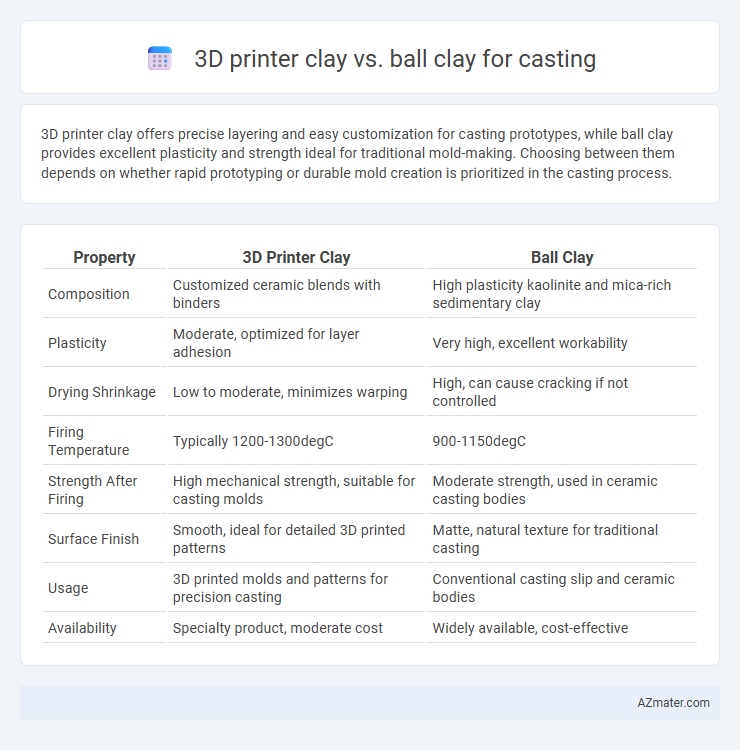
3D printer clay offers precise layering and easy customization for casting prototypes, while ball clay provides excellent plasticity and strength ideal for traditional mold-making. Choosing between them depends on whether rapid prototyping or durable mold creation is prioritized in the casting process.
Table of Comparison
| Property | 3D Printer Clay | Ball Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Customized ceramic blends with binders | High plasticity kaolinite and mica-rich sedimentary clay |
| Plasticity | Moderate, optimized for layer adhesion | Very high, excellent workability |
| Drying Shrinkage | Low to moderate, minimizes warping | High, can cause cracking if not controlled |
| Firing Temperature | Typically 1200-1300degC | 900-1150degC |
| Strength After Firing | High mechanical strength, suitable for casting molds | Moderate strength, used in ceramic casting bodies |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, ideal for detailed 3D printed patterns | Matte, natural texture for traditional casting |
| Usage | 3D printed molds and patterns for precision casting | Conventional casting slip and ceramic bodies |
| Availability | Specialty product, moderate cost | Widely available, cost-effective |
Understanding 3D Printer Clay: Composition and Uses
3D printer clay, often composed of fine ceramic particles combined with binders, is formulated for precision in additive manufacturing, enabling detailed and complex designs in casting molds. Unlike ball clay, which is a natural, highly plastic sedimentary clay prized for its workability and strength in traditional slip casting, 3D printer clay supports rapid prototyping with minimal shrinkage and consistent layer adhesion. The controlled composition of 3D printer clay allows for customization in particle size and binder types, enhancing its suitability for intricate mold making and reducing post-processing compared to conventional ball clay.
What Is Ball Clay? Properties and Applications
Ball clay is a highly plastic fine-grained sedimentary clay composed primarily of kaolinite, mica, and quartz, known for its exceptional plasticity, strength, and drying properties. It enhances the workability and mechanical strength of ceramic mixtures, making it ideal for casting applications, especially in pottery, sanitaryware, and porcelain production. Compared to 3D printer clay, ball clay offers superior green strength and shrinkage properties, which are crucial for traditional slip casting processes.
Key Differences Between 3D Printer Clay and Ball Clay
3D printer clay is a specially formulated, fast-drying material designed for additive manufacturing processes, offering precise layering and minimal shrinkage, whereas ball clay is a highly plastic, fine-grained natural clay commonly used for traditional casting due to its excellent moldability and strength. The drying and firing properties differ significantly; 3D printer clay is optimized for digital fabrication with controlled curing, while ball clay undergoes conventional kiln firing with variable shrinkage rates. Mechanical strength and surface finish also contrast, with 3D printer clay enabling intricate, smooth designs ideal for prototyping, and ball clay providing durability and flexibility suited for industrial casting molds.
Casting Techniques: How 3D Printer Clay Performs
3D printer clay offers superior precision and detail in casting due to its fine particle size and uniform consistency, enhancing mold accuracy in ceramic and metal casting techniques. Unlike traditional ball clay, which can vary in plasticity and moisture content, 3D printer clay maintains consistent flowability and reduces defects such as air bubbles and cracks during mold formation. This optimized performance leads to higher-quality castings with minimal post-processing in lost-wax and investment casting applications.
Casting With Ball Clay: Traditional Approaches
Casting with ball clay utilizes its fine particle size and high plasticity, making it ideal for producing detailed mold impressions in traditional ceramic casting. Unlike 3D printer clay, which is formulated for layer-by-layer additive manufacturing, ball clay offers superior strength and flexibility to withstand repeated use in slip casting processes. Its natural composition enhances slip adhesion and reduces warping, ensuring consistent quality in handcrafted pottery and sculpture production.
Surface Quality and Detail: A Comparative Analysis
3D printer clay offers superior surface quality and fine detail resolution compared to ball clay, making it ideal for intricate casting projects. The controlled composition of 3D printer clay ensures a smooth finish and sharp edges, whereas ball clay, with its higher plasticity and coarser particles, often results in rougher textures. For applications demanding precision and high-definition detail, 3D printer clay significantly outperforms ball clay in casting outcomes.
Drying and Firing: Shrinkage and Warping Concerns
3D printer clay typically exhibits more controlled drying and firing shrinkage compared to ball clay, reducing warping risks during casting. Ball clay, known for its high plasticity and fine particle size, tends to shrink significantly and can warp if not dried evenly or fired carefully. Managing moisture content and gradual firing schedules are critical for both materials to maintain dimensional stability in casting applications.
Strength and Durability: 3D Printer Clay vs Ball Clay
3D printer clay offers enhanced strength and durability due to its precise formulation and controlled manufacturing process, making it ideal for intricate, load-bearing castings. Ball clay, while known for its plasticity and smooth texture, typically exhibits lower mechanical strength and can be more prone to cracking under stress in casting applications. Choosing 3D printer clay over ball clay significantly improves the structural integrity and longevity of ceramic cast components.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
3D printer clay offers moderate cost efficiency but may involve higher initial investment due to specialized equipment, while ball clay provides a more budget-friendly option with widespread availability and consistent quality for casting applications. Ball clay's natural properties ensure reliable plasticity and strength at lower costs, making it a preferred choice for large-scale casting projects. The accessibility of ball clay in various regions supports steady supply chains, whereas 3D printer clay's dependence on manufacturing processes can limit availability and increase lead times.
Choosing the Right Clay for Casting: Practical Recommendations
When selecting clay for casting, 3D printer clay offers enhanced precision and reduced shrinkage, making it ideal for detailed molds and prototypes. Ball clay provides superior plasticity and strength, ensuring durability and smooth finishes in traditional casting processes. Practical recommendations emphasize using 3D printer clay for intricate designs and ball clay for robust, larger-scale casting projects requiring high workability.
Infographic: 3D printer clay vs Ball clay for Casting
 azmater.com
azmater.com