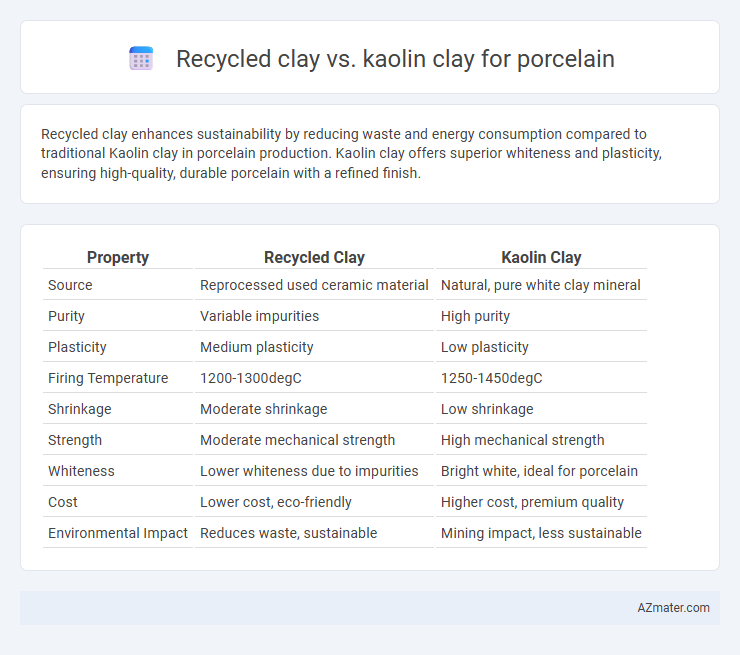
Recycled clay enhances sustainability by reducing waste and energy consumption compared to traditional Kaolin clay in porcelain production. Kaolin clay offers superior whiteness and plasticity, ensuring high-quality, durable porcelain with a refined finish.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Clay | Kaolin Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Reprocessed used ceramic material | Natural, pure white clay mineral |
| Purity | Variable impurities | High purity |
| Plasticity | Medium plasticity | Low plasticity |
| Firing Temperature | 1200-1300degC | 1250-1450degC |
| Shrinkage | Moderate shrinkage | Low shrinkage |
| Strength | Moderate mechanical strength | High mechanical strength |
| Whiteness | Lower whiteness due to impurities | Bright white, ideal for porcelain |
| Cost | Lower cost, eco-friendly | Higher cost, premium quality |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste, sustainable | Mining impact, less sustainable |
Introduction to Porcelain Clay Types
Porcelain typically utilizes two primary clay types: recycled clay and kaolin clay, each influencing the final product's quality and characteristics. Recycled clay, derived from previously fired or processed porcelain, offers cost efficiency and sustainability but can contain impurities affecting strength and translucency. Kaolin clay, known for its high purity and fine particle size, contributes to porcelain's whiteness, durability, and smooth texture, making it the preferred choice in high-quality porcelain manufacturing.
What is Recycled Clay?
Recycled clay consists of previously used or discarded clay materials that are reclaimed, cleaned, and processed for reuse in ceramics, offering an eco-friendly and cost-effective alternative to virgin clays. Kaolin clay, a primary ingredient in porcelain production, is a fine, white, and pure clay known for its high plasticity and firing temperature, resulting in strong, translucent porcelain bodies. Using recycled clay in porcelain manufacturing reduces waste and energy consumption while maintaining material quality when properly processed and blended with kaolin.
Defining Kaolin Clay for Porcelain
Kaolin clay, also known as china clay, is a primary material in porcelain production due to its high purity, fine particle size, and excellent plasticity, which contribute to the smooth texture and translucency of finished porcelain. Recycled clay, while eco-friendly, often contains impurities and inconsistencies that can affect the strength and whiteness critical to high-quality porcelain. The defining characteristic of kaolin clay is its minimal iron content and high aluminum silicate composition, which ensures durability and the iconic translucence of fine porcelain products.
Key Differences: Recycled Clay vs Kaolin Clay
Recycled clay contains a mixture of previously fired materials and impurities, resulting in variable plasticity and mineral composition, while kaolin clay is a pure, white, and highly refractory clay essential for the whiteness and translucency of porcelain. The plasticity of recycled clay is lower than kaolin, affecting the workability and structural integrity of porcelain pieces. Kaolin's high alumina and low iron content improve vitrification and reduce defects, whereas recycled clay may introduce inconsistencies that impact the strength and aesthetics of porcelain products.
Physical Properties Comparison
Recycled clay for porcelain typically exhibits higher porosity and reduced plasticity compared to Kaolin clay, which has a fine particle size and exceptional whiteness, contributing to smooth texture and translucency in finished products. Kaolin clay's low shrinkage rate and high firing temperature enhance durability and resistance to thermal shock, whereas recycled clay may contain impurities that affect vitrification and strength. The mineral composition of Kaolin ensures uniformity in porcelain's physical properties, while recycled clay's variability can lead to inconsistent mechanical performance.
Workability in Porcelain Production
Recycled clay often contains variable impurities and inconsistent particle sizes, which can reduce the workability and plasticity essential for fine porcelain production. Kaolin clay, characterized by its pure, fine-grained structure and high refractory properties, provides superior plasticity and moldability, crucial for achieving the delicate forms and smooth finishes of high-quality porcelain. The consistent mineral composition of kaolin enhances the ease of shaping and reduces defects during firing, making it the preferred choice for porcelain manufacturers focused on precision and durability.
Firing Temperatures and Outcomes
Recycled clay typically fires at slightly lower temperatures, around 1100-1250degC, resulting in a denser but less translucent porcelain compared to kaolin clay, which requires firing between 1250-1450degC for its characteristic whiteness and translucency. Kaolin clay's high purity and low iron content produce a smoother texture and higher vitrification level, while recycled clay often contains impurities that can affect firing consistency and surface finish. The choice between recycled clay and kaolin clay significantly impacts the porcelain's durability, translucency, and color after firing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Recycled clay reduces waste by repurposing leftover materials, lowering the demand for new kaolin clay extraction, which typically involves extensive mining with significant environmental disruption. Kaolin clay mining often leads to deforestation, soil erosion, and water pollution, whereas recycled clay contributes to circular economy principles by minimizing resource consumption and decreasing landfill deposits. Sustainable porcelain production increasingly favors recycled clay due to its lower carbon footprint and potential for conserving natural kaolin reserves.
Cost Analysis: Recycled vs Kaolin Clay
Recycled clay offers a significant cost advantage for porcelain production due to lower raw material expenses and reduced processing requirements, making it a budget-friendly alternative to premium kaolin clay. Kaolin clay, renowned for its purity and whiteness, incurs higher costs attributed to mining, refining, and transportation, impacting overall manufacturing budgets. Evaluating cost-efficiency, recycled clay supports sustainable practices while providing substantial savings, whereas kaolin clay guarantees superior quality that justifies its premium price in high-end porcelain applications.
Choosing the Right Clay for Porcelain Projects
Recycled clay offers an eco-friendly and cost-effective option for porcelain projects, retaining essential plasticity and mineral content suitable for shaping and firing. Kaolin clay, known for its high purity and whiteness, provides superior strength and translucency in finished porcelain, essential for fine, high-quality pieces. Selecting the ideal clay depends on project goals: recycled clay suits sustainable practices and experimental work, while kaolin is preferred for professional-grade porcelain requiring durability and aesthetic refinement.
Infographic: Recycled clay vs Kaolin clay for Porcelain
 azmater.com
azmater.com