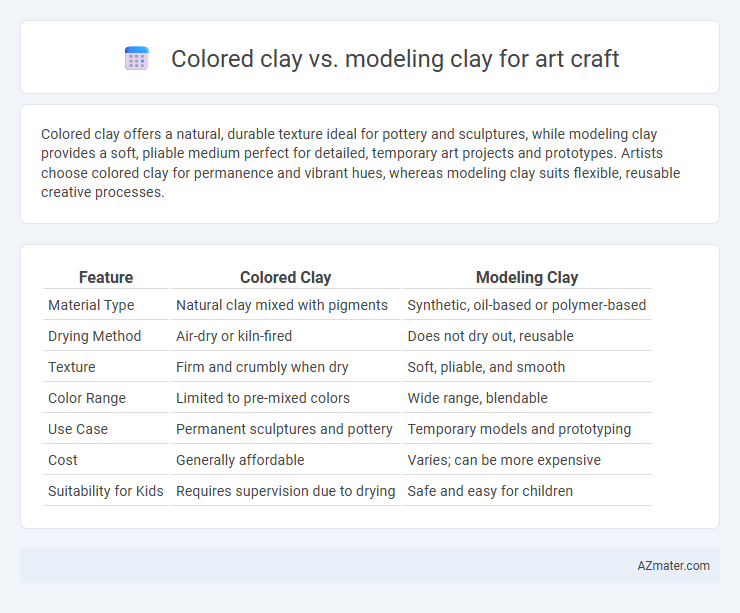
Colored clay offers a natural, durable texture ideal for pottery and sculptures, while modeling clay provides a soft, pliable medium perfect for detailed, temporary art projects and prototypes. Artists choose colored clay for permanence and vibrant hues, whereas modeling clay suits flexible, reusable creative processes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Colored Clay | Modeling Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural clay mixed with pigments | Synthetic, oil-based or polymer-based |
| Drying Method | Air-dry or kiln-fired | Does not dry out, reusable |
| Texture | Firm and crumbly when dry | Soft, pliable, and smooth |
| Color Range | Limited to pre-mixed colors | Wide range, blendable |
| Use Case | Permanent sculptures and pottery | Temporary models and prototyping |
| Cost | Generally affordable | Varies; can be more expensive |
| Suitability for Kids | Requires supervision due to drying | Safe and easy for children |
Introduction to Colored Clay and Modeling Clay
Colored clay, typically made from natural materials with added pigments, offers a firm texture ideal for sculpting detailed art projects and pottery crafting. Modeling clay, often composed of synthetic polymers or non-drying materials, provides a pliable, reusable medium favored for animation, prototyping, and educational purposes. Both types support creative expression but differ in permanence, texture, and intended artistic applications.
Composition and Material Differences
Colored clay typically consists of natural clay mixed with pigments, offering an earthy texture and the ability to harden through air-drying or kiln firing, making it ideal for ceramic art and permanent sculptures. Modeling clay, often made from synthetic polymers or oils, remains pliable and does not dry out, allowing for easy reshaping and reuse in detailed, temporary craft projects. The compositional difference affects durability, texture, and application, with colored clay excelling in permanent creations and modeling clay favored for flexible, non-permanent modeling.
Color Variety and Blending Options
Colored clay offers a wide range of vibrant hues pre-mixed into the material, ideal for projects needing consistent color without extra mixing. Modeling clay, often available in primary colors, provides extensive blending options, allowing artists to create custom shades and gradients by mixing different clays. The choice between colored clay and modeling clay depends on whether precise color consistency or versatile color blending is more critical for the art craft project.
Workability and Texture Comparison
Colored clay offers a firmer texture ideal for detailed sculpting and maintaining shape over time, while modeling clay provides a softer, more pliable consistency suited for easy manipulation and blending. Workability in colored clay demands more pressure and precision, making it excellent for intricate designs, whereas modeling clay's malleability supports quick adjustments and smooth surface finishes. Both materials serve different artistic purposes, with colored clay favored for permanence and modeling clay chosen for flexibility during dynamic creative processes.
Drying and Curing Processes
Colored clay typically requires longer drying and firing times as it often contains natural minerals that harden through gradual moisture evaporation and kiln curing, resulting in a durable finish. Modeling clay, such as polymer or air-dry clay, cures either through baking at low temperatures or air exposure, offering faster drying but generally lower heat resistance. The choice between colored and modeling clay affects project durability, with colored clay's kiln curing providing more structural integrity compared to the quicker, but softer, curing of modeling clay.
Suitability for Various Art Techniques
Colored clay excels in techniques requiring firm shaping and detailed textures, making it ideal for sculpting and pottery projects. Modeling clay offers superior flexibility and softness, suited for animation, prototyping, and hands-on molding where repeated reshaping is necessary. Both types adapt to diverse craft styles, with colored clay favoring permanence and modeled clay emphasizing versatility in artistic expression.
Durability and Finished Project Longevity
Colored clay often consists of natural materials that dry hard, offering superior durability and a long-lasting finish ideal for permanent art projects. Modeling clay, typically made from oil-based or synthetic components, remains pliable and does not harden, reducing its suitability for artworks requiring permanence. Artists prioritize colored clay for sculptures and crafts intended to endure over time, while modeling clay suits temporary designs and prototyping due to its flexible, reusable nature.
Safety and Non-Toxicity Considerations
Colored clay often contains natural minerals and pigments, making it a safer choice for children and sensitive users, as it typically avoids harmful chemicals found in some modeling clays. Modeling clay, especially oil-based types, may contain solvents and synthetic ingredients, posing potential health risks if ingested or used improperly, so non-toxic labels and safety data sheets should be carefully reviewed. For art and craft projects requiring prolonged contact or use by young artists, selecting certified non-toxic materials ensures a safer creative experience.
Cost-Effectiveness for Artists and Crafters
Colored clay, often made from natural materials like talc and kaolin, tends to be more cost-effective for artists and crafters seeking long-term projects due to its durability and reusability without added preservatives. Modeling clay, typically polymer-based and requiring baking to harden, can be more expensive per use because of single-use batches and additional costs like curing equipment. Artists aiming for budget-friendly options should consider colored clay for its affordability in larger quantities and versatility across various artistic techniques.
Which Clay is Best for Your Art Project?
Colored clay offers vibrant hues and a smooth, malleable texture ideal for detailed sculptures and decorative projects, while modeling clay provides greater flexibility and reusability, making it suitable for practice and iterative designs. For permanent art pieces requiring vivid color retention and fine detail, colored clay is often preferred, whereas modeling clay excels in educational settings and preliminary modeling due to its non-drying composition. Choosing the best clay depends on project goals: use colored clay for lasting, polished artworks and modeling clay for experimental or practice purposes.
Infographic: Colored clay vs Modeling clay for Art craft
 azmater.com
azmater.com