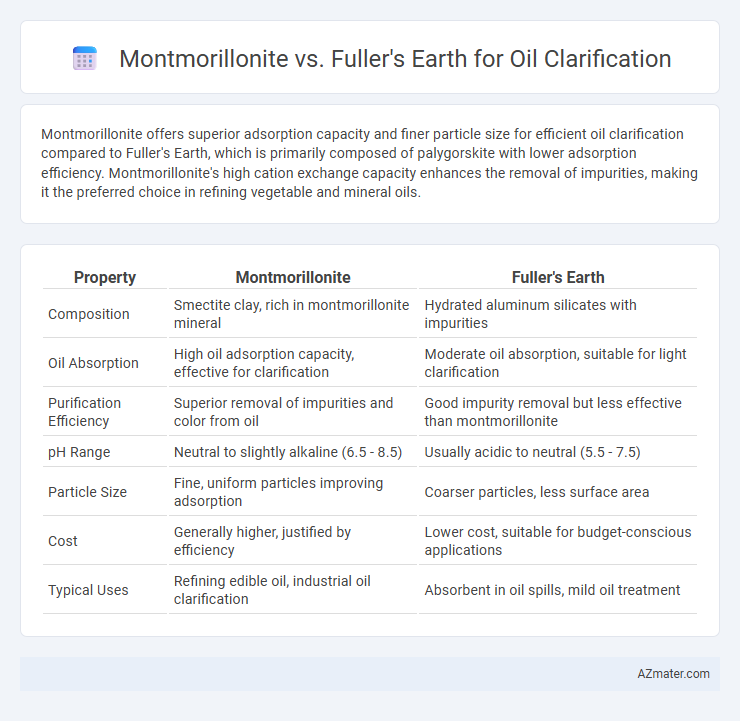
Montmorillonite offers superior adsorption capacity and finer particle size for efficient oil clarification compared to Fuller's Earth, which is primarily composed of palygorskite with lower adsorption efficiency. Montmorillonite's high cation exchange capacity enhances the removal of impurities, making it the preferred choice in refining vegetable and mineral oils.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Montmorillonite | Fuller's Earth |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Smectite clay, rich in montmorillonite mineral | Hydrated aluminum silicates with impurities |
| Oil Absorption | High oil adsorption capacity, effective for clarification | Moderate oil absorption, suitable for light clarification |
| Purification Efficiency | Superior removal of impurities and color from oil | Good impurity removal but less effective than montmorillonite |
| pH Range | Neutral to slightly alkaline (6.5 - 8.5) | Usually acidic to neutral (5.5 - 7.5) |
| Particle Size | Fine, uniform particles improving adsorption | Coarser particles, less surface area |
| Cost | Generally higher, justified by efficiency | Lower cost, suitable for budget-conscious applications |
| Typical Uses | Refining edible oil, industrial oil clarification | Absorbent in oil spills, mild oil treatment |
Introduction to Oil Clarification
Oil clarification involves the removal of impurities such as suspended solids, free fatty acids, and trace metals to enhance oil quality and stability. Montmorillonite and Fuller's Earth are both clay minerals widely used as adsorbents in this process due to their high surface area and cation exchange capacity. Montmorillonite offers superior adsorption efficiency and regenerability compared to Fuller's Earth, making it a preferred choice for effective oil purification.
What is Montmorillonite?
Montmorillonite is a type of smectite clay mineral characterized by its high cation exchange capacity and layered structure, making it highly effective for adsorbing impurities in oil clarification. This clay's unique properties allow it to remove contaminants such as phospholipids, free fatty acids, and color pigments from oils, thereby improving oil stability and purity. Compared to Fuller's Earth, Montmorillonite offers superior adsorption performance due to its larger surface area and enhanced swelling capacity.
What is Fuller’s Earth?
Fuller's Earth is a naturally occurring clay material composed mainly of hydrous aluminum silicates known for its exceptional adsorptive properties, making it highly effective in oil clarification processes. It works by attracting and trapping impurities, such as color bodies, gums, and oxidation products, thereby improving oil color and stability. Compared to montmorillonite, Fuller's Earth typically offers higher oil bleaching efficiency due to its dense microporous structure and greater surface area.
Composition Differences: Montmorillonite vs Fuller’s Earth
Montmorillonite primarily consists of hydrated aluminum silicates with a high cation exchange capacity, making it highly effective in adsorbing impurities during oil clarification. Fuller's Earth contains a mixture of clay minerals including montmorillonite, kaolinite, and other silicates, offering a broader mineral composition that affects its absorbency and oil refining performance. The higher purity of montmorillonite provides more consistent oil decolorization and impurity removal compared to the variable composition of Fuller's Earth.
Mechanism of Oil Clarification
Montmorillonite and Fuller's Earth both function as effective adsorbents in oil clarification by utilizing their high surface area and layered silicate structure to trap impurities and pigments. Montmorillonite's swelling capacity enhances its ability to encapsulate oil contaminants, improving the adsorption of polar molecules and oxidation products. Fuller's Earth works through ion exchange and absorption mechanisms, effectively removing free fatty acids, phospholipids, and oxidation residues to clarify and stabilize oils.
Efficiency Comparison in Oil Clarification
Montmorillonite exhibits higher adsorption capacity than Fuller's Earth, making it more efficient in removing impurities from edible oils. Its finer particle size and larger surface area enhance decolorization and deodorization processes, resulting in clearer, more stable oil products. Fuller's Earth, while effective, often requires higher dosage and longer retention time, reducing overall efficiency compared to Montmorillonite in oil clarification applications.
Adsorption Capacity and Surface Area Analysis
Montmorillonite exhibits a higher adsorption capacity compared to Fuller's Earth due to its larger specific surface area and unique layered structure, which enhances its ability to trap impurities during oil clarification. Surface area analysis reveals that Montmorillonite typically possesses a surface area ranging from 200 to 800 m2/g, significantly surpassing Fuller's Earth's average of 100 to 300 m2/g, enabling more efficient removal of polar contaminants and moisture. The superior adsorption properties and expansive surface area make Montmorillonite a preferred choice for refining and purifying edible and industrial oils.
Cost-effectiveness for Industrial Use
Montmorillonite provides excellent adsorption properties for oil clarification at a relatively low cost, making it a favorite in large-scale industrial applications. Fuller's Earth, while effective in adsorbing impurities, tends to be more expensive due to its intensive processing requirements and lower availability. Industrial users often prefer montmorillonite for its cost-effectiveness and consistent performance in maintaining oil quality over time.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Montmorillonite and Fuller's Earth are both clay minerals used for oil clarification, with Montmorillonite often preferred for its higher adsorption capacity and lower environmental footprint due to its natural abundance and minimal processing requirements. Fuller's Earth, while effective, may involve more intensive extraction and processing, resulting in increased energy consumption and potential habitat disruption. Both clays are generally safe when handled properly, but Montmorillonite's lower dust generation reduces respiratory risks for workers, enhancing overall safety in industrial applications.
Final Recommendations: Which is Better for Oil Clarification?
Montmorillonite offers superior adsorption capacity and finer particle size, making it highly effective in removing impurities and improving oil clarity. Fuller's Earth, while more cost-effective, has larger particles and lower adsorption efficiency, leading to less optimal oil purification. For critical applications requiring high-quality oil clarification, Montmorillonite is the preferred choice due to its enhanced performance and reliability.
Infographic: Montmorillonite vs Fuller’s Earth for Oil Clarification
 azmater.com
azmater.com