Raku clay contains grog and fluxes that withstand rapid thermal shock during firing, making it ideal for raku firing techniques in sculpture. Earthenware clay is more porous and fires at lower temperatures, resulting in softer, more fragile sculptures suited for decorative rather than functional art.
Table of Comparison
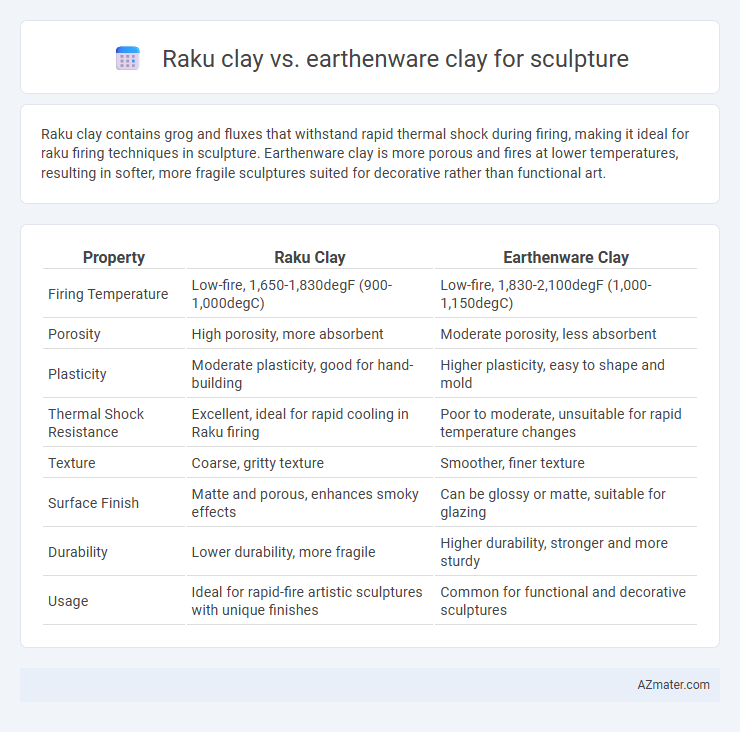
| Property | Raku Clay | Earthenware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Firing Temperature | Low-fire, 1,650-1,830degF (900-1,000degC) | Low-fire, 1,830-2,100degF (1,000-1,150degC) |
| Porosity | High porosity, more absorbent | Moderate porosity, less absorbent |
| Plasticity | Moderate plasticity, good for hand-building | Higher plasticity, easy to shape and mold |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent, ideal for rapid cooling in Raku firing | Poor to moderate, unsuitable for rapid temperature changes |
| Texture | Coarse, gritty texture | Smoother, finer texture |
| Surface Finish | Matte and porous, enhances smoky effects | Can be glossy or matte, suitable for glazing |
| Durability | Lower durability, more fragile | Higher durability, stronger and more sturdy |
| Usage | Ideal for rapid-fire artistic sculptures with unique finishes | Common for functional and decorative sculptures |
Introduction: Raku Clay and Earthenware Clay Overview
Raku clay is a porous, low-fire clay known for its thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for raku firing techniques that involve rapid cooling and smoke exposure. Earthenware clay, typically fired at lower temperatures between 1,000degC to 1,150degC, offers a more plastic and workable texture but remains more absorbent and less durable than stoneware or porcelain. Both clays provide unique finishes and tactile qualities, influencing the aesthetic and structural outcomes in sculpture creation.
Composition Differences: Raku vs Earthenware
Raku clay features a lower firing temperature and contains more grog and organic materials to withstand rapid thermal shock during the raku firing process, whereas earthenware clay is composed mainly of natural earthen materials with a higher porosity and typically fires at higher temperatures. The grog in raku clay enhances thermal resistance and reduces shrinkage, making it ideal for the thermal cycles in raku firing, while earthenware clay's finer composition allows for smoother surfaces but less durability under rapid temperature changes. These compositional differences influence their suitability for distinct sculptural techniques and firing methods, with raku clay favored for dynamic, crackled finishes and earthenware for detailed, stable forms.
Workability and Sculpting Techniques
Raku clay features high porosity and lower firing temperatures, making it ideal for hand-building and surface texturing but less suitable for fine detail compared to earthenware clay, which offers greater plasticity and smoother consistency for intricate sculpting and carving. Earthenware clay's balanced workability allows for diverse techniques such as wheel throwing, coiling, and slab building, whereas Raku clay's porous nature demands careful handling to prevent cracking during drying and firing. Sculptors often prefer earthenware for detailed work and fine finishes, while Raku clay is favored for expressive forms and unique surface effects achieved through rapid cooling and reduction firing.
Firing Temperature and Kiln Requirements
Raku clay typically fires at a lower temperature range of 1,650degF to 1,830degF (900degC to 1,000degC), requiring a specialized raku kiln capable of quick heating and rapid cooling cycles. Earthenware clay fires at a higher temperature range of 1,830degF to 2,100degF (1,000degC to 1,150degC), demanding a conventional electric, gas, or wood kiln with precise temperature control. The rapid thermal shock in raku firing necessitates a kiln designed for fast firing and reduction, whereas earthenware benefits from slow, controlled heating to avoid cracking.
Color and Surface Texture Variations
Raku clay offers vibrant color variations and unpredictable surface textures due to its rapid cooling and reduction firing process, creating unique metallic and crackled effects ideal for expressive sculpture. Earthenware clay provides a more uniform color palette, typically ranging from red to buff tones, with a matte or slightly textured surface suitable for traditional and detailed sculptural work. The porous nature of earthenware also allows for versatile surface treatments like glazing or painting, contrasting with the characteristic raw, organic finishes of raku-fired pieces.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Raku clay offers moderate durability with its porous structure, making it more prone to chipping compared to earthenware clay, which provides stronger resistance due to its higher firing temperature and vitrification process. Earthenware clay exhibits greater strength and structural integrity for sculptures, especially when fired at cones 06 to 04 (1828degF to 1940degF), enhancing durability against physical stress. However, raku's unique thermal shock resistance and aesthetic qualities make it suitable for decorative sculptures rather than functional or load-bearing pieces.
Glazing and Finishing Options
Raku clay offers unique glazing possibilities with its quick-firing process that produces crackled, metallic, and smoky surface effects, ideal for artistic sculptures emphasizing texture and unpredictability. Earthenware clay is compatible with a wide range of colorful glazes, providing smooth, glossy finishes but requires low to mid-range firing temperatures and is more porous, often necessitating a sealing glaze for durability. Scultors choose Raku for expressive, tactile finishes and rapid results, while earthenware supports vibrant, stable colors suited for detailed, polished pieces.
Artistic Applications in Sculpture
Raku clay, known for its thermal shock resistance and porous texture, enables artists to create sculptures that undergo rapid firing and cooling processes, producing unique crackles and color variations ideal for expressive, organic surfaces. Earthenware clay offers versatility with a softer texture and lower firing temperature, allowing detailed modeling and smoother finishes suited for traditional, intricate sculptural forms and functional art. Both clays provide distinct artistic applications: Raku clay excels in spontaneous, experimental effects, while earthenware supports precision and classic sculptural techniques.
Cost and Accessibility
Raku clay typically costs more than earthenware due to its specialized formulation that withstands thermal shock during rapid firing cycles, making it less accessible for beginner sculptors or those with a limited budget. Earthenware clay remains the most affordable and widely available option, often found in local art supply stores, ideal for artists prioritizing cost-efficiency without complex firing requirements. Accessibility to raku clay may be restricted by regional kiln services and safety regulations, whereas earthenware's compatibility with standard electric kilns enhances its practicality and ease of use.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Sculpture Project
Raku clay offers excellent thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for artists who want to achieve unique glaze effects through rapid firing and cooling processes, whereas earthenware clay is more porous and requires lower firing temperatures, suitable for traditional and decorative sculptures. The choice depends on the firing technique, desired durability, and texture; Raku clay can handle the intense thermal cycling of raku firing, while earthenware provides versatility and ease of use for beginners. Sculptors seeking vibrant surface finishes and a robust, crack-resistant body may prefer Raku clay, while those prioritizing affordability and simplicity might opt for earthenware.
Infographic: Raku clay vs Earthenware clay for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com