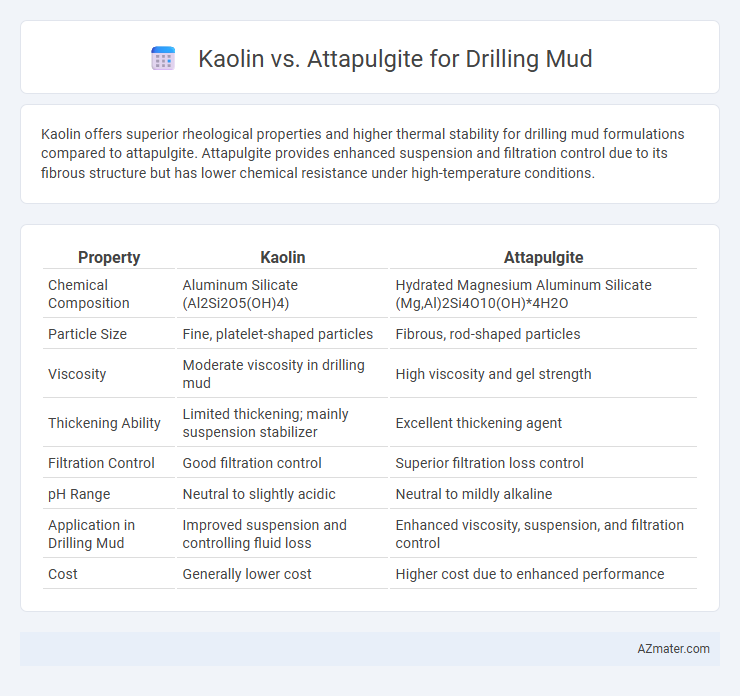
Kaolin offers superior rheological properties and higher thermal stability for drilling mud formulations compared to attapulgite. Attapulgite provides enhanced suspension and filtration control due to its fibrous structure but has lower chemical resistance under high-temperature conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Kaolin | Attapulgite |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Aluminum Silicate (Al2Si2O5(OH)4) | Hydrated Magnesium Aluminum Silicate (Mg,Al)2Si4O10(OH)*4H2O |
| Particle Size | Fine, platelet-shaped particles | Fibrous, rod-shaped particles |
| Viscosity | Moderate viscosity in drilling mud | High viscosity and gel strength |
| Thickening Ability | Limited thickening; mainly suspension stabilizer | Excellent thickening agent |
| Filtration Control | Good filtration control | Superior filtration loss control |
| pH Range | Neutral to slightly acidic | Neutral to mildly alkaline |
| Application in Drilling Mud | Improved suspension and controlling fluid loss | Enhanced viscosity, suspension, and filtration control |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to enhanced performance |
Introduction to Drilling Mud Minerals
Kaolin and attapulgite are critical clay minerals used in drilling mud formulations to optimize rheological properties and stability during drilling operations. Kaolin, a hydrated aluminum silicate, enhances viscosity and filter cake formation, improving borehole stability in water-based mud systems. Attapulgite, a magnesium aluminum phyllosilicate with a fibrous structure, provides excellent thixotropic behavior and suspension capacity, preventing sedimentation of cuttings and enhancing lubrication in both water- and oil-based drilling fluids.
Overview of Kaolin in Drilling Applications
Kaolin clay is widely used in drilling mud due to its excellent rheological properties, enhancing viscosity and suspension of cuttings in the drilling fluid. Its fine particle size and chemical inertness improve mud stability and reduce fluid loss, making it effective in water-based drilling fluids. Kaolin's low abrasiveness also helps protect drilling equipment, contributing to more efficient and cost-effective drilling operations.
Attapulgite: Properties and Uses in Drilling
Attapulgite, a clay mineral with high absorbency and thixotropic properties, enhances drilling mud by increasing viscosity and stabilizing boreholes during drilling operations. Its fibrous structure facilitates superior suspension of weighting materials and cuttings, optimizing mud performance under dynamic conditions. Widely used in oil and gas drilling, attapulgite improves fluid loss control and reduces formation damage, making it a preferred additive compared to kaolin in challenging subterranean environments.
Comparative Chemical Composition: Kaolin vs Attapulgite
Kaolin consists primarily of the mineral kaolinite, with the chemical formula Al2Si2O5(OH)4, featuring a low cation exchange capacity (CEC) and a layered silicate structure that provides excellent plasticity in drilling mud. Attapulgite, composed mainly of magnesium aluminum silicate with the formula (Mg,Al)2Si4O10(OH)*4H2O, has a higher CEC and a fibrous structure that enhances viscosity and thixotropic properties in drilling fluids. The key chemical differences, including aluminum content and structural morphology, influence their performance: kaolin offers better filtration control, while attapulgite delivers superior suspension stability and shear thinning behavior.
Rheological Behavior of Kaolin-Based Muds
Kaolin-based drilling muds exhibit superior rheological behavior compared to attapulgite, characterized by higher viscosity and enhanced gel strength, which improves suspension and cuttings transport efficiency in drilling operations. The fine particle size and plate-like structure of kaolin contribute to its thixotropic properties, enabling better control over mud flow under varying shear rates. In contrast, attapulgite's fibrous morphology provides different rheological profiles, often resulting in lower plastic viscosity and yield point values.
Attapulgite's Performance in Challenging Well Conditions
Attapulgite exhibits superior performance in challenging well conditions due to its high thixotropic properties and exceptional gel strength, which maintain mud stability under high temperature and shear stress. Unlike kaolin, attapulgite's unique fibrous structure enables better suspension of drill cuttings, reducing fluid loss and enhancing borehole stability in deep and deviated wells. These characteristics make attapulgite a preferred additive for drilling mud formulations in demanding environments where maintaining rheological properties is critical.
Cost Analysis: Kaolin Versus Attapulgite
Kaolin typically presents a lower cost per ton compared to attapulgite, making it a more economical option for large-scale drilling mud formulations. Attapulgite, although more expensive, offers superior viscosity and stability at elevated temperatures, which can reduce overall operational costs in complex drilling environments. Cost analysis should consider not only raw material price but also performance benefits that affect drilling efficiency and mud maintenance expenses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Kaolin and attapulgite differ significantly in their environmental impact and sustainability profiles within drilling mud applications; kaolin, a naturally occurring clay mineral, typically exhibits lower toxicity and better biodegradability, reducing long-term environmental harm during disposal or leakage. Attapulgite, while effective for viscosity control due to its fibrous structure, poses greater concerns related to its mining impact and potential persistence in ecosystems, requiring careful management to prevent soil and water contamination. Sustainable drilling practices increasingly favor kaolin for its more favorable ecological footprint and compatibility with environmentally sensitive regulations.
Field Case Studies: Kaolin vs Attapulgite
Field case studies reveal Kaolin's superior performance in enhancing drilling mud viscosity and suspension capabilities under high-temperature conditions, particularly in deepwater drilling operations. Attapulgite demonstrates better fluid loss control and thinning resistance in highly saline environments, as evidenced by multiple reservoir projects in the Gulf of Mexico. Comparative analyses indicate that selecting Kaolin or Attapulgite depends on specific well conditions, with Kaolin favored for its thermal stability and Attapulgite preferred for complex brine-based mud formulations.
Choosing the Right Mineral for Optimal Drilling Mud Performance
Kaolin offers excellent suspension properties and high plasticity, making it ideal for enhancing drilling mud viscosity and reducing fluid loss in water-based muds. Attapulgite's unique fibrous structure provides superior thixotropic behavior and filtration control, which helps maintain borehole stability and improve cuttings suspension. Selecting between kaolin and attapulgite depends on specific well conditions, with kaolin suited for lower temperature formations and attapulgite preferred in high-temperature, high-salinity environments to optimize drilling mud performance.
Infographic: Kaolin vs Attapulgite for Drilling Mud
 azmater.com
azmater.com