strength but may require blending to enhance durability. Fire clay offers superior heat resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for refractory bricks and applications demanding thermal stability. Selecting the right clay depends on the intended use: China clay suits decorative and low-load bricks, while fire clay is preferable for structural and high-temperature environments.
Infographic: China clay vs Fire clay for Brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com