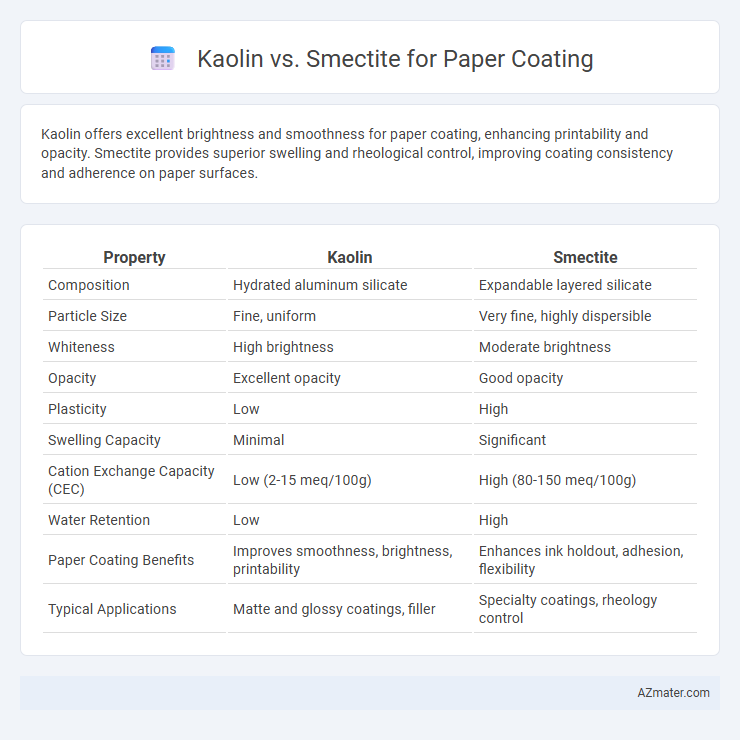
Kaolin offers excellent brightness and smoothness for paper coating, enhancing printability and opacity. Smectite provides superior swelling and rheological control, improving coating consistency and adherence on paper surfaces.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Kaolin | Smectite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Hydrated aluminum silicate | Expandable layered silicate |
| Particle Size | Fine, uniform | Very fine, highly dispersible |
| Whiteness | High brightness | Moderate brightness |
| Opacity | Excellent opacity | Good opacity |
| Plasticity | Low | High |
| Swelling Capacity | Minimal | Significant |
| Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) | Low (2-15 meq/100g) | High (80-150 meq/100g) |
| Water Retention | Low | High |
| Paper Coating Benefits | Improves smoothness, brightness, printability | Enhances ink holdout, adhesion, flexibility |
| Typical Applications | Matte and glossy coatings, filler | Specialty coatings, rheology control |
Introduction to Paper Coating Minerals
Kaolin and smectite are essential minerals used in paper coating to enhance surface properties and printability. Kaolin, a fine white clay, improves gloss, brightness, and smoothness due to its platelet structure and high purity. Smectite offers excellent swelling and binding properties, contributing to ink holdout and flexibility, making both minerals complementary in optimizing paper coating formulations.
What is Kaolin?
Kaolin is a fine, white clay mineral primarily composed of kaolinite, widely used in paper coating for its excellent opacity, brightness, and smoothness enhancement. Its plate-like particles improve printability and surface gloss, making it an ideal filler for high-quality paper production. Compared to smectite, kaolin provides better control over coating viscosity and film formation, resulting in superior paper surface properties.
What is Smectite?
Smectite is a group of clay minerals characterized by its high cation exchange capacity and swelling properties, making it highly effective in paper coating applications. Unlike kaolin, smectite offers superior rheological control and improved ink receptivity due to its unique layered structure and ability to retain moisture. These attributes enhance surface smoothness and print quality in coated paper products.
Physical Properties Comparison: Kaolin vs Smectite
Kaolin exhibits a platy particle shape with high brightness and low oil absorption, making it ideal for smooth paper coating surfaces, while smectite features a swelling, layered structure with high cation exchange capacity and greater oil absorption, enhancing coating flexibility and adhesion. Kaolin's lower plasticity and higher bulk density provide better dry opacity and gloss, whereas smectite's fine particle size and plasticity contribute to improved rheological properties and ink receptivity. The distinct differences in particle morphology and surface chemistry between kaolin and smectite critically influence their performance in paper coating formulations.
Impact on Paper Gloss and Smoothness
Kaolin enhances paper gloss and smoothness by providing a fine particle size that fills surface imperfections, resulting in a smoother and more reflective finish. Smectite, with its layered silicate structure and higher swelling capacity, improves smoothness but can reduce gloss due to its light-scattering properties. Optimizing the balance between kaolin and smectite in paper coating formulations significantly affects the final paper's surface quality, influencing printability and aesthetic appeal.
Influence on Printability and Ink Absorption
Kaolin enhances paper coating by providing a smooth surface that improves printability through its fine particle size and high brightness, promoting sharp ink transfer and vibrant colors. Smectite, with its swelling properties and higher cation exchange capacity, increases ink absorption, resulting in better ink holdout and reduced set-off in printing processes. The choice between kaolin and smectite influences the balance between gloss, opacity, and ink drying speed, crucial for high-quality paper printing applications.
Cost Considerations: Kaolin vs Smectite
Kaolin offers a lower-cost option for paper coating due to its abundant availability and relatively simple processing, making it economically favorable for large-scale production. Smectite, while providing superior rheological properties and improved printability, generally incurs higher costs because of more complex extraction and purification processes. Cost considerations often lead paper manufacturers to select kaolin when prioritizing budget constraints, whereas smectite is chosen for specialty papers where enhanced performance justifies the increased expense.
Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Kaolin offers a lower environmental impact due to its abundant natural deposits and minimal processing requirements, resulting in reduced energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to smectite. Smectite, while providing excellent rheological properties for paper coating, often requires extensive mining and chemical treatment, raising concerns about habitat disruption and water pollution. Sustainable paper production increasingly favors kaolin for its better recyclability and lower ecological footprint in coating applications.
Industry Applications and Preferences
Kaolin is widely preferred in the paper coating industry due to its fine particle size, brightness, and excellent opacity, enhancing printability and surface smoothness. Smectite, with its high swelling capacity and rheological properties, is favored in specialty coatings requiring improved viscosity and gel strength. The choice between kaolin and smectite depends on the desired paper quality, cost considerations, and specific functional requirements of the coating formulation.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Mineral for Paper Coating
Kaolin offers excellent brightness, smoothness, and opacity, making it ideal for high-quality paper coatings requiring a glossy finish. Smectite provides superior rheological properties and swelling capacity, enhancing suspension stability and printability in coated papers. Selecting kaolin or smectite depends on the desired paper properties, where kaolin suits optical enhancement and smectite excels in improving coating viscosity and gloss.
Infographic: Kaolin vs Smectite for Paper Coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com